Displaying potentiometer value and temperature using LM35
In my previous tutorial series on displaying sensor data (value) on OLED display, I explained how to display values of different sensors such as potentiometer, LM35, soil moisture sensor, DHT, HC SR04, etc. . This time, I will demonstrate and explain how to display multiple sensor values on a multi-color TFT LCD screen.
TFT LCDs are widely used attractive displays that can display TEXT, digits, numbers, pictures, images, graphics, etc.
- Small – 1.4”, 1.8”, 2.4”
- Medium – 2.8”, 3.2”, 3.5”
- Large – 5”, 7”
Most of these TFT LCDs work on the SPI protocol. All these TFT LCDs can be easily interfaced with Arduino because Arduino has SPI pins (MOSI, MISO, SCK). In Arduino IDE, there is also a TFT library.
Displaying sensor data on a TFT LCD looks very attractive because it has 64 thousand to 256 thousand colors. Also, it is possible to show colorful TEXT or image animation on this TFT LCD using Arduino. Here, I am using a 1.8” TFT LCD with 128×160 pixels, as shown in the figure. It works on the SPI protocol and has eight pins for interfacing with Arduino.
NO PIX
Let's start with a simple analog sensor – potentiometer (POT). I will show you how to display POT value on TFT LCD. The circuit diagram is followed by its connections, functioning and operation.
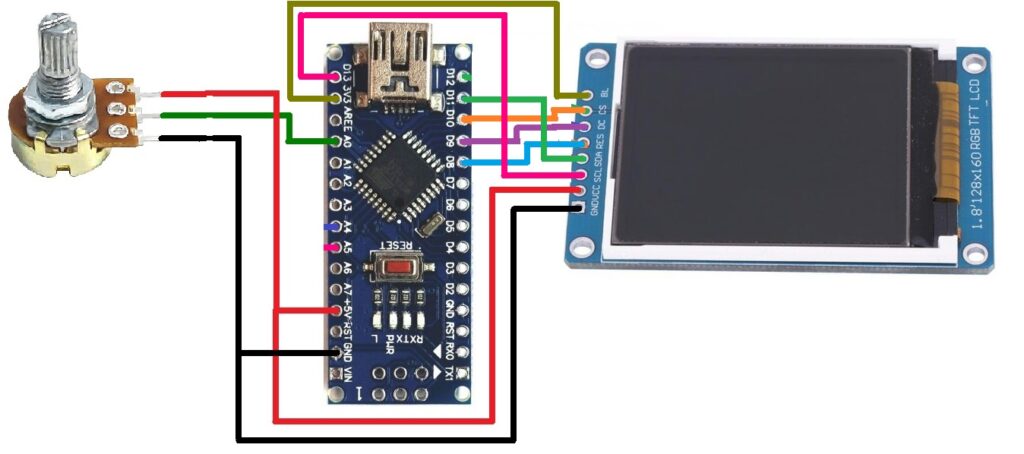
Circuit Diagram
The figure shows that the circuit consists of just three components – POT (potentiometer), Arduino NANO board and 1.8” TFT LCD.

Circuit Connections
The potentiometer has three terminals. The final two terminals are connected to the +5V and GND pins of the Arduino board as shown. The middle slider terminal is connected to analog input pin A0. Thus, turning the POT's analog input voltage on pin A0 varies from 0 to 5V.
The TFT LCD has a total of eight pins. It works on the SPI protocol, so its pins are connected to the SPI pins of the Arduino board.

The Arduino 5V power output directly powers the circuit. As the Arduino is powered by the computer's USB port (PC/laptop), there is no need for any external power supply.
Circuit operation
POT is used to vary the analog voltage from 0 to 5V. This analog voltage is supplied to the Arduino pin A0 as input. The Arduino reads this analog voltage and converts it to a digital value between 0 and 1023. It is first converted to a string and then to a character matrix because the TFT LCD can only display characters. The value is displayed as characters on the TFT LCD. Arduino has a TFT library “TFT.h” which is used here along with two other libraries, “SPI.h” and “wire.h”.
The Arduino TFT library has direct functions to display TEXT, graphics and images in various colors on the TFT LCD. Since TFT LCD works on SPI, we need SPI library and wire library to communicate. Below is the software program on Arduino IDE to display POT value on TFT LCD
Here is the snapshot of the circuit arrangement with the potentiometer value displayed on the TFT LCD screen.

Now we can connect any analog sensor to Arduino and display its data on the TFT LCD.
I will replace the POT with an accurate and widely used temperature sensor, the LM35. Provides analog output voltage of ten mV/ o C. Now, I will show you how to measure the room temperature accurately and display it on the TFT LCD. First, see the circuit diagram below.
Circuit Diagram
 As shown in the circuit, I replaced the LM35 sensor module in place of the POT.
As shown in the circuit, I replaced the LM35 sensor module in place of the POT.
The LM35 temperature sensor module also has three pins (terminals) (1) +V (2) G(-) and (3) S (signal). +V and G(-) are connected to +5V and GND of the Arduino board. S (signal) is the analog output of the sensor and is connected to the Arduino analog input pin A0.
Circuit operation
The LM35 sensor detects ambient temperature and provides 0 to 1V analog voltage output. This analog voltage is supplied to the Arduino pin A0 as input. The Arduino reads this analog voltage and converts it into a digital value between 0 and 1023. This value is multiplied by a factor of 0.488* to obtain the exact value of the ambient temperature. This value is the float number. It is first converted to a string and then to a character array because TFT LCD can only display characters.
Now we will display this temperature reading on the TFT. It is again handled similarly by the TFT library functions. Here is the program code to display room temperature on TFT LCD
Here is the snapshot of the circuit arrangement with the potentiometer value displayed on the TFT LCD screen.

In the next article in this tutorial series, I will demonstrate how to display temperature, humidity and soil moisture content on a TFT LCD using the DHT11 and soil moisture sensor.
*Note – detailed explanation is provided in the program code
(tagsToTranslate)Arduino