The effects of earthquakes on structures can be devastating and sometimes catastrophic. Structures must be built to resist seismic activity in order to mitigate the effects of such events. The underlying cause of structural collapse due to earthquakes often has to do with design, construction and maintenance. In this article, we discuss the main causes of structure collapse during an earthquake and provide civil engineers with information on the design and construction of structures resilient to seismic activity.
One of the main causes of building collapse during earthquakes is poor construction. For example, buildings that are not designed to withstand the lateral forces of an earthquake can easily collapse. Furthermore, buildings that are not properly reinforced are also at risk of collapsing. In many cases, the use of inferior materials and construction methods can also contribute to the collapse of a building during an earthquake.
Another cause of collapse is poor construction. This can happen when buildings are not constructed according to construction plans. For example, if the foundation of a building is not properly excavated or the building is not properly reinforced, it is more likely to collapse in an earthquake.
The third cause of building collapses is lack of maintenance. When buildings are not properly maintained, they become weaker and more susceptible to damage. This is particularly true for buildings in areas with high seismic activity. For example, if the building's foundation cracks, it could cause the building to collapse during an earthquake.
As a civil engineer, it is important to design and construct earthquake-resistant buildings. Furthermore, it is important to properly maintain buildings to ensure their strength and stability.
Foundation failure due to soil liquefaction
Soil liquefaction occurs when loose, water-saturated soil temporarily loses its strength and rigidity. This phenomenon is also called earthquake ground failure because it occurs most frequently in areas of high seismic activity that have loose, saturated soils.
Even low-magnitude earthquakes can cause buildings to collapse due to soil liquefaction, especially if the soil is sandy or unconsolidated. Soil liquefaction can cause significant property damage and loss of life. Anyone who has ever built a landfill should be aware of the risk of soil liquefaction in a large earthquake.
More information about the soil liquefaction article could be forwarded.
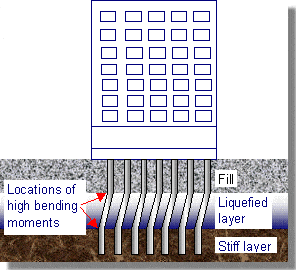
Failure of pile foundations due to soil liquefaction in soil layers at intermediate levels below ground. These flaws are significant and go unnoticed.


When the inner soil layers liquefy, as shown in the figure above, additional bending moments and shear forces are created in the pile, which would result in failure of the pile foundation if the section reinforcements were insufficient to support the additional load.
When planning based on well survey data, it is the designer's responsibility to determine the risk of soil liquefaction and take the necessary measures to prevent such failures in the event of an earthquake.
Furthermore, the project must pay attention to the interaction between soil, pile and structure to understand the behavior of the structure during this interaction.
Short column effect
Short supports lead to structural failures in buildings. A short column is a type of column that has a significantly shorter height than other columns. Although the frame structure itself is the same height as the columns, structural partitions can reduce the effective height of the columns.
The following are some of the reasons for creating short columns.
- Construction of building on sloping ground. The height of the column decreases at the top of the slope.
- With beam at the intermediate height of the supports
- Installation of brick/block partitions adjacent to the pillar


When lateral loads are applied, the ground bends sideways. Likewise, the top of the spine moves laterally relative to the bottom. Regular columns have more freedom of movement than short columns. The short column resists movement, although it must also have the same lateral deflection as the other columns. As a result, the resistance to movement is attracted by a greater load. This leads to failure of the short columns.


Excessive billing
Soil liquefaction: Compressed soil that has not been properly treated prior to construction of the structure can become excessively deformed by the seismic event.
Liquefaction of the inner layer of soil can cause the top layers of soil to settle along with the building's foundation.
When vibrations cause the soil's capabilities to become imbalanced, buildings are at risk of toppling.
Buildings falling
The collapse of the building could have occurred for two main reasons.
- Soil bearing capacity error
- P – Delta Effect
Failure in the bearing capacity of the soil
Shaking the building in both vertical and horizontal directions places excessive stress on the soil beneath the foundation. This poses a risk of foundation failure.
With a shallow foundation, soil failure in a portion of the foundation can cause the building to collapse.
P-Delta Effect
Excessive deflection of the building results in eccentricity of the building load. Furthermore, permanent deformation due to the action of an earthquake leads to a displacement of the structure's load center.
This poses a risk of the building collapsing.


Convenience stores
From a technical point of view, the low transverse bracing compared to the other floors can be seen as a soft floor effect.
When lateral loads act due to earthquakes, soils with high lateral security can withstand the forces and control lateral deflections. However, in soft soils, excessive lateral deformation occurs, leading to soil failure. This type of failure causes structures to collapse.


What a smooth story in the making
In the residential building there are many partitions that can be built with blocks and bricks. The ground floor would be used as a parking space. Therefore, the lateral stiffness on the ground floor would not be sufficient.
Furthermore, we may have many openings on some floors. For example, there will be classroom windows between two floors. This will provide smooth story effects.
Block failure due to an earthquake
When buildings topple due to lateral loads caused by lateral loads Due to the strong stresses caused by earthquakes, in addition to other structural damage to the superstructure, the block plates may also rupture.


Failure can occur at the block joint if excessive loads are applied. As the pile top plate together with the floor beams has a very high stiffness, the connection between the pile and the pile top plate would be the weak point where failure could occur. Furthermore, the interaction between soil and structure would further aggravate the situation.
Irregularities in floor plans and rigidity
Designers prefer to organize the first two modes in both translation directions. This prevents the torsional behavior of the structure from dominating.
The torsional behavior of a structure during an earthquake would cause severe damage to the structure if not taken into account in structural design. The most common approach is to change the stiffness of the structure to prevent torsional modes from becoming dominant.


As shown in the figure above, the lateral deformation of the low stiffness region has a larger lateral deflection compared to the shear wall region. The geometric center and the center of rigidity do not coincide.
Columns in areas subject to greater lateral deflections can develop high bending movements and shear forces. If the load-bearing capacity of the columns is insufficient to absorb these forces, the column may fail, which may result in the collapse of parts of the structure or entire structures.
Insufficient ductility
The ductility of the structure is a very important factor to take into account when designing structures against seismic loads. The right structure absorbs more energy and can lead to failure. However, if the structure is ductile, it will have more deformations.
The ductility of the structure is controlled by the reinforcement details. When detailing the reinforced concrete element, special requirements must be met. Furthermore, failure of the beam-to-column and column-to-foundation connections can lead to structural failure.
The hinge is located near the support column connection. This area must be designed so that it does not fail due to cyclic loading from seismic stimuli and has sufficient ductility.
Insufficient lateral rigidity
The lateral loads acting on the structure are shared by the reinforced concrete structure and the shear walls. In some structures there are shear walls. In these situations, the frame structure will support the loads.
If there are load-bearing walls and frame structures, the interaction between load-bearing walls and frames can be taken into consideration in the design as they are the lateral load absorption capacity.
To avoid failure, it is essential to correctly position shear walls and provide sufficient wall area to accommodate the applied loads.