Boring machines and their milling processing
The boring machine is a machine tool used to process holes with larger dimensions and higher precision requirements, especially for processing hole systems with high mutual positional accuracy requirements distributed in different parts locations.
It is generally used for further processing of cast, forged or drilled holes.

According to their purpose and structure, there are several types of boring machines.
- Horizontal milling and boring machine
- Coordinated boring machine
- Precision boring machine
- Vertical boring machine
- Deep Hole Drilling Machine
I. The main processing range of boring machines

- a) Boring with a single-point cutting tool;
- b) Boring with double-ended cutting tools for coaxial holes;
- c) Making large diameter holes using protruding boring bars;
- d) Boring shafts and milling flat surfaces with end mills;
- e) Cutting internal channels with boring bars mounted on a front plate;
- f) Cutting end faces with turning tools mounted on a faceplate.
II. Features of boring machining
Boring is a process of enlarging the diameter, improving precision, reducing surface roughness and correcting the position of cast, forged or drilled holes.
The main movement of boring is the rotation of the boring tool, while the feed movement can be an axial or radial movement of the spindle, or a longitudinal or transverse movement of the work table.
Boring tools have a simple structure and wide variety, which makes them more versatile. However, boring machining (especially single-point boring) has low production efficiency.
Boring machining is suitable for batch production of parts with high positional accuracy requirements.
III. Common types of boring machines
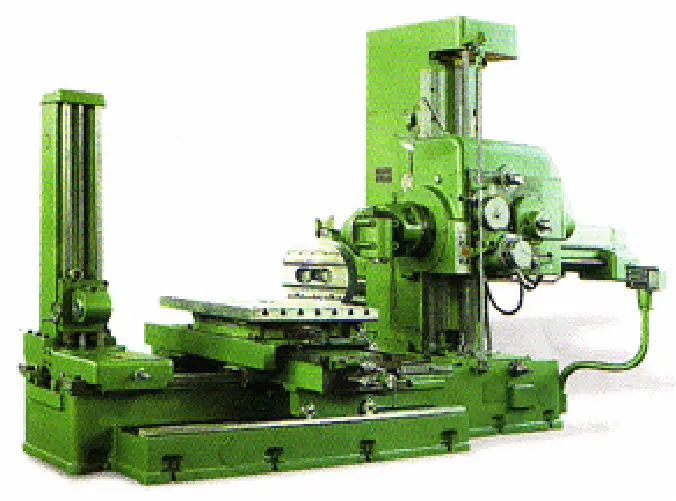
1. Horizontal milling and boring machine

Features of horizontal milling and boring machine:
The horizontal arrangement of the spindle makes it suitable for processing holes in individual parts or small batches with conventional precision.
2. Coordinate boring machine

Coordinate boring machine features:
Coordinate boring machines are equipped with precise measuring devices for coordinated positions, which ensures precise relative positioning between the tool and the workpiece.
Holes processed by coordinate boring machines can achieve high dimensional and shape accuracy, as well as precise positional accuracy between holes or between holes and a reference surface.
Coordinate boring machines can be used for precision tracing and contouring, as well as for precise measurements of hole distances and straight lines.
They are mainly used to process precision components, fixtures, molds, gauges and other items that require high precision.
3. Precision boring machine (diamond boring machine)

Precision boring machine (diamond boring machine) features:
Precision boring machines were formerly named after their diamond tools (now made of hard alloys).
The precision boring machine has a high cutting speed and extremely small cutting and feed quantities, which allows precise and fine boring of holes in the workpiece. This results in extremely high dimensional accuracy and low surface roughness.
They are mainly used for batch processing of precision holes in important parts such as connecting rods, pistons, hydraulic pump casings, cylinder liners and other components.
2. Planer and its machining process
Planer is a machine tool used to process various flat surfaces and grooves.
According to different machining positions, planers can be divided into two types: planer and shaper.


