Introduction to Power Quality
Power quality is a critical aspect of modern electrical systems. Represents the compatibility between the electrical energy supplied and the electrical systems used. When power quality problems arise, they can affect the efficient functioning of equipment and cause outages and failures.
Power quality is a broad field. It includes various factors such as voltage fluctuations, frequency fluctuations, and waveform distortions. One of the most important factors that affect power quality are “transients”. This article takes an in-depth look at the definition of transients in power systems, their types, causes and effects, and how to deal with them effectively.
What are transients in power systems?
Transients in power systems, also known as electrical transients, are short-term, transient voltage or current surges in an electrical circuit. They usually occur during sudden changes in the power system, such as: B. when turning devices on or off or in the event of a lightning strike.
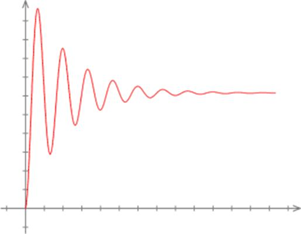
These transients, also called transient disturbances, can be of two types: impulse transients and oscillation transients.

Causes of transients
Transients can have many causes and can be of natural or artificial origin. For example, lightning is a significant natural source that often causes impulse transients. Artificial sources are most often associated with switching processes in the electrical network, such as: B. starting or stopping a large motor or transformer, which results in impulse and oscillation transients.
Understanding the causes of transients is the first step towards effective transient disturbance management.

Types of transients
There are two main types of transients in power systems: impulse and oscillatory transients.
A sudden change in steady-state voltage or current characterizes impulse transients . They are usually caused by lightning strikes or switching operations.
Oscillating transients , on the other hand, represent a constant and cyclical change in the steady state. Its most common cause is therefore inductive or capacitive network elements of the power network.
Effects of transients on power quality
Transients can have a negative impact on power quality and therefore the operation of electrical devices. Excessive transient voltages can damage insulation and semiconductors in electrical devices, causing equipment malfunction or failure. This can lead to unexpected outages and costly repairs, affecting the reliability of the entire power system.
Understanding the impact of transients on the electrical grid is critical to implementing effective power quality solutions.

Transient detection and measurement
To deal with transients, they must first be recognized. This is achieved by monitoring power quality. To accurately measure voltages and transient currents, special devices such as oscilloscopes and power quality analyzers are used.
By detecting and measuring transients, we can assess their potential impact, develop effective strategies to improve energy quality and efficiency, and protect power systems.
Mitigation and protection against temporary outages
To mitigate transients, strategies must be implemented to limit the occurrence of transients and protect devices from their effects. Surge protection devices (SPDs) and power conditioning devices are often used to mitigate transients.
One method of protecting against transients is transient overvoltage suppression (TVSS). Additionally, grounding techniques are used in power systems to prevent transient-related damage.
Transient standards and guidelines
Several international bodies have established guidelines and standards for power quality, including transients. One such body is the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), which has several IEEE power quality standards.
These standards help define acceptable transient levels in power systems and provide guidance in developing transient mitigation strategies.
Case studies or practical examples
To better understand the effects of transients, let's look at some real-world examples.
In one case, there were frequent production line failures at a production facility. A detailed analysis of power quality revealed that the cause was transient surges caused by switching in the electrical system. The solution was to install lightning arresters in critical locations to successfully mitigate surges and restore efficient operation.
In another example, server failures occurred repeatedly in a data center. Investigations revealed that the servers were affected by pulse spikes caused by lightning. Installing a comprehensive surge protection system mitigated the problem.

The term “transient” has long been used in the context of studying imbalances in electrical networks to describe transient events in nature. The idea of a damped periodic transient due to an RLC network is probably what power engineers think of when they hear the word “temporary”.
Station automation theory
Outbreak is another common word considered synonymous with temporary. For example, a utility engineer might consider a surge to be the short period of time caused by lightning and that a surge limiter is used to protect against it.
End users often use the word indiscriminately to describe anything unusual that may occur in the network's supply, from dips, spikes and outages. Because this word presents several potential uncertainties in the area of power quality, we avoid misuse unless we have clearly stated what it means.
Conclusion
Understanding transients in power systems is critical to ensuring high power quality and reliable operation of electrical devices. Our quest for better power quality continues, from identifying the causes and types of transients to implementing effective transient mitigation strategies. By adhering to established power quality standards and utilizing state-of-the-art power quality measurement tools, temporary outages can be resolved and power system reliability can be improved.
common questions
1. What are transients in power systems?
Transients in power systems are temporary, short-term surges in voltage or current in a circuit that often occur due to sudden changes in the power system.
2. What is the impact of transients on power quality?
Transients can have a variety of adverse effects on power quality, such as causing damage to electrical equipment, equipment malfunction or failure, and degrading the overall reliability of the power system.
3. How are transients detected and measured?
Transients are detected and measured using specialized equipment such as oscilloscopes and power quality analyzers. These tools allow accurate measurements of transient voltages and currents.
4. What strategies are there for temporary containment?
Strategies to mitigate transient disturbances may include the use of surge protection devices (SPDs), power conditioning equipment, grounding techniques in power systems, and transient overvoltage suppression (TVSS).
5. What standards apply to transients in power systems?
International organizations such as IEEE establish standards for transients in power systems. These standards define acceptable transient levels and serve as a basis for developing transient mitigation strategies.