Let's move on to the details to find out what the chip contains and how it works.
Some details of the information provided by the company:
1. It is from the ThinkGear AM family of products, where A stands for ASIC and M stands for Module.
2. The chip model number is TGAM1, revision number 2.3.
3. The module dimension is 29.9mm x 15.2mm x 2.5mm (1.1in x 0.60in x 0.10in).
4. Module weight is 130 mg (0.0045 oz).
5. The operating voltage of this module is 2.97V – 3.63V
6. Maximum input noise the module can filter is 10mV peak to peak. Afterwards, we will measure our noise and make sure it is within the module's range for the best results.
7. The maximum power consumption of the module is 15mA @3.3V. We will check these values with a multimeter and measure each parameter. It will be fun to check these values for yourself.
8. ESD protection of the device is 4kV for contact discharge and 8kV for air discharge. It is important to note that electrostatic discharge is the flow of electricity between two charged objects caused by contact, dielectric breakdown, or electric shock. It is mainly caused by a two-body static charge. Static electricity can be built up by induction or tributary charging (certain materials become electrically charged after coming into contact with different materials)
9. The device can communicate serially with baud rates of 9600, 1200, 57600 bps. There are configuration pins with the help of which we can change the baud rate. I'll make sure to cover that part later.
Here is the PIN diagram of this TGAM1 (NeuroSky Chip).
This is the view we see when we open the mindflex band.
Here, when we see these two images, we can see that the 5 pins on the right side of photo1 are the five pins on the left side of photo2.
Let me briefly tell you about the pins of this chip.
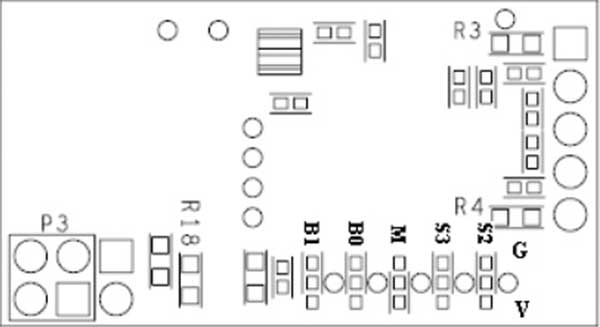
In P3
In P4
In P1
The label marks “” are labeled on the PCB.

Figure 1: NeroSky Chip PIN Diagram

Figure 2: Graphic Image showing the NueroSky chip configuration
Now let's see how we can change the serial transmission speed of the NeuroSky Chip and its data content. You can find this chip in some other Brain Headband and if you want to change the transmission speed or data content, this article is for you.
Well, ThinkGear ships the following packages, usually in series. The codes that may appear on packages are:
TGAM1 supports the following command bytes:
These commands can change the transmission rate and data content of the NeuroSky EEG chip.
Settings
The TGAM1 has a built-in configuration panel that can be used to change default settings. There are two types of default settings that can be changed, namely baud rate and data content. The configuration blocks are located on the back of the TGAM1 chip. B0 is used to configure the baud rate and B1 is used to configure the data content. The M pad is used to set the frequency of the notch filter.

Figure 3: Image showing a side view of the NeuroSky EEG chip

Fig. 4: Table listing the NeuroSky EEG chip configuration parameters
In normal output, the chip transmits low quality value, EEG value, attention value and meditation value.
In Standard mode, B0 and B1 are connected to ground to communicate at 9600bps with normal output.
We can also change this configuration by sending commands serially to the chip. I previously discussed the commands supported by TGAM.
So, by sending the command 0x01, 0x02, 0x00 we can change the configuration serially. But as soon as the system is restarted, it will return to hardware reset and continue in the configuration defined by B0 and B1.
Now, TGAM has notch filters to reduce external noise. The frequency of the notch filter can be set by pin M. It is generally used to reduce ambient 50 Hz or 60 Hz noise. Also in our previous articles we saw that there was noise coming from the 50 Hz environment in India. This is because the supply we receive from the Government is 50 Hz and the 50 Hz magnetic field fluctuates in the environment. This is the reason why there is a sensation of this field in the brain waves.
To remove this extra signal from our brain waves, TGAM1 has notch filters. The M pin should set this to 50Hz or 60Hz. If the M pin is connected to Vcc then it is running at 60Hz and if the M pic is connected to Ground then it is running at 50Hz.
By default, the TGAM1 pin configuration is 9600 bps with normal output and 60Hz frequency notch filer. I hope now if you see this TGAM1 chip, you can work on its configuration and perform the desired task.
How it works?
After going through the components and configuration of the EEG chip, it is important to know how it works to extinguish the fire of exploration in our mind. So let's start with this.

Fig. 5: Image showing the top view of the NeuroSky EEG chip
Here is my detailed guess for how this chip will work. I'm not really sure about this, but this information was collected from several sources.
The Chip has 5 inputs including EEG, shield, ground and reference. Now the EEG electrode is directly connected to the EEG pin with a shield. The reference for this data is the reference electrode that is finally connected to our ear. Now the TGAM1 chip has a processor with filters. These filters serve to filter noise and separate different types of brain waves.
Let's say an EEG signal from our brain enters the TGAM1 chip. This signal first enters a filter that separates all signals with a frequency higher than 100Hz. Probably the highest frequency wave, i.e. the gamma wave is up to 100 Hz. After that, according to the M pin configuration, extra 50Hz or 60Hz frequency signals are removed. Now we have a signal with a frequency ranging from 0.3 Hz to 100 Hz. Now the filters will divide it according to the type of Brainwave. For example, waves from 3 Hz to 7 Hz are separated differently compared to those from 7 Hz to 13 Hz and so on.
Now, these signals are sampled at the rate of 512 Hz and later sent to the ADC with 12-bit resolution. This ultimately ends up getting a digital value for each separate type of brain waves. Now, for many digital values of a single Brainwave type, the FFT power is calculated by the processor. After obtaining the FFT power values from all Brainwave types, the processor looks for the configuration pins. We recently discussed configuration pins. Now, after the configuration pins, the processor sends the digital FFT values for each type of Brainwave in series through the Tx pin at the baud rate defined by the configuration pin. The default value is 9600 with normal output.
The mindflex board receives these serial values and then does its own calculations to transmit this signal wirelessly. This summarizes the EEG details of the NeuroSky chip. Stay tuned for more information about brainwave experimentation .