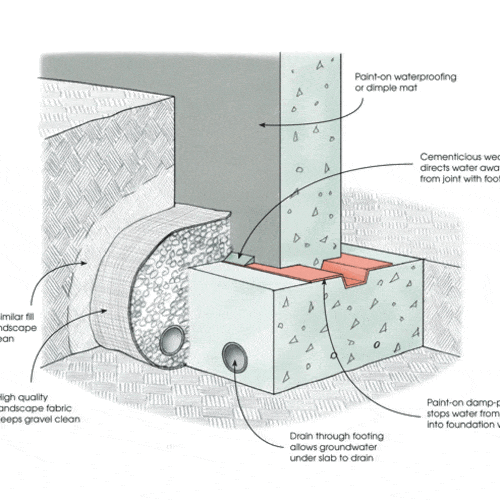
Foundation drainage is a system that reduces the pressure exerted on the foundation. This is also used to reduce the pressure of irrigation water applied to the foundation. Retaining walls .
Because it is a type of foundation drainage, it is sometimes called foundation drainage when used for foundations.
Foundation drainage consists of a perforated drainage pipe, geotextile, and single-layer metal installed around the pipe. The pipe is covered with single-layer metal and the metal is covered with geotextile.
Below you will find some important data about drainage.
- The pipe diameter is generally in the range of 100 – 150 mm. This may vary depending on the drain. Furthermore, instead of a single tube, multiple tubes can be placed at different heights.
- The size of metals can be 20 mm or 40 mm. It is important that metals are only one size. When we use graded metal, voids are filled and discharge is reduced.
- The size of the rubble package can start from 300 x 300 mm. This can be increased depending on the drainage arrangement and drainage.
- Also, we can use draining concrete or thin concrete to drain the water. As draining concrete has higher strength compared to normal rubble filling, we can easily use draining concrete even under the foundation.
Purpose of Foundation Drainage
- The main purpose of foundation drainage is to reduce irrigation water pressure under the foundation. When the irrigation water pressure under the foundation is reduced, it improves the stability of the foundation.
- In addition, reduced irrigation water pressure is used in retaining walls. When the irrigation water pressure is reduced, the water pressure in the retaining wall is reduced. If water pressure increases more than expected, it may fail the retaining wall . The article Forces acting on retaining walls For more information about loads acting on retaining walls, see.
- Good drainage reduces moisture in the foundation and increases the durability of the structure.
- It is necessary to protect the foundation with waterproofing. If we have a good drainage system, the need for waterproofing is minimal.


Foundation drainage or foundation drainage can be divided into four main categories. This categorization is based on the drainage arrangement or function of the drainage.
- French foundation drainage
To drain the water, a perforated pipe is laid in a gravel embankment.
- Foundation drain
It is the type of drainage shown in the figure above.
- Drainage gradation
A finished surface is maintained to allow water to drain across the surface.
- swamp well
The collection well is used to collect and pump water. Especially in areas with high groundwater levels and low groundwater penetration, water is collected in the collection well and then pumped out.
Advantages of Foundation Drainage Systems
- Reduces the effect of water accumulation
- Reduce structure settlement
- Reduce erosion
- Reduce moisture in the building structure.
- Proper drainage improves the durability of the structure
- Reduces the subsequent pressure exerted on retaining walls. This allows sections to be reduced and construction costs to fall.
Disadvantages of Foundation Drainage Systems
- Certain additional costs apply
- If built incorrectly, functionality can suffer over time.
- There are maintenance difficulties.
- A high level of specialized knowledge is required for construction
Related articles
- Early thermal cracking (calculate R/F requirements)
- Influence of construction practices on the formation of cracks
- Formation of cracks in concrete (basics, types and causes)
- Physical reasons for cracks
- Basics of crack formation in immature concrete
- Types of Foundation Cracks, Why They Are Serious
- Basement Wall Cracks (A Detailed Study)
- What is concrete spalling – causes and repairs
- 20 factors that affect the durability of concrete
- Durability of concrete (requirements and problems)
- Concrete shaking (methods and correct procedure)
- 6 Factors That Affect Concrete Curing Time
- 11 Methods for Hardening Concrete
- A detailed study of concrete (from scratch)
- Types of concrete shrinkage (detailed study)