Concrete hardness is an indicator of how hard the concrete is. It is a kind of measure of the stiffness of concrete. The hardness of concrete can depend on many factors, which will be discussed in this article.
What is concrete hardness
Hardness is a physical property. Indicates how rigid the concrete is. There is no method for calculating hardness.
Hardness testing is basically a surface property.
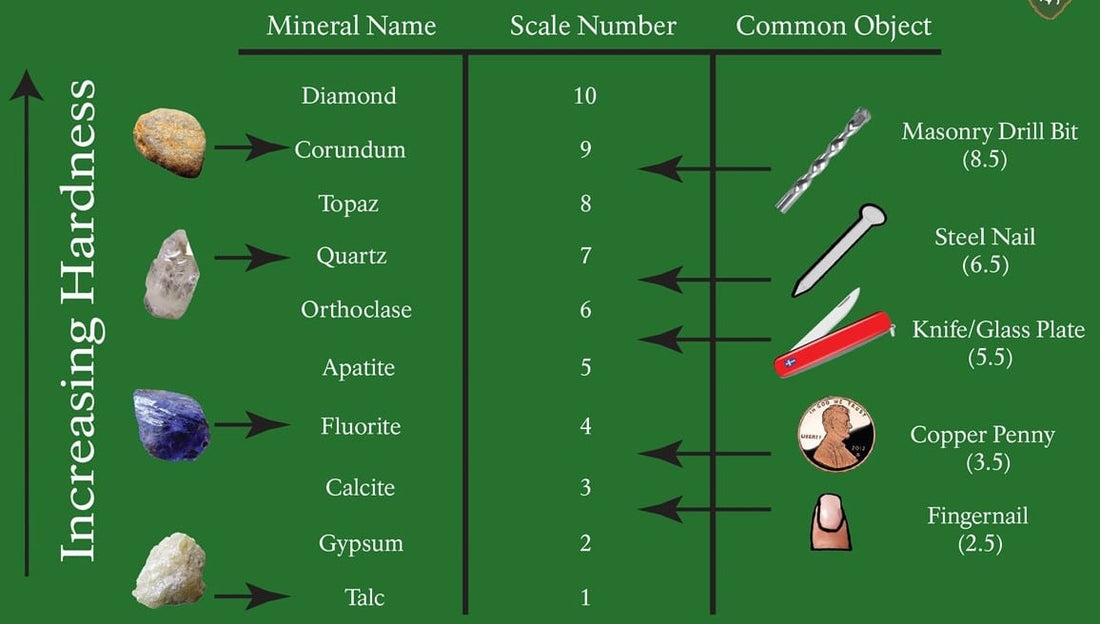
Diamonds are the hardest material in the world and are used as a reference to determine the hardness of other materials.
Knowing the hardness of concrete is not essential, nor is knowing the compressive strength of concrete. However, sometimes gravity is important because it is involved in determining the in-situ compressive strength of the concrete.
Factors Affecting the Hardness of Concrete
As already mentioned, hardness is a type of rigidity of concrete. It is influenced by the materials of the concrete sample. Some of the factors that affect the hardness of concrete are as follows.
- Concrete quality
The quality of concrete is a property related to hardness. The higher quality of concrete the harder it is. Furthermore, hardness appears to be directly related to density.
As the quality of concrete increases, the density of concrete also changes. This therefore affects the hardness.
- Cure
Curing is one of the most commonly performed treatments to improve the properties of concrete. Sufficient moisture of concrete surfaces allows the hydration process (reaction of cement with water) to be completed.
When the reaction is complete, the surface hardness is greater as the concrete reaches its strength.
- Aggregate
The largest volume of concrete is occupied by coarse aggregates. Therefore, the hardness of the aggregates can be influenced by the hardness of the concrete.
- compression
The better the compaction, the greater the density of the concrete. When concrete is properly compacted, its strength also increases. Therefore, the hardness of concrete will increase with better compaction of concrete.
How to measure the hardness of concrete
Hardness is measured as a property of a surface. There is always a difference between measuring actual hardness or correct hardness.
As we know, during the Carbonation of concrete the hardness of the upper layer increases. If carbonation progresses to a certain extent, the test result will give a false representation of the actual condition. Therefore, these tests should be used with great caution.
Hardness can be compared to the Mohs hardness scale. It is developed considering the hardness of diamond as 100%. The hardness of other materials is compared in relation to this.


Rebound Hammer Test
One of the most commonly used testing methods for measuring surface hardness is the rebound hammer test. This is a non-destructive testing method for determining the compressive strength of concrete.
The rebound hammer test cannot be used directly to measure the strength of concrete. However, it can be used by correlating it with concrete core test results. You can read the In-Place Compressive Strength Review article for more information on this topic.


Scratch Test
This test is also called the Mohs scratch test.
The scratch test is a very simple test to determine hardness. This method can also be used to measure the hardness of concrete.
The hardness of a surface can be measured using a scratch pencil.


These tests are indicators of the compressive strength of concrete. Therefore, they are very important to us during construction.
Related articles
- Mas Concrete
- Laminated concrete
- Self-compacting concrete
- concrete
- All about concrete
- Concrete construction
- Reinforced concrete
- Ready-made concrete
- Advantages and disadvantages of reinforced concrete
- How to choose the quality of concrete
- Concrete properties
- Additive Testing