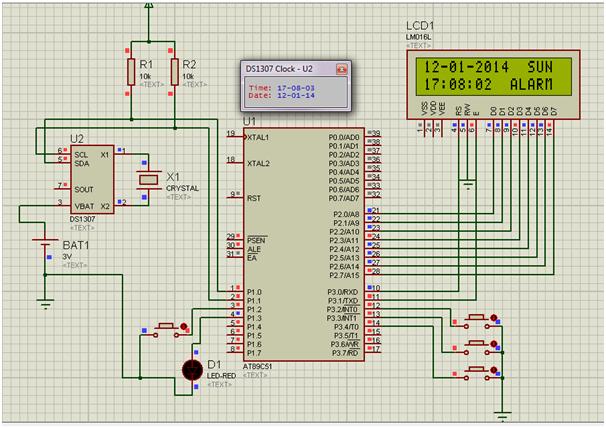
Real time clock is a digital clock that displays real time on a 16×2 LCD display. Here in this circuit we can also set alarm and time. The DS1307 real-time serial clock (RTC) is a low-power binary coded (BCD) full decimal clock/calendar plus 56 bytes of NV SRAM. Address and data are transferred serially via a bidirectional I²C bus. ck/calendar provides information about seconds, minutes, hours, day, date, month and year. The month end date is automatically adjusted for months with fewer than 31 days, including corrections for leap years. The clock works in 24 or 12 hour format with AM/PM indicator. The DS1307 has a built-in power detection circuit that detects power failures and automatically switches to the backup source. The timing operation continues while the part operates from the backup source.

Fig. 1: Circuit diagram of 8051 microcontroller and IC DS1307 based real time clock
Figure 1.1: Real-time digital clock Proteus circuit
Description:-
In this circuit, port 2 of microcontroller connected to data pins of 16×2 LCD display and bits P3^0 and P3^1 of port 3 connected to command pin of 16×2 LCD display rs and en respectively. And SDA serial data and SCL clock pin of ds1307 connected to P1^0 and P1^1 of microcontroller respectively. 4 switches/buttons also used to set the time and alarm. Bits P3^2, P3^3,P3^4 and P1^2 are configured as increment digit, increment value, time setting and alarm setting respectively. And an alarm indicator LED also connected to P1^3 to indicate alarm. When the alarm time coincides with the real clock time then the LED will be activated. In this watch, RTC is used in 24-hour mode which gives accurate time and can be displayed on LCD through microcontroller. The microcontroller continuously reads data from the RTC. The program continuously reads data from the ds1307 and shows it on the display. Bit P3^4 is activated low when a low signal arrives at the program calls, time setting function and bits P3^2 and P3^3 are also activated low level for setting time/date/day as well as the alarm time after pressing the P1^2 bit.

Fig. 2: Overview of 8051 microcontroller and DS1307 IC-based real-time clock
Figure 1.3: RTC circuit diagram
Component used
Component used: –
89S52 Microcontroller
A microcontroller is a small computer on a single integrated circuit containing a processor core, memory, and programmable input/output peripherals. Program memory in the form of NOR flash or OTP ROM is also typically included on the chip, as well as a typically small amount of RAM. Microcontrollers are designed for embedded applications, in contrast to microprocessors used in personal computers or other general-purpose applications.

Fig. 3: Typical image of the AT89S52 8051 microcontroller
LCD 16×2
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) screen is an electronic display module and finds a wide range of applications. A 16×2 LCD display is a very basic module and very commonly used in various devices and circuits. These modules are preferred over seven-segment and other multi-segment LEDs. The reasons are: LCDs are economical; easily programmable; It has no limitation on displaying special and even custom characters (unlike seven segments), animations and so on.
A 16×2 LCD means it can display 16 characters per line and there are 2 such lines. In this LCD, each character is displayed in a 5×7 pixel matrix. This LCD has two registers namely Command and Data.
The command register stores the command instructions given to the LCD. A command is an instruction given to the LCD to perform a predefined task such as initializing it, clearing the screen, setting the cursor position, controlling the display, etc.
The data register stores the data to be displayed on the LCD. The data is the ASCII value of the character to be displayed on the LCD. Click to learn more about the internal structure of an LCD.

