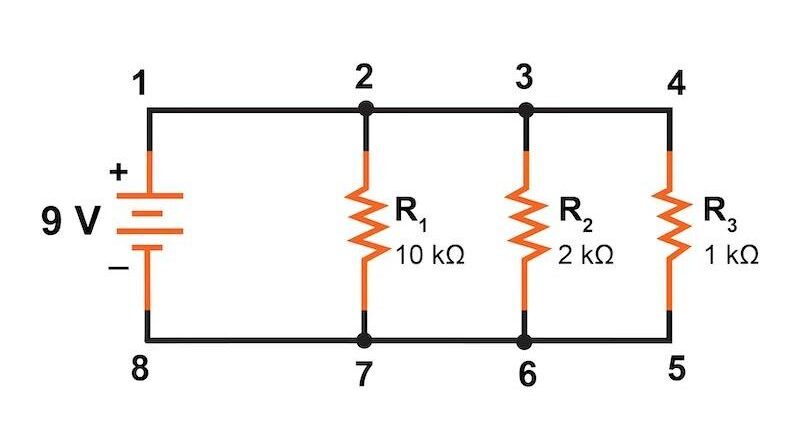
Resistors must be connected “in parallel” when their terminals are connected to each terminal of the opposite resistor(s). In a parallel resistor network, the circuit current follows a very specific path because there are multiple nodes.

What is magnetomotive force?
Thus, we can sketch together a parallel resistor circuit where the resistors are connected at 2 constant points (or nodes) and characterized by being a current path connected to a typical voltage source. In our parallel resistor example below, the voltage across the resistor is R1 equals the voltage across resistor R2 , which corresponds to the voltage across R3 and the available voltage. Therefore, for a parallel resistor network, this can be stated as follows:
v R1 = V R2 = V R3 = V ABSENT =12V

Series resistance network, we tend to see that the total resistance is R T circuit, was equal to the sum of all individual resistances along the way. For resistors in parallel, the equivalent resistance of the circuit is R T is calculated differently.
Here, the reciprocals (1/R) of the individual resistors are everything else and not the resistors themselves, with the inverse of the algebraic sum giving the corresponding resistance, as shown below:

Then, the reciprocal of the equivalent resistance of two or more resistors connected in parallel is the algebraic sum of the reciprocals of the individual resistors. The equivalent resistance is often just the smallest resistance in the parallel network; therefore the total resistance is R T, it can continually decrease by adding additional parallel resistors.
What is electromagnetic force? ?

Currently we assume that the resistors connected between 2 constant points are in parallel. However, a parallel resistance circle can take several other forms than the obvious form given above; many examples of resistors are connected in parallel.
Resistors connected in parallel
When resistors are connected in parallel in a circuit, their total resistance and other relevant quantities can be calculated using certain formulas and principles. Here is some content that explains the behavior and calculations of resistors in a parallel circuit:
definition
In a parallel circuit, resistors are connected next to each other so that multiple current paths are possible. Each resistor has the same voltage, but can allow different currents to flow through it. The total resistance of the parallel connection is less than the smallest individual resistance.
Total resistance (Rₜ)
Total resistance can be calculated using the following formula:
1/Rₜ = 1/R₁ + 1/R₂ + 1/R₃ +… + 1/Rₙ
Where R₁, R₂, R₃, …, Rₙ are the resistances of the individual resistors. Once you have the inverse of the total resistance, you can calculate its inverse to find Rₜ.
Equivalent resistance (Req)
Equivalent resistance is another name for the total resistance (Rₜ) of the parallel connection.
Power distribution (I)
In a parallel circuit, the total current supplied by the source is divided between the parallel branches based on the resistance of each chapter. The unit with the lowest resistance has the highest wind and the section with the highest resistance has the lowest current.
Voltage (V) between resistors
Since the same voltage is present across resistors connected in parallel, the voltage across each resistor is equal to the voltage in the parallel circuit.
Energy waste
The power consumed by each resistor in a parallel circuit can be calculated using the following formula:
P = (V²/R)
Where P is the power, V is the voltage across the resistor and R is the resistance value of that specific resistor.
Current calculation
To calculate the current flowing through each resistor, you can use Ohm's law:
I = V/R
where I is present, V is the voltage across the resistor and R is the resistance value of that particular resistor.
Forms
Parallel connected resistors are commonly used in various circuits such as voltage dividers, speaker systems, and parallel LED setups.
Remember to use appropriate units (Ohms, Volts, Amps) and ensure the accuracy of your calculations based on the specified resistances and voltages.