With technological development in this area and due to its ease of construction, the use of structural steel is becoming increasingly popular.
Construction time is one of the most important factors considered when choosing the material to be used. It is common knowledge that concrete buildings take much longer to complete than steel buildings.
The availability of prefabrication methods and ease of installation have led to the greater popularity of steel construction.
This article explains the section classification of steel beams. A section can be divided into four categories based on the stage at which it fails. This selection is made mainly based on proportions.
- Class 01 – Plastics area
- Class 02 – Compact Section
- Class 03 – Semicompact Section
- Class 04 – Slim Section
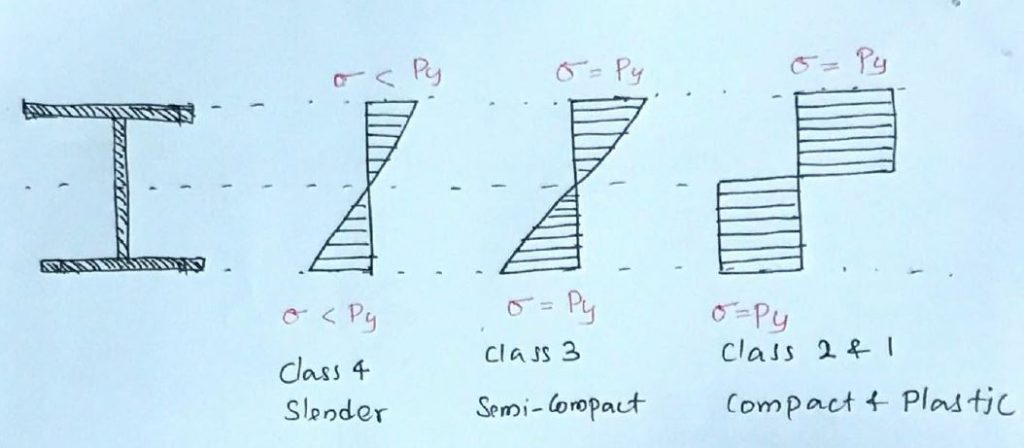
The voltage fluctuation in a section can be shown as in Figure 1.


The equation to be used to calculate bending capacity varies depending on the section classification. Mainly the section module changes in each class.
| Classroom | Bending moment capacity |
| Class 4 Lean |
M = σ Z xx |
| Class 3 Semi-compact |
M = p j Z xx |
| Class 1 and 2 Plastic and compact |
M = P j S xx |
The behavior of the section can be represented as shown in Figure 2. The variation of the section rotation with the bending moment is given in Figure 2.


As explained previously, the variation of the section's rotational moment clearly shows the behavior of the section and its evolution of the bending moment as the section rotates.
Plastic area
Profiles that reach the plastic moment (Mp) and maintain the bending moment forming the plastic hinge as shown in figure 2. These types of profiles are classified in class 1.
Compact section
Sections that reach the plastic moment (Mp) and cannot maintain the plastic moment due to local buckling are classified in Class 2 – Compact section.
Semi-compact section
Sections that do not achieve plastic moment (Mp) due to local buckling of one or more cross-sectional elements are called semi-compact sections and are classified in class 3. Furthermore, extreme fibers can achieve structural strength before local buckling occurs .
Thin section
Profiles that do not reach the required load capacity due to local buckling as a result of higher cross-sectional ratios are classified in class 4 – thin profiles.
SECTION CLASSIFICATION
When
b/T < 9ε – the flange is made of plastic
d/t < 80ε – the orbit is plastic
When
b/T < 10ε – the flange is compact
d/t < 100ε – The Web is compact
When
b/T < 15ε – flange is semi-compact
d/t < 120ε – The fabric is semi-compact
where all designations correspond to the code and
ε = (275/P j ) 0.5
Based on the section data, the section classification of the universal beam can be made. Likewise, other sections subject to axial loads, etc. may also be classified in accordance with Table 11 of BS 5950:2000.