According to their purpose and structure, planers can be divided into several types, including:
- Bullhead planer: The bullhead planer has a horizontal cross rail and is suitable for processing large parts with a wide range of applications.
- Gantry Planer: The gantry planer has a gantry structure and a large working surface, making it suitable for processing large and heavy workpieces.
- Cantilever planer: The cantilever planer features a single column structure and is suitable for processing long and narrow workpieces.
- Contour Planer: The contour planer is designed for processing curved surfaces and complex shapes.
I. The main processing range of planers

- a) Flattening of flat surfaces;
- b) Flattening of vertical surfaces;
- c) Flattening of inclined surfaces;
- d) Planing of dovetail grooves;
- e) Flattening of T-slots;
- f) Flattening of straight grooves;
- g) Flattening of contour surfaces.
II. Features of planing machining
The planer tools are simple and have good versatility. They are easy to grind, have a short preparation period for production and low cost.
Planing machining has working offsets and non-working offsets, which results in lower productivity.
During planing cutting, an impact occurs that can easily damage the cutting tool. The cutting speed is limited and the cutting heat is low. Therefore, cooling with cutting fluid is generally not necessary (except for precision planing).
The main movement of planing machining is the reciprocating linear movement of the planer (bullhead planer) or the worktable (gantry planer), and the feed movement is the intermittent transverse movement of the workpiece driven by the worktable (planer). bullhead) or the intermittent transverse movement of the planer driven by the tool holder (gantry planer).
III. Commonly Used Planers and Shapers
1. Bullhead Planer

Bullhead Planer Features:
The bullhead mechanical planer has simple structure, reliable operation and easy adjustment and maintenance.
The hydraulic planer has greater transmission force, smooth movement and can achieve stepless speed regulation. However, it has a more complex structure and higher cost.
Bullhead planers are mainly used to process medium and small workpieces, and the workpiece length generally does not exceed 1 meter.
Bullhead planers are widely used in the manufacturing processes of various large-scale parts, such as bases, foundations, sliding blocks, gearbox covers and so on.
2. Gantry Planer

Gantry Planer Features:
The main movement of the gantry planer uses a DC motor, which can achieve a wide range of stepless speed regulation. This makes it easier to control the cutting speed of the surface and ensures that the worktable runs smoothly.
Gantry planers have four tool holders, and the feed direction and speed are easy to operate, making them suitable for processing flat surfaces and side surfaces of workpieces with different heights.
The main movements of the machine tool such as feeding, lifting, beam locking and releasing, working table rapid advancement, rapid feeding and retreating can be centrally operated to achieve automatic cycling.
Gantry planers are mainly used to machine large parts and can be used for roughing and finishing operations. They can also perform multiple tasks in a single operation, such as planing, milling and grinding.
3. Cantilever planer

Cantilever planer features:
The working characteristics of a cantilever planer are similar to those of a gantry planer.
It is especially suitable for machining parts with a large width, but which do not need to be machined across the entire width.
However, the beam stiffness of a cantilever planer is lower than that of a gantry planer. As a result, machining accuracy is limited.
4. Slotting machine (vertical planer)

Slot Machine Features:
The main movement of a slotting machine is the reciprocating movement of the ram and cutting tool, while the feeding movement is the rotary movement (circumferential feeding) of the circular worktable driven by the workpiece and the longitudinal and transverse movement of the vertical slide.
It is mainly used for machining various keyways, vertical planes and forming surfaces in single part or small batch production.
3. Grinding machine and its grinding process
A machine tool that uses a grinding wheel or other abrasive tool to perform grinding operations on a workpiece is called a “grinder.” Grinding machines are mainly used to process quenched and tempered steel parts. Through grinding it is possible to obtain high precision and low roughness surfaces. In general, it is the final process of mechanical machining.
According to their different purposes and structures, grinding machines can be divided into the following types:
- Surface grinding machine
- Thread grinding machine
- Cylindrical grinding machine
- Gear Grinding Machine
- Internal grinding machine
- Guide Grinding Machine
- Tool Grinding Machine
- Special grinding machine.

