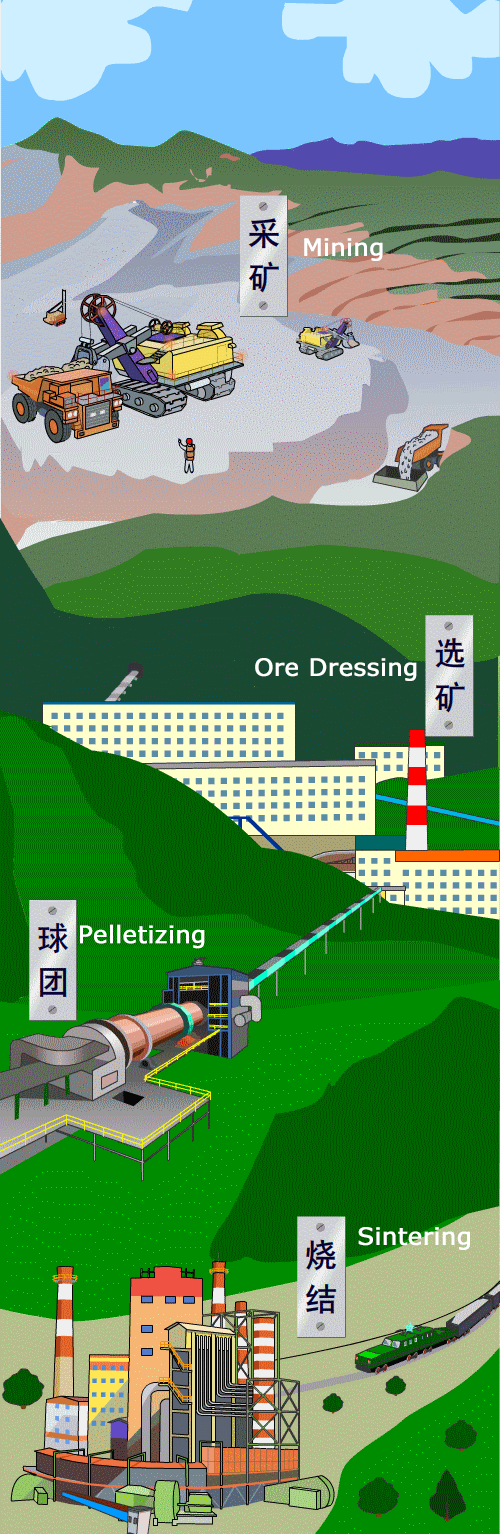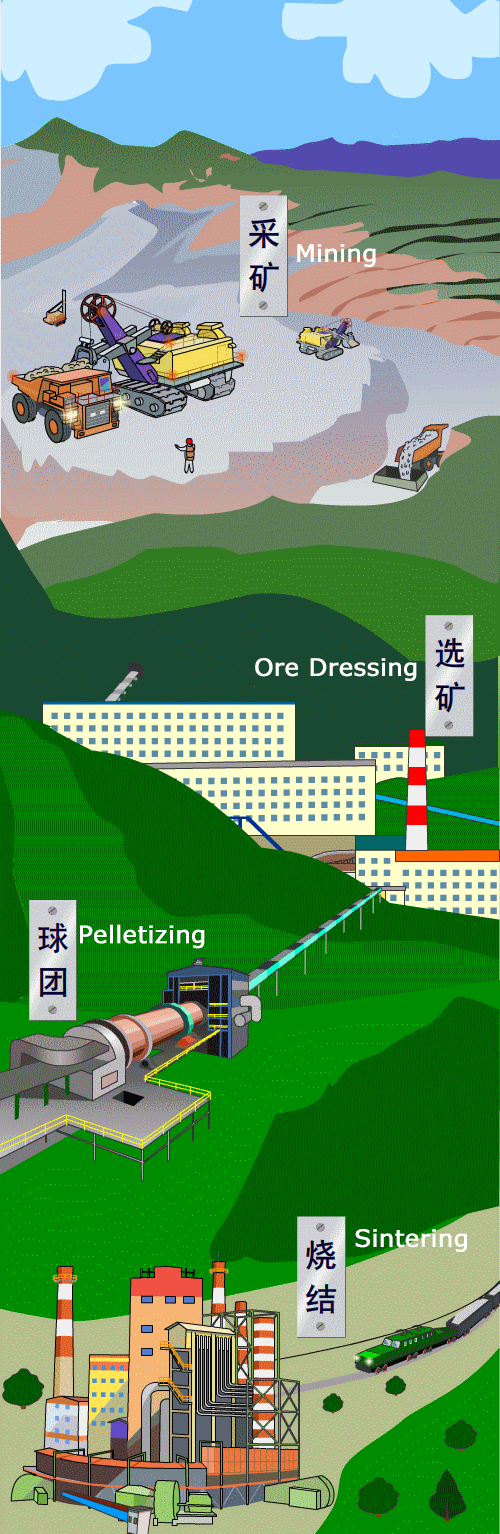
How is steel produced?
The main raw material for iron smelting is iron ore, which mainly consists of Fe2O3. Coke is the second raw material used in the production of iron.
During the iron manufacturing process, some of the coke is left in the cast iron, resulting in the presence of carbon in the cast iron.
Iron and steel production involves the transformation of iron ore into pig iron, which is then used as a raw material to make steel.
The steel production process mainly involves the removal of carbon, although it cannot be completely eliminated.







