Leakage is one of the common failures in mechanical equipment. The reasons for causing leaks are mainly two: firstly, they are caused by machining, and the surface of mechanical products must have defects or deviations in shape and size, which inevitably results in gaps in the joints of mechanical parts; secondly, there is a pressure difference between the sealing sides and the working medium will leak through the gaps.
Reducing or eliminating gaps is the main way to prevent leaks. The function of the seal is to seal the gaps between the contact surfaces, isolate or cut the leak channel, increase the resistance in the leak channel, or add small energy conversion devices in the channel to apply pressure to the leaked material, which can compensate partially or completely balance the pressure difference that causes leakage, so as to avoid leakage.

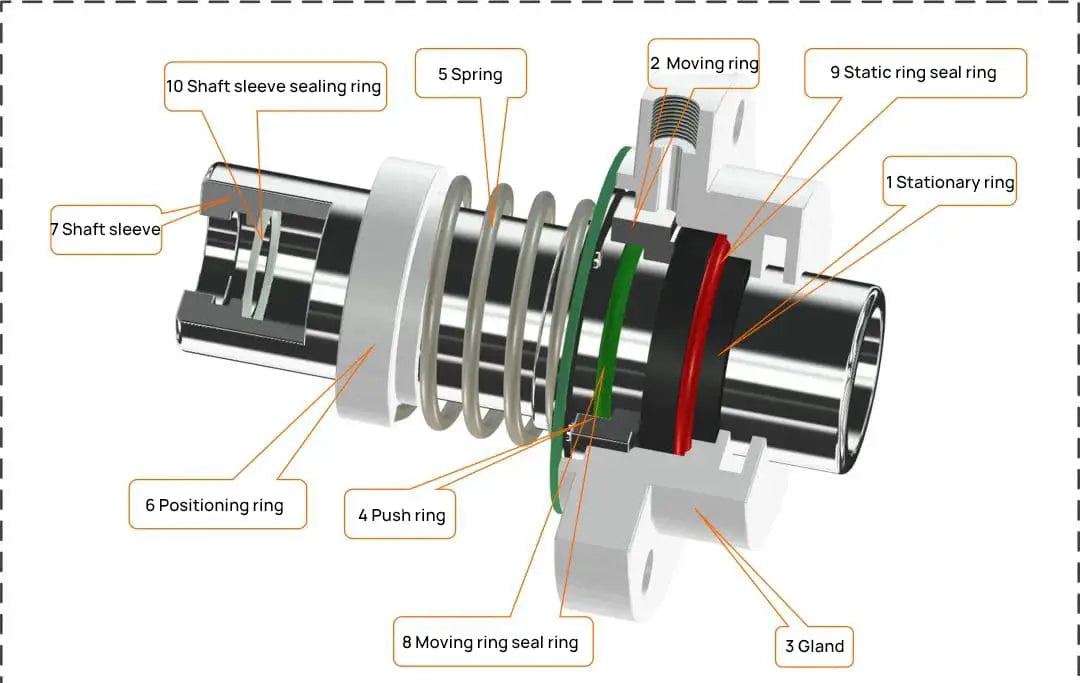
The basic components of a mechanical seal include:
1) stationary ring
2) rotating ring
3) gland
4) collar
5) spring
6) locating ring
7) shaft sleeve
8) O-ring for swivel ring
9) O-ring for stationary ring
The basic concept of mechanical seal
Mechanical seal refers to a device that prevents fluid leakage, which is composed of at least one pair of end faces perpendicular to the axis of rotation and maintained in close contact and relative sliding under the action of fluid pressure and the elasticity of the mechanism compensation (or magnetic force) as well as assisted sealing. The auxiliary seal of the compensation ring is called a mechanical bellows seal.
Mechanical Sealing Components
The main components of the mechanical seal include the following four parts:
- Main sealing parts: the moving ring and the stationary ring.
- Auxiliary sealing parts: the sealing ring.
- Pressing parts: the spring and the pusher.
- Transmission parts: the drive seat and fixing key or screw.

Issues to be observed during mechanical sealing operation
- Installation Notes
The. Pay close attention to avoid installation deviations during the installation process.
(1) The clamping cover must be installed after aligning with the coupling, and the screws must be tightened evenly to prevent the end face of the cover from deviating. Check each point with a meter and the error should not exceed 0.05mm.
(2) Check the adjustment clearance (i.e. concentricity) between the clamping cap and the outer diameter of the shaft or shaft sleeve, and it should be uniform on all sides. Check each point with a gauge and the allowable deviation should not exceed 0.01mm.
