In the vast field of civil engineering and earthquake analysis, one term often comes into focus: response spectrum. By providing valuable information about structural response, it has become an indispensable element in this field. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the nuances of the response spectrum, decipher its complexities, and clarify its importance.
What is the response spectrum
Essentially, the response spectrum represents the maximum response of a structure to different frequencies of ground motion. It is a graphical representation that shows the relationship between the maximum response of the structure and the corresponding input frequency. By plotting these values on a diagram, engineers can gain a holistic understanding of how a structure behaves during specific seismic events.
How is the response spectrum determined?
Obtaining a series of answers requires several steps.
- First, a series of ground motion records are selected, usually presented as acceleration time histories. These records can come from historical earthquakes or can be created artificially through simulations.
- Subsequently, each ground motion record becomes a structural analysis using numerical methods or computer simulations. The resulting peak responses are then extracted and plotted against the corresponding input frequencies, creating the response spectrum curve.
Response Spectrum Meaning
The response spectrum serves as a fundamental tool in earthquake engineering for several reasons. First, it helps in designing frameworks by providing valuable information about potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses. By analyzing the response spectrum, engineers can identify critical periods of resonance where the structure is susceptible to increased responses. With this knowledge, appropriate design measures can be implemented to effectively mitigate these risks.
Furthermore, the response spectrum is crucial for evaluating the performance of existing structures. By comparing it to design criteria and codes, engineers can assess whether a structure can withstand expected ground movements. This assessment is particularly crucial for evaluating the safety of older buildings or structures in seismically active regions.
Response spectrum components
The response spectrum consists of several main components that together define the structural response. These components include:
- Earth movement
Ground movements represent the shaking of the Earth caused by seismic events. They include various frequency components, amplitudes and directions and serve as input for response spectrum analysis.
- Transfer Function
The transfer function characterizes the relationship between the input soil movement and the response of the structure. It takes into account the dynamic properties of the structure, such as mass, stiffness, and damping, to determine the gain or damping of various frequency components.
- Acceleration of the reaction
It is a type of measurement of how the structure accelerates in response to ground shaking. It is a key parameter used in response spectrum analysis and helps identify critical vibration modes and potential structural weaknesses.
- damping
Damping is the dissipation of energy created by the vibration of the structure. To accurately capture the dynamic behavior of the structure, damping effects must be taken into account in the response spectrum analysis.
Response spectrum curve
The response spectrum curve itself contains valuable information that is useful in structural analysis. It consists of two different areas: the elastic area and the inelastic area. In the elastic region, the structure behaves linearly and presents reactions directly proportional to the intensity of the ground movement. The inelastic region, on the other hand, represents the point at which the structure exceeds its elastic limit and starts to behave in a non-linear way, leading to an increase in reactions.
The shape of the response spectrum curve is influenced by several factors, including the characteristics of the ground motion, the natural frequency of the structure, and the damping ratio. By carefully analyzing the curve, engineers can identify the predominant frequencies that significantly influence the structural response.
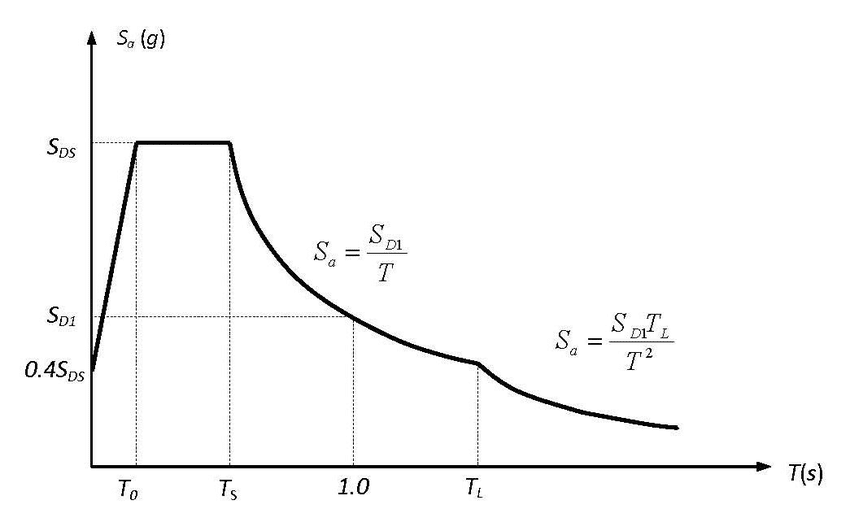
The image below shows a similar spectrum designed for design based on your area. This needs to be developed.


Application of response spectrum analysis
Response spectrum analysis is widely used in many areas of engineering. It plays an important role in the design and evaluation of structures in earthquake-prone areas. By considering the response spectrum during the design process, engineers can optimize structural parameters and select appropriate materials to improve seismic performance.
Additionally, the response spectrum helps in developing seismic regulations and standards. By studying the behavior of different structures under a variety of ground motions, experts can refine and update existing guidelines, ensuring the safety of structures in the face of earthquakes .
Advantages and limitations
The response spectrum approach offers several advantages in earthquake analysis and design :
- It provides a comprehensive understanding of structural response to a wide range of ground motion frequencies.
- It enables the identification of critical vibration modes, allowing engineers to focus on the most vulnerable aspects of the structure.
- Enables efficient optimization of structural parameters such as stiffness and damping to improve seismic performance.
Limitations of response spectrum analysis:
- It is assumed that ground motion can be represented by a series of independent harmonic motions, which may not fully capture the complexity of real earthquakes.
- This does not take into account spatial fluctuations in ground motion, which in certain situations can significantly influence the structure's response.
common questions
F1. Can response spectrum analysis be applied to all types of structures? Yes, response spectrum analysis can be applied to a variety of structures, including buildings, bridges, dams, and industrial facilities. However, the specific application and interpretation may vary depending on the type of structure and purpose.
F2. How accurate is response spectrum analysis in predicting structural response? Response spectrum analysis provides a good approximation of the structural response to seismic forces. However, to obtain a more accurate prediction, it is important to consider other factors, such as site-specific conditions and soil-structure interaction.
F3. Is response spectrum analysis only applicable to earthquakes? Although response spectrum analysis is often used in the field of earthquake engineering, it can also be applied to other dynamic loads such as: B. vibrations caused by wind or machines to evaluate the structural response.
F4. Can response spectrum analysis be used for nonlinear structural analysis? Response spectrum analysis is typically used for linear structure analysis. For nonlinear analysis, more advanced techniques such as time history analysis may be required to accurately capture the nonlinear behavior of the structure.
Q5. How does response spectrum analysis contribute to building code requirements? Response spectrum analysis plays an important role in the development of building codes and earthquake safety requirements. It helps establish guidelines for designing structures that can withstand expected ground movements in specific regions.