Sulfate-resistant cement is used when construction is carried out in aggressive environments where chemicals such as sulfate are present.
Sulfate-resistant cement is a special type of cement used in construction. However, it is not commonly used and is sometimes not used due to lack of knowledge about sulfate-resistant concrete.
What is sulfate resistant cement
In short, it is a type of cement used in construction to resist sulfate attacks. It is a type of cement that has been adapted with tricalcium aluminate (C3A) to achieve the required properties.
According to BS EN 197-1:2011 there are three main types of sulphate resistant cement.
- Sulfate-resistant Portland cement
| Type | C 3 A clinker content |
| CEM I-SR 0 | 0% |
| CEM I-SR 3 | ≤3% |
| CEM I-SR 5 | ≤ 5% |
- Sulfate-resistant blast furnace slag cement
| Type | C 3 A clinker content |
| CEM III/B-SR | No requirements |
| CEM III/C-SR | No requirements |
- Sulfate-resistant pozzolanic cement
| Type | C 3 A clinker content |
| CEM IV/A-SR | ≤ 9% |
| CEM IV/B-SR | ≤ 9% |
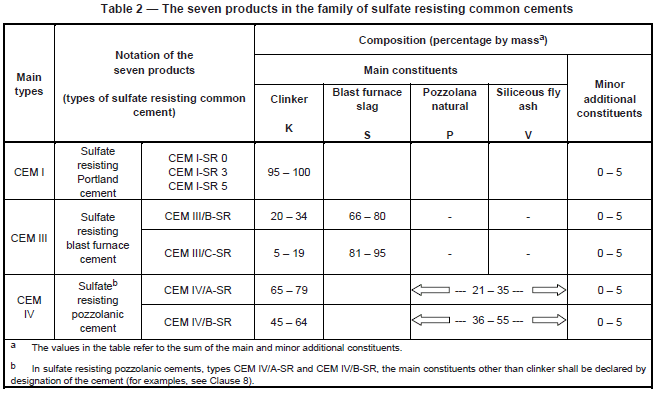
Furthermore, the following table from BS EN 197-1 lists the clinker contents and proportions of other additives for each type of cement.


Properties of sulfate-resistant cement
- Fineness 280±10 µm 2 /kg
- Setup time 80 minutes
- Final setting time 240 minutes
- Ignition Loss 0.02
- Greater compressive strength
- Maintain strength and durability
- Low heat of hydration – prevents cracking
Use of sulfate-resistant cement
- Coastal structures – dikes, breakwater structures
- Bridge pier
- Water storage/treatment
- Sewer lining
- chemical industry


Advantages of sulfate-resistant cement
- Excellent resistance to sulfate attacks
- Low heat of hydration reduces cracking.
- At low heat of hydration, the formation of delayed ettringites is also lower.
- Fewer shrinkage cracks
- High compressive strength allows for economical construction
- Increase the durability of concrete
- Minimum risk of reinforcement corrosion
Disadvantages of sulfate-resistant cement
- When producing sulfate-resistant concrete for use in marine environments, sulfate-resistant cement must be used with great care.
- If there is a risk of chloride attack, it is not advisable to use this type of cement.
- Proper hardening of concrete has to be done
- The cost of this type of concrete could be higher.
Related articles
- Types of cement
- cement
- Low heat cement
- Cement classification
- Cement and cement additives
- Cement Tests