I. The main processing range of grinding machines

- a) External cylindrical grinding
- b) Internal cylindrical grinding
- c) Surface grinding (peripheral grinding)
- d) Surface grinding (final grinding)
II. Features of grinding processing.
1) Grinding processing is a commonly used precision machining method for hardened steel, hard alloys, etc. It can achieve high precision (IT6-5) and low surface roughness (Ra = 0.8-0.4μm) of the workpiece.
2) The high-speed rotation of the grinding wheel relative to the workpiece is the main movement. The circumferential speed of the grinding wheel is generally around 35 m/s.
3) The grinding wheel is a non-metallic cutting tool composed of abrasive materials (such as alumina Al 2 Ó 3 , silicon carbide, boron carbide, etc.) and binders. Due to the high grinding speed and hardness of the workpiece, a large amount of cutting heat is generated during the grinding process.
Therefore, sufficient cooling and lubrication with cutting fluid are necessary to improve surface quality and production efficiency.
III. Commonly used grinding machines
1. Universal cylindrical grinding machine

Features of universal cylindrical grinding machine:
1)The rotary movement of the grinding wheel is the main movement of grinding, with three feeding movements: the spindle drives the workpiece to rotate for radial feeding movement, the table drives the workpiece for reciprocating linear movement for feeding movement longitudinal and the intermittent movement of the grinding wheel along the radius direction towards the workpiece is the transverse feed movement.
In addition, there are two auxiliary movements: for the convenience of grinding wheel movement and to save idle time, the grinding wheel can perform rapid transverse movement with a fixed stroke; to load and unload the part, the tailstock sleeve can have telescopic movement.
2) Universal cylindrical grinding machine can not only grind the outer cylindrical surface of cylindrical parts, but also can grind the inner hole and conical surface (the table has horizontal rotation function); Suitable for precision machining of single or small batch parts.
2. Internal grinding machine

Features of internal grinding machine:
1) The rotational movement of the grinding wheel is the main grinding movement. There are three feed movements: the rotation of the workpiece driven by the spindle is the circumferential feed movement, the reciprocating linear movement of the head driven by the work table is the longitudinal feed movement, and the movement of the grinding wheel structure along the saddle is the transverse feeding movement.
2) Due to the limitation of the diameter of the workpiece to be ground, the diameter of the grinding wheel is generally small, and to achieve the cutting speed required for precision machining, the rotational speed of the grinding wheel is generally above 10,000 r/min.
It is suitable for internal precision grinding of parts in single-piece or small batch production.
3. Flat grinding machine for horizontal axis rotary table

Features of horizontal spindle flat grinding machine:
1) The rotational movement of the grinding wheel is the main movement. The reciprocating linear movement of the worktable driven by the workpiece is the longitudinal feed movement. The transverse movement of the grinding wheel along the slide is the transverse feeding movement, and the vertical feeding movement is achieved by the combined movement of the grinding wheel frame and slide along the pillar guide rail.
2) The workpiece is electrically positioned on the worktable, making positioning and clamping very convenient.
3) The longitudinal advance is hydraulically controlled, and the transverse advance can be controlled hydraulically or manually, while the vertical advance is controlled manually, facilitating the operation.
4) It has a wide processing range and high production efficiency, and is suitable for precision machining of flat parts in single-piece or batch production.
4. Vertical Axis Rotary Table Flat Grinding Machine

Features of a vertical spindle surface grinding machine:
1) The rotational movement of the grinding wheel around the vertical spindle is the main movement. The rotary table driven by the workpiece is the feeding movement (and the rotary table can also move longitudinally along the base guide rail). The movement of the grinding wheel frame along the column is vertical feed movement.
2) Due to the large diameter of the grinding wheel, inserts are often used for grinding.
3) It has high production efficiency and is suitable for precision machining of small batch-produced parts or flat surfaces and end faces of large-diameter ring-shaped parts.