Concrete and steel are among the most common building materials, and many construction projects may use either one for their underlying structure. Each material has advantages and limitations, as with any engineering decision, and this article provides a general comparison. No material can be considered better than another for all cases, and the best option is determined by project conditions.
Reduce the cost of your next construction project.
Concrete construction
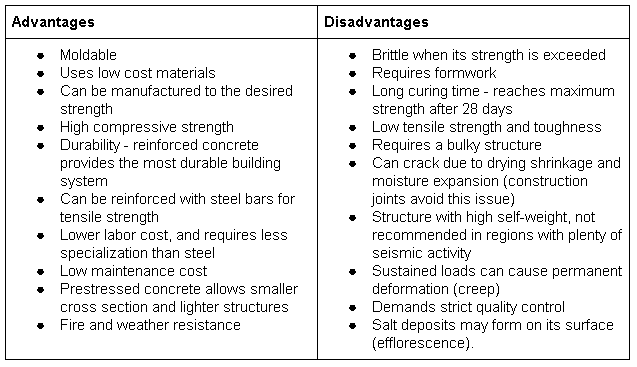
Concrete is the second most used material in civil construction after water: it offers versatility, durability and ease of manufacture, and can be molded into any shape.
-
Concrete structures are very resistant to compression, but they cannot withstand tension effectively.
-
For this reason, most concrete structures are reinforced with steel bars that provide additional support for tensile loads, this combination being called reinforced concrete.
Concrete structures can be built in different ways, using different types of concrete. The three most common types are plain cement concrete, reinforced concrete and prestressed concrete.
Simple cement concrete is obtained by combining cement, coarse aggregate (gravel), fine aggregate (sand) and water in a pre-determined proportion according to the needs of the project. When hardened, these materials become a homogeneous mass.
-
Structures made with plain cement concrete have high compressive strength but almost no tensile strength.
-
Therefore, plain cement concrete is most often used in roads and concrete blocks for walls, since these structures are subjected to compressive loads.
Reinforced concrete is basically plain cement concrete with steel bars that provide additional tensile strength. This is the most common type of concrete used in civil construction, having applications not only in buildings, but also in structures such as water tanks.
Prestressed concrete is preloaded by applying compressive stress before being subjected to any load beyond its own weight. Compression is produced by tensioning high-strength steel tendons within the concrete volume before applying external loads. This improves its performance once in service.
The following table summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of concrete structures:

Steel Construction
Steel is an alloy of iron, carbon and other elements. Depending on its chemical composition, it is classified as mild steel, medium carbon steel, high carbon steel, low alloy steel or high alloy steel.
As its name suggests, structural steel is a category of steel used in the construction industry . The shapes and structural properties of steel are regulated by standards such as those of the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC).
-
Most structural steel profiles are elongated beams, with a specific cross section.
-
The most common form is the I-beam, which is very rigid relative to the cross-sectional area. Therefore, it can withstand high loads without deformation
The following tables summarize the advantages and disadvantages of steel construction:

Direct comparison between concrete and steel
Both materials offer numerous benefits, as described in the previous sections. When choosing between a concrete structure and a steel structure, the following differences can be expected: 
The most suitable building material for your building is determined by the specific needs of the project. For example, concrete allows for lower construction costs in exchange for a longer construction time, while steel is preferred when quick construction is the priority. In cases where space is a limitation, steel saves space compared to the bulkier concrete structure.