Air brake introduction:
An air brake, or more formally a compressed air brake system, is a type of friction brake for vehicles in which compressed air pressing on a piston is used to apply pressure to the brake pad necessary to stop the vehicle. Air brakes are used on large, heavy vehicles, particularly those with multiple trailers that must be connected to the braking system, such as trucks, buses, trailers, and semi-trailers, in addition to their use on railway trains.
Construction of air brakes:
Air brake components and their functions:
Following are the main parts of an air brake:
1. Air compressor
- It is used to increase and maintain air pressure.
- The function of the air compressor is to build up and maintain the air pressure necessary to operate air brakes and pneumatic accessories.
- A compressor is designed to pump air into a reservoir, which results in pressurized air.
- The compressor is driven by the vehicle's engine, either by belts and pulleys or shafts and gears.
- The compressor is in constant motion with the engine. Whenever the engine is running, so is the compressor.
2) Reservoir
- The reservoir is used to store compressed air. Reservoirs are pressure-rated tanks that maintain a supply of compressed air until it is needed for braking or operating auxiliary air systems.
- They must store a sufficient volume of air to allow multiple brake applications if the engine stops or the compressor fails.
- The number and size of reservoirs in a vehicle will depend on the number of brake chambers and their size, along with the parking brake configuration.
3. Air dryer
- An air dryer can be installed between the compressor and the wet reservoir to help remove moisture from the compressed air.
- It may be partially filled with a highly moisture-absorbent desiccant and an oil filter, or it may be hollow with baffles designed to aid in separating moisture from the air.
4. Safety valve
- A safety valve protects the reservoirs from becoming overpressurized and bursting if the regulator malfunctions and fails to bring the compressor into the discharge stage.
- The valve consists of a spring-loaded ball that will allow air to escape from the reservoir into the atmosphere. Valve pressure setting is determined by spring force
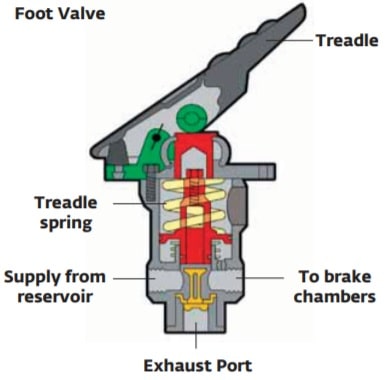
5. Foot valve.
- The foot valve is used to extract compressed air from the reservoirs when needed for braking.
- This pedal-operated valve applies air to operate the brakes.
- The amount of air supplied to the brakes is regulated by the driver according to the distance the brake pedal or pedal is pressed. Releasing it exhausts the air in the service brakes through its exhaust port.
- The distance the foot valve pedal is depressed by the driver determines the air pressure that will be applied, but the maximum application will not exceed the pressure in the reservoir. Releasing the foot valve pedal releases the brakes.
 air foot valve diagram
air foot valve diagram- When the driver applies the brakes by partially depressing the pedal, the foot valve will automatically maintain the applying air pressure without the driver having to adjust the foot pressure on the pedal.
- Releasing the pedal allows application air to be released through the exhaust ports to atmosphere. Pneumatic pedals are spring-loaded, producing a different “feel” than hydraulic brake applications.
(v) Brake chamber.
- The brake chamber is used to transfer the force of compressed air to the mechanical links.
- Service brake chambers convert the energy of compressed air pressure into mechanical force and movement, which actuates the vehicle's brakes.
- A brake chamber is a circular container divided in half by a flexible diaphragm.
- Air pressure pushing on the diaphragm causes it to move away from the pressure, forcing the pressure rod outward against the slack adjuster.
 Brake chamber assembly
Brake chamber assembly- The force exerted by this movement depends on the air pressure and the size of the diaphragm. If a leak occurs in the diaphragm, air can escape, reducing the effectiveness of the brake chamber.
- A brake chamber is usually mounted on the axle, close to the wheel that will be equipped for braking.
(vi) Brake assembly
- The brake assembly includes the brake chamber and the slack adjuster mounted on the backing plate due to steering action.
- A brake chamber is usually mounted on the axle, close to the wheel that will be equipped for braking.
- Air pressure is fed through an inlet port. Air pushes on the diaphragm and rod.
 air brake assembly
air brake assembly- The rod is connected by a shackle and pin to a crank arm-type lever called a “slack adjuster.”
- This converts the pushing motion of the brake chamber pressure rod into a twisting motion of the brake camshaft and S cams.
- When the air runs out, the return spring in the brake chamber returns the diaphragm and rod to the released position.
 air brake used for motor vehicles
air brake used for motor vehicles
Air brake system operation :
Air brake system diagram:
 air brake system diagram
air brake system diagramWorking principle:
As shown in the figure, in air brakes compressed air (about 700 kPa) is used to activate the brake mechanism. The figure shows the complete layout of the air brake system. It consists of air filter, unloader valve, air compressor, air reservoir, brake valve and 4-number brake chamber. The compressor takes atmospheric air through the air filter and compresses the air. This air is stored under pressure in the air reservoir. From this reservoir, the air goes to various vehicle accessories that run on compressed air. Some of the air goes to the brake valve. The brake valve is controlled by a driver who controls the braking intensity in an emergency.
Pressed pedal: When the brake pedal is pressed, compressed air from the reservoir is transmitted through tubes equally in all directions to the brake chambers via the brake valve, which further applies the brake.
Pedal released: When the driver releases the brake pedal, the master cylinder piston returns to its original position due to the return spring, and the pressure drops. It releases the brake shoes from the brake drum to their original position and the brakes are released
Difference between air brakes and hydraulic brakes:
Air Brakes Hydraulic Brakes 1. Compressed air is used as a working substance.1. Hydraulic oil is used as a working substance.2. The air brake is more powerful than a hydraulic brake.2. The hydraulic brake is less powerful than the air brake.3. Components: Air compressor, unloader valve, brake valve, brake chamber.3. Components: Master cylinder, wheel cylinder, oil reservoir.4. Air brake system is used in trucks, buses, trains, etc.4. Hydraulic oil brake system is used for light vehicles such as cars, light trucks, etc.5. The air compressor uses a certain amount of engine power.5. No engine power is used.6. It is not self-lubricating.6. Hydraulic brakes are self-lubricating.
Air Brake System Probable Causes and Solutions
Advantages of air braking system :
2. Air brake parts are easily located where the chassis design is simple.
3. Compressed air can be used to inflate tires, windshield wipers, horns and other accessories.
4. It only uses air as the working medium, which is easily available.
5. It is easy to store air at high pressure.
6. Provides strong braking effect used in heavy vehicles and trucks.
7. Provides better control.
8. Reduces stopping distance.
9. Mainly allows less wear on parts.
10. It has a flexible hose connection.
Disadvantage of air brake system :
1. If there is any leakage in the passage, the entire system will fail. Therefore, air sealing is very difficult.
Air braking system applications:
(1) Trucks.
(2) Bus.
(3) Trailers
(4) Semi-trailers
(5) Railway Train.

























































3 comments
Thank you very much for sharing this information it really helped me on my school assignments as it is well explained
This information is helpful. There is none or less information missing. Thank you!
This information is helpful. There is none or less information missing. Thank you!