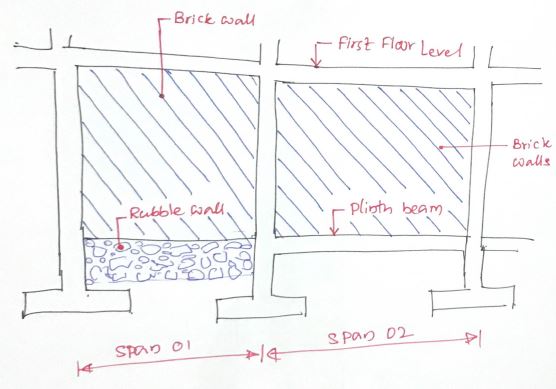
Base beams are constructed at foundation or ground floor level and serve as tie beams at base level to reduce the effective height of supports.
In addition, they support the load of the wall on the ground floor on supports and act as a winding controller.
The base beams control the cracks in the brick wall, enclosing the wall panels. In other words: an infill wall is created that resists the formation of cracks in the wall.


In section 01 of the illustration above, there is no base beam above the rubble foundations. However, in section 02 there is a plinth beam at ground floor level.
If there are different settlements, the resulting stresses cannot be supported by the rubble foundations. This causes cracks in the rubble foundation and eventually cracks in the brick wall (span 2).
If beams are present, they can accommodate the additional tensile/bending/shear forces. This minimizes the formation of cracks in the brick wall.
They also support the loads of the ground floor walls.
The sizing of the beams and the sizing of the reinforcement must be carried out according to the wall load.
In low-rise buildings, in most cases floor loads are not transferred to the base beams. If the slab loads are transferred to the base beams, these must be designed as normal beams, taking into account the slab loads.