The relay operates based on several techniques and inputs, including monitoring the status of circuit breaker control circuits, measuring circuit breaker coil current, or analyzing voltage and current waveforms. It continuously evaluates circuit breaker performance and compares it to predefined criteria or expected operating sequences.
Circuit breaker failure relays are commonly used in high voltage transmission and distribution networks where the failure of a circuit breaker can have serious consequences. They provide an additional layer of protection and act as fail-safe devices to ensure the integrity and reliability of the power system.
Circuit breaker failure relay for relay protection
Circuit breaker failure relays are called backup protection devices and are used as circuit breaker protection relays for most relays. For example, a circuit breaker failure relay is used as a backup device for the differential relay of a power transformer and additionally for the distance relay of a conductor.

Why is a circuit breaker failure relay necessary?
In the condition of a device failure, the fuse of that device is expected to be tripped by the device's main protective relays if a failure occurs in the fuse trip circuit or the fuse itself. In this case the backup will not be triggered. To isolate this fault, the bus to which this device is connected must be completely isolated by time-tripping all devices connected to it. So the only device connected to the current bus is the one that is faulty. In this case, the faulty device does not experience power surge; therefore, it is often separated mainly by isolation.
Buchholz relay principle
The Buchholz relay is a special protection device used in oil-filled power transformers to detect and respond to internal faults and anomalies. It works based on the principle of detecting gas and oil flow in the oil-filled tank and transformer expansion tank.
The main purpose of the Buchholz relay is to provide early warning and protection of faults in the active parts of the transformer such as windings and core. It is particularly effective in detecting and responding to faults such as internal short circuits, partial discharges and excessive heating.
The Buchholz relay is usually installed in the line connecting the transformer main tank to the expansion tank. It consists of a gas chamber, an oil flow chamber and a floating unit. The gas chamber is connected to the top of the transformer tank, while the oil flow chamber is connected to the piping between the tank and the expansion tank.

During normal operation, transformer oil circulates between the main tank and expansion tank, ensuring a balanced oil level in both chambers of the Buchholz relay. However, if a transformer failure occurs, certain conditions can cause changes in oil and gas flow patterns and trigger the protective action of the Buchholz relay.
The importance of multiple conditions for the operation of a circuit breaker failure relay is to improve the reliability and accuracy of the protection system. Conditions mentioned typically include:
Trigger signal of any main protection relay
The BFR depends on receiving a trip signal from the primary protective relay of the faulty device. This ensures that a fault condition has been detected and confirms the need for backup protection.
The fuse of the faulty device remains switched on.
The fuse and associated normally open (NO) auxiliary contact confirm that the faulty device is still connected to the system. If the fuse blows or the additional contact opens, this indicates an open circuit and the BFR may no longer need to be operated.
Presence of electricity, even at very low levels
The BFR can also take into account the presence of current flowing through the faulty device, regardless of its intensity. This condition further confirms the need for backup protection as it means that the faulty section is still connected to the mains.
Buchholz relay operation
The operation of the Buchholz relay can be divided into two phases:

Gas accumulation
If a transformer failure occurs, e.g. B. a short circuit, the resulting electrical discharge produces hydrogen and methane gas. These gases rise and accumulate in the upper part of the transformer tank. When the gas enters, it enters the gas chamber of the Buchholz relay.
Oil flow interruption
The accumulation of gas in the gas chamber causes the oil level to drop. This drop in oil level actuates the floating assembly in the oil flow chamber. The floating unit is equipped with mechanical contacts that react to changes in the oil level. When the oil level drops below a certain threshold, the floating unit activates the connections and initiates a protective measure.

The protection measures initiated by the Buchholz relay may vary depending on the transformer configuration and system requirements. Common responses include generating alarms, creating transformer trip signals, or activating mechanical interlocks to isolate the transformer from the electrical system.
The Buchholz relay works on the principle of gas accumulation and interruption of oil flow in the oil-filled tank and transformer expansion tank. By detecting changes in gas and oil flow patterns, internal failures in power transformers are warned and protected in advance. This helps prevent serious damage and ensure the safety and reliability of the transformer system.
Circuit Breaker Failure Relay Conditions and Meaning
For the circuit breaker failure relay to operate, it must meet three conditions. These are:
- Trigger a signal from a main protection relay that may be present in the faulty system.
- The fuse of the faulty device remains switched on (no auxiliary fuse contacts are used).
- However, this is currently happening with this device. It's an incredibly small amount.
Although one of the second and third conditions is reserved for the proper functioning of the circuit breaker failure relay, it is desirable to use both for safety reasons.

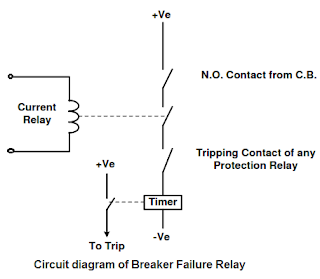
The schematic layout shows the circuit breaker failure relay circuit. The tripping pattern of the circuit breaker failure relay is analogous to the tripping circuit of the bus protection relay. Generally, the circuit breaker failure relay can use a trip circuit equivalent to the bus protection relay.