Shallow foundations are foundations built at a shallower depth as opposed to deep foundations. In general, the depth of the foundation is about 1 m. This is a general value based on the nature of the soil. Depending on the type of structure, this depth may vary.
The design foundation is the most commonly constructed type of foundation. The construction cost is lower compared to other types of foundations .
Types of Shallow Foundations
Shallow foundation selection is based on the nature of the subsoil and the loads acting on it.
The basic type of foundation is the strip foundation or individual foundation. When the load increases or the bearing capacity decreases, they become strip foundations or combined foundations. If the load increases further, these foundations become slab foundations.
Let us discuss the types of shallow foundations in detail.
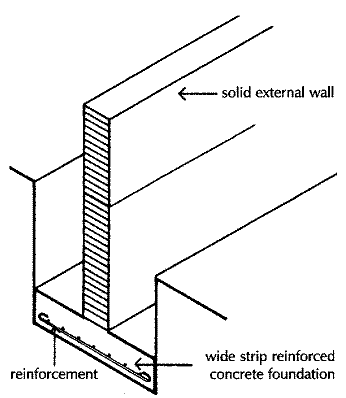
Wall foundations
Wall foundations may consist of quarry stone masonry or reinforced concrete foundations. Depending on the type of structure and the applied loads, the type of foundation is selected.


Rubble stone foundations are constructed to support brick walls in single-story buildings, partition walls, and other simple structures. Reinforced concrete structures are also constructed as wall foundations. Reinforced concrete foundations are constructed especially for retaining walls and in weak soil conditions.
Isolated support
Insulated foundations are the most common type of formwork foundation.
Isolated foundations are also called area foundations or individual foundations. Most buildings up to five stories are based on isolated or combined foundations.
Insulated foundations are the simplest foundations in terms of design, detailing and construction. Reinforcement arrangements are also very simple compared to other types of foundations.
Combined foundations
The combination of two or fewer columns into a single foundation is called a combined foundation.
A combined foundation is erected when the supports are very close to each other, since with low bearing capacities the foundation area increases, with increasing axial loads the foundation area increases, etc.
Belt foundations
Due to limited space on the property, it may be necessary to extend the building to the boundary wall. In these cases, the pillar cannot normally be placed in the center of the foundation.
The support is located at the edge of the foundation. Due to the eccentricity of the support, the stress under the support increases. This leads to bearing failure or increased settlement due to the ineffectiveness of the foundation.


To maintain balance under the foundation, we build strap beams. There is a special procedure for constructing strip foundations and beams.
Strip foundations
The next development of individual foundations and combined foundations is strip foundations. Strip foundations are not commonly constructed types of shallow foundations compared to individual foundations.
- For closed columns, we build strip foundations to support the row of columns.
- We design strip foundations to support walls and other structures with linear loads.
- If the load capacity is low, we combine all individual foundations and create strip foundations.
Strip foundations offer advantages over individual foundations.
- Reduces pressure under the foundation.
- Minimize different settlements
- Inverted T-strip foundations are more effective in controlling differential settlement and supporting higher axial loads.
Slab foundations
Slab foundations are types of foundations constructed for low-rise buildings. These types of foundations are constructed especially for single-story buildings.
There are no special bases for this type of foundation. The plate serves as a base. If necessary, the plate stiffness is increased and adjusted according to design requirements.
The article, Slab Foundations For more information, see this page.
Slab foundations
A slab foundation is a type of shallow foundation in which the slab is used as the foundation. This type of foundation is somewhat similar to a slab foundation.
Generally, the slab is suspended and supported on beams or other structures such as concrete walls. If the slab rests on the ground, it is called a ground slab.
Mat foundations
Mat foundations are also called slab foundations.
Slab foundations are concrete slabs built into the ground. When the area of individual foundations increases with increasing axial loads of the columns, we construct slab foundations. Foundation thickness varies depending on bending and shear requirements.
Buildings up to 10 floors high can be constructed on a mat basis, provided the soil has sufficient load-bearing capacity.
Slab foundations are designed using computer software because manual calculations are too difficult. Reinforcement detailing is done in the same way as for smooth slabs.
The article, treadmill base For more information, see this page.
Liquid foundations
A grid foundation is a type of shallow foundation for lightweight structures. A truss foundation can be constructed, especially for single-story buildings with good load-bearing capacity.
Truss foundations are concrete beams built to support walls. In this project, the rubble foundations are replaced by a set of concrete beams.
If a structure needs to be built on rock or a very hard surface, these types of foundations are more suitable.


How to choose the type of foundation
When selecting the type of foundation, you can proceed as follows.
- Calculate supporting loads or foundation loads
- If the structure is a low-rise building, it may be built on shallow foundations.
- Calculate the area of the foundation. If it is possible to select insulated foundations, proceed to the design.
- If the area of the foundation increases significantly, the options of combined foundations or strip foundations can be examined.
- If neither strip foundations nor combination foundations are applicable, the slab foundation option may be selected.
How to Design Shallow Foundations
Shallow foundations are placed directly into the ground. When planning these types of foundations, the following procedure is followed.
- Calculate operating load and breaking load
- Calculate the foundation area based on the allowable bearing capacity of the soil
- Simple foundations are designed for bending and shear. This can be done through manual calculations.
- Strip foundations, slab foundations, etc. are analyzed using computer-based software. Sizing can then be carried out using manual calculation.
- The quality of concrete is selected based on strength and durability requirements. The article on How to choose concrete types For more information, see this page.
Advantages of Shallow Foundations
- Shallow foundations are economical compared to other types of foundations such as cast-in-place concrete bored piles.
- Simple construction compared to deep foundations
- Quality control and assurance processes are simple and observations can be made with the naked eye.
- No heavy equipment is required for assembly.
- Construction can be done quickly.
Related articles
- pillar foundation
- Foundations
- Deep foundations
- Foundation failure
- support
- Eccentrically loaded foundations
- Shallow foundation failure
- Pile slab foundations
- mat base
- Foundation pile
- Driven pile foundations
- Pile foundations
- Buoyancy pressure in foundations
- How to determine the type of foundation
- Excavation for foundation
- Foundation waterproofing
- Laying shallow foundations
- Slab foundations