B. The amount of spring compression must be carried out in accordance with the specified requirements, and oversizing or undersizing phenomena are not allowed. The error must be within 2.00mm. Excessive size will increase the end face pressure rate and accelerate end face wear. Undersize will cause insufficient pressure ratio and cannot achieve sealing effect.
w. After installing the movable ring, make sure it can move flexibly on the shaft. The movable ring must be pressed against the spring and it must rebound automatically.
- Notes on disassembly
The. During disassembly of the mechanical seal, it must be handled carefully, hammers and flat chisels are strictly prohibited to avoid damage to the seal components. Two steel wire hooks can be used to insert into the transmission seat gap in the positive-negative direction to pull out the sealing device. In case of disassembly difficulties caused by encrustation, clean it before disassembly.
B. If mechanical seal is used at both ends of the pump, take care of both ends during the assembly and disassembly process to avoid neglecting either end.
w. For mechanical seal that has been in operation, if the clamping cap is loosened, causing the seal to move, the moving and stationary parts of the ring should be replaced instead of tightening and continuing to use.

Questions regarding normal operation and maintenance of the mechanical seal
- Preparation work and precautions before starting
(1) Perform a comprehensive inspection of the mechanical seal, accessory devices and piping installation to ensure they are complete and meet technical requirements.
(2) Before starting the mechanical seal, carry out a static pressure test to check whether there is any leakage phenomenon. If there is a significant leak, find the cause and eliminate it. If it is still ineffective, disassemble it, inspect it and reinstall it. Generally, the static pressure test pressure is 2 ~ 3 kg/cm².
(3) Rotate the coupling toward the pump and check that it is free and level. If the coupling is stuck or does not move, check whether the assembly size is incorrect or the installation is reasonable.
- Installation and shutdown
(1) Before starting, keep the sealing chamber filled with liquid. To transport solidified media, steam must be used to heat the sealing chamber to melt the media. Before starting, the couplings must be rotated to avoid sudden starting and soft ring fracture.
(2) For mechanical seal using the pump external oil seal system, the oil seal system must be started first. After stopping the pump, stop the oil seal system.
(3) After the hot oil pump stops working, the cooling water of the oil seal chamber and end face seal should not be stopped immediately. When the oil temperature at the end sealing location drops below 80 degrees, the cooling water can be stopped to prevent damage to the sealing parts.
- Operation
(1) If there is a slight leak after starting the pump, observe it for a period. If the leak does not decrease after running continuously for 4 hours, stop the pump for inspection.
(2) The operating pressure of the pump must be stable and the pressure fluctuation must not exceed 1 kg/cm².
(3) During operation, it is necessary to avoid cavitation to avoid dry friction on the end face and damage to the seal.
(4) The sealing condition must be checked regularly. During operation, if the leakage exceeds the standard, the heavy oil should not exceed five drops per minute and the light oil should not exceed 10 drops per minute. If there is no improvement in 2 to 3 days, stop the pump and inspect the sealing device.

Mechanical Seal Structure and Maintenance
- Structure
The typical structure generally consists of a rotating ring, stationary ring, rotating seal, stationary seal, spring, spring seat, fixing screws, anti-rotation pin, etc.
- Principle
When the mechanical seal is working, the axial force caused by the pressure of the sealed fluid and the force of the elastic element makes the rotating and stationary rings fit together and move relatively.
Due to the tight fit of the two sealing end faces, a small gap is formed between the sealing end faces (the sealing interface). When the pressure medium passes through this gap, a very thin liquid film is formed, generating resistance, preventing the medium from leaking and lubricating the end face, achieving a long-term sealing effect.
- Classification
(1) According to the sealed host: mechanical seals for pumps, reactors, compressors, etc.;
(2) According to different working parameters, they are divided into high temperature, medium temperature, low temperature, high pressure, medium pressure, low pressure, high speed, heavy duty, etc.;
(3) According to the structural form, they are divided into balanced and unbalanced, single-end and double-end mechanical seals.
- Installation
(1) Preparation
① Check whether the radial runout, surface roughness, outer diameter tolerance and axial displacement of the shaft and sleeve meet the accuracy requirements;
② Check whether the mechanical seal model and specifications meet the requirements. That the parts are intact, that the sealing ring size is appropriate, and that the surfaces of the rotating and stationary rings are smooth and flat. If there are defects, they must be replaced or repaired.
