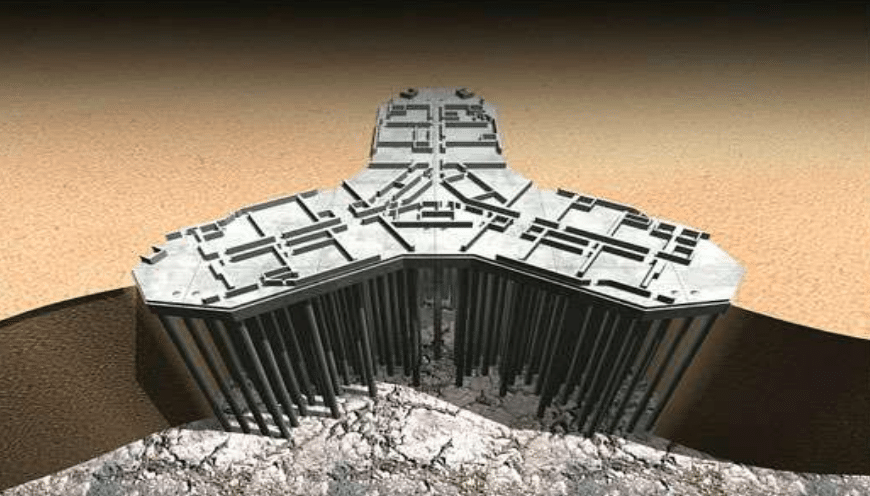
The purpose of a foundation can be discussed in different areas. First, let's see what a base is.
What is foundation
It is a structural element that transmits the loads from the superstructure to the ground through vertical or horizontal reaction, depending on the type of loads acting on it.


There are many types of foundations. However, they can be mainly classified into two types.
- Shallow foundations
Foundations built at a shallower depth are called Shallow foundations. Small individual foundations or the foundation of the entire area can be built.
slab foundation, combined substructure , strip foundation , slab foundations etc. are some examples of shallow foundations.


- Deep foundations
Deep foundations are constructed when the structure cannot be built on shallow foundations due to very high loads imposed on the structure, low bearing capacity of the soil, weak soil conditions that make it impossible to construct shallow foundations, etc.
Pile foundations such as in-situ concrete bored piles, Micropiles , diaphragm walls, etc. are some examples of deep foundations.


Purpose of the foundation
Let's discuss the purpose of the foundation. We build foundations because they are structures.
The structure consists of two components namely superstructure and substructure. Generally, the substructure is called the foundation of the structure.
The main purpose of foundation construction can be listed below.
- Safe cargo transfer
The main purpose of the foundation is to safely and error-free transfer the weight of the superstructure to the ground. Different types of loads are applied to the structure. They must be transferred to the ground without affecting the superstructure.
The structure's own weight, moving loads acting on the structure, other vertical loads acting on the structures, wind loads acting on the structure as lateral loads, seismic loads acting on the structure as vertical and horizontal loads, other accidental loads, etc. must be without structural failure or without violation of maintenance requirements can be transferred to the ground.
- Maintenance of the structure with limit state of use
When lateral loads act on the structure, the deformations caused by them must be controlled. They must be within the permissible limits.
For buildings, we keep floor displacement and overall deflections at a certain level to ensure ease of maintenance. Although the building is good systems for absorbing lateral loads if the foundation moves laterally when using lateral loads these deformations are greater. Therefore, the foundation must have sufficient reinforcement to keep the structure within the limit of use.
- Avoid different settlements
Different foundation settlements affect the superstructure and its other components, such as: B. Brick walls, partitions, other fittings, etc. If these settlements are significant, they can also affect structural stability.
The foundation must be designed to resist any movement. These movements may be due to incorrect sizing of the foundation or the nature of the soil.
If the pressure under the foundation is the same as that of all foundations resting on the same soil, the settlement will be almost the same. So there are no different settings.
Contractions, expansions or soil movements can lead to different settlements. These actions must be taken into account in planning. Strong tension beam systems and foundation planning designed to accommodate such movements could be used.
Related articles for foundations
- Combined underground
- Surface foundation
- Shallow foundations
- pillar foundation
- Foundations
- Deep foundations
- Foundation failure
- support
- Eccentrically loaded foundations
- Shallow foundation failure
- Pile slab foundations
- mat base
- Foundation pile
- Driven pile foundations
- Pile foundations
- Buoyancy pressure in foundations
- How to determine the type of foundation
- Excavation for foundation
- Foundation waterproofing
- Laying shallow foundations
- Slab foundations