Steel requires a specific amount of carbon to achieve optimal performance. To improve its properties, certain alloying elements need to be added after carbon steel is smelted.
Pig iron (cast iron) – 2.0-4.5% C;
Steel (carbon steel) – 0.05-2.0% C;
Wrought iron (pure iron) – C content less than 0.05%;
Iron ore → pig iron → steel.
Steel is an alloy composed of iron, carbon (C), silicon (Si), manganese (Mn), phosphorus (P), sulfur (S) and traces of other elements. The mechanical properties of steel are greatly influenced by its carbon content, making it a type of iron-carbon alloy. Therefore, steel is the most significant and essential metallic material in engineering technology.
What is carbon steel?

Carbon steel refers to an iron-carbon alloy containing less than 2% carbon and small amounts of silicon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur and other impurities.
In industrial applications, the carbon content of carbon steel generally does not exceed 1.4% due to the steel becoming excessively hard and brittle, making processing difficult and decreasing its production and utility value.
Carbon steel can be divided into ordinary carbon structural steel and high-quality carbon structural steel based on its quality.
High-quality carbon structural steel has a lower allowable sulfur and phosphorus content than ordinary carbon steel, resulting in more comprehensive mechanical properties.
Based on its carbon content, carbon steel can be classified as low carbon steel, medium carbon steel and high carbon steel.
As the carbon content increases, the hardness of carbon steel increases while the toughness decreases.
- Low carbon steel — carbon content ≤ 0.25%;
- Medium carbon steel — carbon content > 0.25% ≤ 0.60%;
- High carbon steel — carbon content > 0.60%.
What is alloy steel?

To improve the properties of steel, alloying elements are added to carbon steel during the casting process, resulting in the creation of alloy steel. Common types of alloy steel include chrome steel, manganese steel, chromium-manganese steel, chromium-nickel steel, among others.
Alloy steel, also known as special steel, has unique properties including high hardness, wear resistance, toughness and corrosion resistance.
Alloying elements commonly added to steel include Si, W, Mn, Cr, Ni, Mo, V, Ti and others.
According to the total content of alloy elements, it can be divided into:
- Low alloy steel — total alloy content ≤ 5%;
- Medium alloy steel — total alloying element content is 5% ~ 10%;
- High alloy steel — total alloy content > 10%.
Alloy steel is classified by use:
- Structural steel alloys: used as engineering components (tubes and supports, etc.); Various mechanical parts (shafts, gears, springs, impellers, etc.).
- Alloy tool steel: used as measuring tools, molds, tools, etc.
- Special performance steels: such as stainless steel, heat-resistant steel, etc., with special physical or chemical properties.
What are the differences between carbon steel and alloy steel?
The difference between carbon steel and alloy steel is as follows:
Carbon steel is the main alloying additive in steel.
Alloy steel is used to remove carbon from steel and other metals or materials to improve performance.
Carbon steel is classified according to the amount of carbon contained in the steel.
The four main categories are low carbon steel and low carbon steel, medium carbon steel, high carbon steel and ultra high carbon steel.
0.16-0.29% carbon in carbon steel .
These forms of steel are commonly used because they are relatively low cost and provide acceptable material properties for many applications.
They are ductile, not brittle, and can be further strengthened by carburizing, which increases their surface hardness.
Alloy carbon steel typically contains 0.30-0.59% carbon, striking a balance between ductility and strength and exhibiting good wear resistance.
These steels are commonly used in forging and in the manufacture of large industrial and automotive parts.
0.6-0.99% carbon in carbon steel
Ultra-high carbon steel, which contains approximately 1-2% carbon, is known for its exceptional strength and is often used in the manufacture of high-strength steel wires and springs.
These types of steels can be hardened to substantial hardness, making them ideal for specialized products like axles.
A carbon content of 1.2% or more in steel is typically produced through powder metallurgy.
Steel with a carbon content greater than 2% is generally classified as cast iron. Alloy steels, on the other hand, are composed of varying amounts of metals and materials that improve their properties.
Carbon steel is a base metal widely used in almost every industry in the world, including aerospace, aircraft, automobiles, chemical industry and national defense.
Alloy steel has several properties that can be used in different areas, such as in the construction of gears, tubes, supports and infrastructure.