Non-destructive testing of welds is more common and generally performed compared to destructive testing of welds. Some of the non-destructive testing of welds can be performed quickly and easily. However, some exams require more time.
Below you can see the list of tests carried out as non-destructive tests.
- Visual inspection
- Liquidity Penetration Testing
- Leak Test
- Magnetic Particle Test
- Ultrasound examination
- Eddy current test
- Acoustic Emission Test
- X-ray examination
Let's discuss each type of test in detail.
Visual inspection
Visual weld inspection is the most common and simplest type of NDT weld inspection and can be performed as a first step before performing any other inspection.
As a non-destructive test of weld beads, it can be used to determine the following points:
- Weld size
- Welding defects
- Surface cracks
- Uneven surface
- Slag collection and cleaning
Liquidity Penetration Testing
As the name suggests, this test monitors fluid penetration into the defective weld.
A dye is used to detect defects in the weld.
- This method can only detect surface cracks and discontinuities on weld surfaces.
- First, the welding surface is cleaned.
- The agent is then sprayed onto the welding surface.
- It is then deleted. The active ingredient remains in the fissure area.
- A color-changing silver is applied, which can be used to identify defective areas.
Leak Test
This method can be used to test a liquid container. These types of non-destructive weld testing (END weld testing) can be used to test liquid containers.
Once filled with a liquid, surface leaks can be examined.
This test is relatively simple compared to other types of tests and we can collect information about the strength and other aspects of the weld.
Only interruptions in the weld seam could be examined.
Magnetic Particle Test
This process can be used to detect defects in the surface and near-surface area.
- If there are defects in the weld seam, the magnetic field is turned off.
- This procedure is only applicable for ferromagnetic materials.
Ultrasound examination
Changes in material properties can be assessed using ultrasound testing. Wave speed can be used to determine quality, thickness, etc. of the weld.
This technique cannot evaluate surface defects in welds.
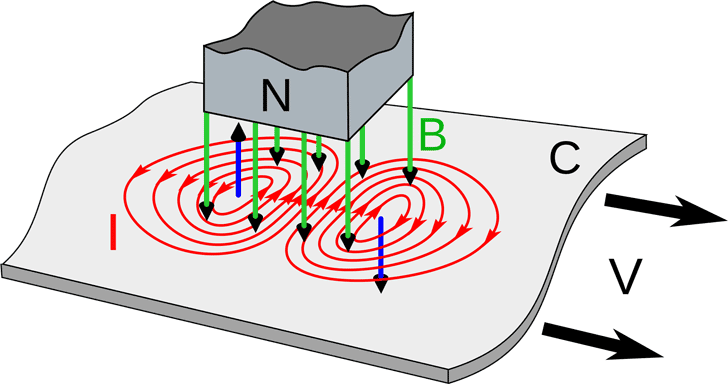
Eddy current test
The resulting eddy current is used to determine the quality of the weld seam. This non-destructive testing of welds cannot be used to determine the strength of welds.
When current flows through a coil and is brought close to the metal, an eddy current is created. This creates a kind of magnetic field.


The fluctuation of the secondary magnetic field due to defects in the weld alters the primary magnetic field, which results from the change in the current passing through the coil.
The change in current can be used to determine discontinuities and deformations in the weld seam. This NDT welding test is used as part of other welding tests.
Acoustic Emission Test
This procedure is often used to evaluate welds on an existing structure or large structures such as pressure vessels.
The emission of ultrasonic stress waves is used to locate the defective material.
Once the defective materials have been evaluated, other NDT welding test methods or destructive test methods are used for further evaluation.
roentgen Check
X-rays or gamma rays are used for non-destructive testing of welding work.
This method is used to identify imperfections in welds.
To evaluate the quality of the weld, X-ray images are examined.
These non-destructive tests of weld beads are expensive.
Some of the articles related to steel structure design are as follows
- Single angle design for tensile stress according to EC3
- Dimensioning of screw connections according to Eurocode 3
- Practical example of constructing a single-angle section
- Design of metallic pillars according to EC3 – worked example
- Steel column design according to Eurocode 3
- Worked example of constructing a steel beam (universal beam)
- Bending and torsion (theory and calculation)
- Steel beam construction to BS 5950
- UB section classification according to BS 5950