Fig. 4: 16X2 character LCD pin diagram
DS1307
The DS1307 real-time serial clock (RTC) is a low-power binary coded (BCD) full decimal clock/calendar plus 56 bytes of NV SRAM. Address and data are transferred serially via a bidirectional I²C bus. The clock/calendar provides information about seconds, minutes, hours, day, date, month and year. The month end date is automatically adjusted for months with fewer than 31 days, including corrections for leap years. The clock works in 24 or 12 hour format with AM/PM indicator. The DS1307 has a built-in power detection circuit that detects power failures and automatically switches to the backup source. The timing operation continues while the part operates from the backup source.

Fig. 5: Typical image of DS1307 RTC IC
Project source code
### #includesbit rs=P3^0; sbit en=P3^1; sbit SDA=P1^0; //data pin for ds1307 bi-directional bit sbit SCL=P1^1; // clock pin for ds1307 output bit sbit alarm_set=P1^2; //set alarm input bit sbit alarm_beep=P1^3; //alarm indicator output bit sbit next=P3^2; //increase digit sbit inc=P3^3; //increase value input bit sbit set=P3^4; //set time input bit void set_time; //time/date/day set function void display; //time/date/day display function void alarm; //alarm set function char ack; unsigned char day1=1; unsigned char k,x; unsigned int date=1, mon=1, year=0x14, hour=0, min=0, sec=0; unsigned int alarm_min, alarm_hour; void I2CStart { SDA=1;SCL=1,SDA=0,SCL=0; } //"start" function for communicating with ds1307 RTC void I2CStop { SDA=0,SCL=1,SDA=1; } //"stop" funci=tion for communicate wit ds1307 RTC unsigned char I2CSend(unsigned char Data) //send data to ds1307 { char i; static bit ack_bit; for(i=0;i<8;i++) { if(Data & 0x80) SDA=1; else SDA=0; SCL=1; Date<<=1; SCL=0; } SDA=1,SCL=1; ack_bit=SDA; SCL=0; return ack_bit; } unsigned char I2CRead(char ack) //receive data from ds1307 { unsigned char i, Data=0; SDA=1; for(i=0;i<8;i++) { Date<<=1; do{SCL=1;} while(SCL==0); if(SDA) Data =1; SCL=0; } if(ack)SDA=0; else SDA=1; SCL=1; SCL=0; SDA=1; return Date; } void delay(unsigned int time) // delay function { unsigned int i,j; for(i=0;i //without time and alarm set #includesbit rs=P3^0; sbit en=P3^1; sbit SDA=P1^0; sbit SCL=P1^1; char ack; char array(7); void I2CStart {SDA=1;SCL=1,SDA=0,SCL=0;} void I2CStop {SDA=0,SCL=1,SDA=1;} unsigned char I2CSend(unsigned char Data) { char i; static bit ack_bit; for(i=0;i<8;i++) { if(Data & 0x80) SDA=1; else SDA=0; SCL=1; Date<<=1; SCL=0; } SDA=1,SCL=1; ack_bit=SDA; SCL=0; return ack_bit; } unsigned char I2CRead(char ack) { unsigned char i, Data=0; SDA=1; for(i=0;i<8;i++) { Date<<=1; do{SCL=1;} while(SCL==0); if(SDA) Data =1; SCL=0; } if(ack)SDA=0; else SDA=1; SCL=1; SCL=0; SDA=1; return Date; } void delay(int time) {unsigned int i,j; for(i=0;i
Circuit diagrams
| Circuit Diagram-8051-Microcontroller-DS1307-IC-Based-Real-Time-Clock |  |
| Circuit Diagram-8051-Microcontroller-DS1307-IC-Based-Real-Time-Clock |  |