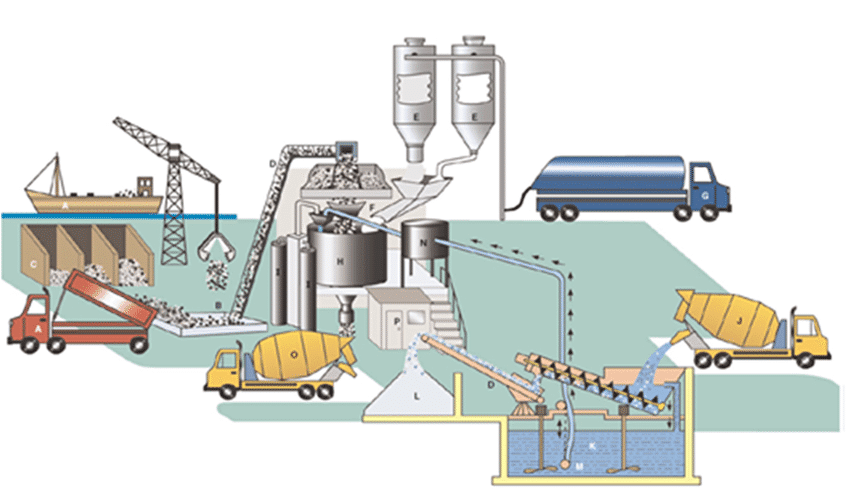
Ready-mixed concrete is concrete produced in a concrete mixing plant according to a mix composition. Ready-mix concrete is the most commonly used type of concrete mix in construction.
In the concrete mixing plant, aggregates (coarse and fine aggregates), cement, water and additives are mixed into a technical mixture to produce ready-made concrete.
After mixing, the mixture turns into concrete and is delivered to the construction site by a concrete truck. Concrete maintains its plasticity until delivery to the construction site.


Types of ready-made concrete
There are mainly three types that are not based on mixing methods. This classification also depends on when they are mixed.
They are as follows.
- Transit Mixed Concrete
- Shrink concrete
- Central mixed concrete
Transit Mixed Concrete
This type of concrete is also known as truck concrete. The concrete is mixed during transport and is done using a concrete mixer truck.
Most often, mixing occurs partially during transportation and completely on site.
The most important thing in this type of mixture is to keep the aggregate and cement mixture separate from the water. Water is added and mixing is stopped just before concrete .
This method solves problems related to workability such as: B. Slum loss is avoided and the plasticity of the concrete is maintained. Furthermore, problems that arise during the transport of concrete from the concrete mixing plant are avoided.
The capacity of the truck may be smaller than that of a normal truck. Therefore, the quantity of concrete per truck could be smaller.
Shrink concrete
Shrinkable concrete is one of the ways to increase the volume transported by truck.
As a measure to reduce volume, cement, aggregates and water are partially mixed.
Complete mixing takes place during transportation or at the construction site. This method can increase the volume that can be loaded onto a truck.
Central mixed concrete
This is the type of concrete widely used in construction and which we mainly know as ready-mixed concrete.
Concrete is mixed in stationary plants and loaded onto trucks. There is no mixing in the truck, but it rotates continuously to maintain the plasticity of the concrete.
This type of ready-mix concrete plant is also known as wet-mix or pre-mix plant.
Now let's look at some important factors related to ready-mix concrete.
- Mix design
Ready-mixed concrete is an engineering concrete produced using a technical process.
Ready-mix concrete is generally dosed by weight, with the entire amount of material added to the mixing vessel depending on the weight.
Additives can be added in the quantity specified by the supplier.
Before a project begins pouring ready-mix concrete, mix tests are performed to ensure that the specific mix has the desired strength for that mix composition.
- Set time
Typically, concrete setting time is about an hour for regular concrete. However, it is not sufficient in normal operation.
It takes more than an hour to pour concrete on slabs, walls, columns, mat base , etc. Additionally, travel time must be taken into account since the total time is the time after mixing.
Concrete needs to be porous and compacted before the first setting time. Otherwise Durability of concrete will be a problem. The formation of cold joints could also be observed.
Therefore, additives are added to prolong the setting time of the concrete.