③ Clean the mechanical seal parts with clean gasoline and then dry them, paying attention to protecting the sealing surface;
④ When installing the mechanical seal, first find the working length of the spring in the instructions, and then use the caliper to measure the free length of the spring to obtain the amount of compression. During installation, the deviation of the spring compression amount should not be more than 1mm.
(2) Inspection and Measurement
① The mobility of the rotating ring requires that there is a certain gap between the rotating ring and the shaft, ensuring that the gap is 0.3 to 0.7 mm.
② Whether the stationary ring is eccentric. In pump mechanical seals, the stationary ring (spring seat) and shaft adopt sliding adjustment and the clearance is very small. If the gap is large, the stationary ring will be eccentric, and the uneven spring force acting on the sealing surface will cause leakage or seal failure.
③ Check the fit between the rotating ring and the sealing surfaces of the stationary ring. When checking, use a 90° square to measure the deviation of the sealing surface from the shaft centerline.
(3) Installation
First, assemble the components on the rotating component and the stationary ring component and preliminarily preload the spring. Then install the rotating ring component on the shaft and the stationary ring component on the pressure cap. First, measure the distance from the sealing end face of the rotating ring to the end face of the sealing cavity and the distance from the sealing end face of the stationary ring to the end face of the end cap. The difference between the two is the amount of preload the mechanical seal spring and the bearing is mounted on. The compression amount is adjusted according to the technical requirements and the measured compression amount, and the pressure cap is tightened.
During the installation process, maintain the cleanliness and integrity of the seal, and do not use tools to strike the seal components to avoid damage to the seal. After the mechanical seal is installed on the shaft, push the rotating ring by hand to make it elastic and smooth, then add some engine oil to the sealing surface and evenly tighten the end cap without pressing it .
(4) Inspection and Pressure Test
After installation, the rotary must operate flexibly and have a certain degree of flexibility. Mechanical seals for important equipment must undergo static and dynamic pressure testing. After passing the test, they can be put into formal use.
- Operation
(1) Pre-departure precautions: Check whether auxiliary equipment and the refrigeration system are installed correctly; clean the pipeline to prevent rust and impurities from entering the sealing cavity; Rotate the coupling manually to check whether the shaft runs smoothly. If it is too heavy, check whether the corresponding dimensions are correct and find out the cause and eliminate the fault.
(2) Test operation and normal operation: First start the liquid sealing system and the cooling water system to fill the sealing cavity with the medium, and then start the main seal for test operation. If a slight leak is found at first but gradually subsides after 1-3 hours, this is a normal running-in process. If the leak does not subside, stop for inspection; If the mechanical seal overheats or smokes, it is generally due to excessive spring pressure, and the spring pressure must be reduced accordingly. After test qualification, it can be put into normal operation under working conditions. The process of increasing temperature and pressure must be slow and observe carefully whether abnormal phenomena occur.
- To switch off
Shut off the main engine first, followed by the auxiliary systems and cooling water systems. If the stopping time is long, empty the middle of the main engine.
- Maintenance
(1) Pay attention to whether the mechanical seal components themselves are loose and leaking, or whether heat and abnormal sounds are generated due to impurities entering the end face of the seal; avoid dry friction; For machines operated intermittently, pay attention to crystallization formed by the dry medium or temperature reduction during shutdown. When starting, take measures such as heating or washing to avoid scratching the edges.
(2) Observe whether auxiliary devices and instruments, such as washing and cooling, are working properly;
(3) Pay attention to whether there are abnormal phenomena during the operation of the machine, such as vibration or damage to bearings, which will affect the use of the mechanical seal.
- Revision
(1) Requirements for dismantling work:
① Be familiar with the relevant data, drawings, types and structures of mechanical seals before disassembly;
② Do a good job of preparation and prepare the necessary facilities and tools, and do a good job of security protection;
③ Disassemble in order and mark for easy reassembly; observe during disassembly and analyze and find the cause of the leak;
④ After dismantling the old parts, they should be stored for a period of time before processing. When there is no data or incomplete data, new parts can be obtained according to the material and specifications of the old part.
(2) Review method:
① When severe wear or cracks occur on the surfaces of the rotating and stationary rings, replace them with new ones. Small scratches can be rectified; check the deviation of the end faces of the rotating and stationary rings in relation to the shaft center line. If it exceeds 0.05mm, it must be adjusted or repaired;
② When the auxiliary sealing rings and springs are damaged, replace them with new ones; When selecting springs, select those that are parallel to the end face and perpendicular to the centerline, with consistent headroom and deformation;
③ Adjust the axial displacement to the specified range;
④ Check whether the shaft or sleeve is worn. If there is wear, timely repair welding, heat treatment and machining.