- Additions
Various types of additives are added to ready-mixed concrete in the concrete mixing plant.
The type of additive addition depends on the manufacturer's instructions. When different types of additives are added to mixed concrete, compatibility must be checked before addition.
There is a method called redosing that is used to mix the ready-mixed concrete in the truck mix. Especially if the loss of slump is controlled by redosing. If a new dosage is carried out, it must be done very carefully and with the approval of the engineer.
Additionally, there are restrictions on adding additives to concrete. The maximum limit specified by the supplier may not be exceeded under any circumstances.
- Theft at the concrete mixing plant and on site
As the concrete is mixed, it is loaded into the truck where a sample is taken to check the slump. The fall at the factory is noted on the delivery note, which must be presented to the engineer at the construction site. This record provides information about the slump of the mixture.
When the ready-made concrete is delivered to the construction site, Slump Test is carried out to check the degree of slump of the construction site. Site slump is the project slump specified in the mix composition. If within limits, concrete may be used as long as other requirements are acceptable.


- Concrete temperature
The temperature of ready-mixed concrete must be controlled to achieve a low heat of hydration. Therefore, several measures are taken to reduce the temperature of ready-mixed concrete.
Some of them are as follows.
-
- Use ice water to mix concrete.
- Aggregate cooling
- Add ice to replace some water
- Cooling truck concrete mixing tank – place jute bags and apply water
- Aggregate
Once the mix design and test mixes (cubes tested for 7 days and 28 day strength) are complete, no changes can be made to the aggregate.
As we know, when the material sources (not only the aggregate, but also other additives) change, the composition of the mixture changes and the results obtained from the sample mixture are no longer valid.
As we also use the new generation Flow Agent Changes in the origin of materials such as additives have a detrimental effect on the concrete mix as they are very sensitive to changes.
For this reason, no changes can be made to the material source once it has been selected and determined through a sample mix test.
Advantages of Rady mixed concrete
- Concrete Quality: Unlike other methods, all mixing suggestions are added accurately and without errors. Further mixing is carried out in a controlled manner and the addition of water and additives is also carried out in accordance with technical requirements. Therefore, we can obtain a quality mixture.
- Consistency of ready-made concrete: The consistency of the concrete mix can be maintained regardless of whether we mix 20m 3 or 200m 3 As all the work, including loading the mix into the truck, is carried out by mechanical and electronic devices, the possibility of errors occurring is insignificant.
- Production quantity: There are no minimum or maximum quantity limits. Production can be done according to project needs.
- Efficient production: Concrete production can be done more efficiently. The quantity of product depends on the size of the mixing container. However, production can be continuous until the planned work is completed. Furthermore, the time required to produce a one meter cube of concrete is less compared to other manual methods.
- No material storage on site: If the concrete batching plant is not located on the construction site, no space allocation is required. In some cases, especially in large construction areas, concrete batching plants are built on site due to construction requirements. In these situations we need space to store materials.
- Savings on materials: As materials are used in a controlled manner, waste is minimal. In particular, the cement is stored in the silo and there is no residue when it is transported to the mixing vessel or silo.
- Ecological damage: The environmental impact of the production method is minimal. There is no need to burn gas as all devices are powered by electricity.
Disadvantages of Ready-Mixed Concrete
- Influence on setting time: Most of the time, concrete mixing plants are located far from the construction site. Therefore, it takes some time for the concrete mix to reach the construction site. The concrete setting time must be adjusted accordingly. Furthermore, the time to the construction site can also cause traffic jams.
- Slump loss: If the construction site travels a significant distance, there will be slump loss. This means that the workability of the concrete is lost. Therefore, the mix must be designed in such a way that the loss of slump due to distance cannot affect the concreting.