What is a battery?
A battery is an electrochemical device that can store energy in the form of chemical energy. This translates into electrical energy when the battery is connected in a circuit due to the flow of electrons due to the specific placement of chemicals. It was invented by Alessandro Volta, while Gaston Plante invented the rechargeable battery.
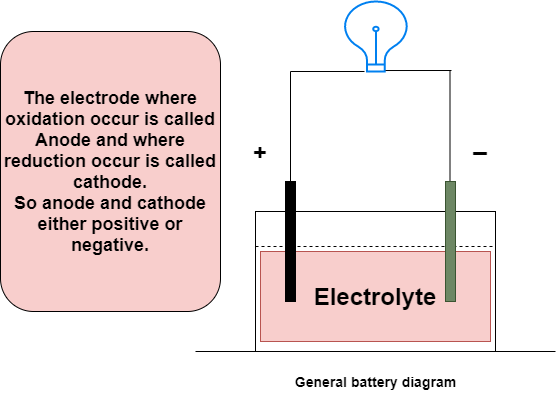
The battery is made up of three elements: the negative side, the positive side and the electrolyte (the chemical substance that reacts with both sides), as shown in the image below. The electrolyte is used as a means of transporting electrons between the anode and the cathode.
It works due to electrochemical reactions called oxidation and reduction. In this reaction, electrons flow from one side to the other when the external circuit is connected to the anode and cathode.

General battery diagram.
Battery chemistry may vary for different applications, specifications, sizes, etc., which are explained below under battery types.
Battery Applications
Battery is used in applications where it is necessary to store energy for future purposes. Portable, emergency, and low-power devices often use batteries. A portable device, like a mobile laptop, has a battery to use wherever you want. An emergency device like inverter, torch, etc. is used when there is no electricity. Low power consumption devices such as watches, oximeters, etc. can work for a long time after battery replacement. The electrical network is not suitable for all situations.
The requirements of a battery depend on various conditions, such as how much power is needed or how portable the device is. But what about the wall clock? Why isn't this plugged into an outlet?
The wall clock consumes very little energy. A 1.2V battery can last almost two years, but that's not the main reason. The clock must be turned on every moment to obtain the correct time; This can be done by battery. A single hindrance in power will cause a delay in time. That's why it's designed to run on less power, thus allowing the watch to run for a longer period of time and making the battery an efficient way of constantly providing power.
Let's look at another example. Generally, a vehicle runs on gasoline. In a self-starting vehicle, the initial ignition of the engine is done by an ignition coil and a motor. The engine is used to achieve specific engine rpm and the ignition coil is used as the ignition source. This vehicle ignition coil draws about four Amps. This current can vary between different manufacturers and there is a lot of space in the vehicle. This is why to fulfill the higher current requirement, lead acid battery is perfect for this.

Vehicle ignition.
From the above example, we can say that the usage of batteries depends on the condition and application.
Types of batteries
Based on functionality, there are two types of batteries available in the market.
- Primary Batteries.
- Secondary Batteries.
Primary Batteries
Batteries made for single use and incapable of recharging are called primary batteries . This type of battery is discarded after use. It is also known as non-rechargeable batteries . It is a very simple and convenient power source for portable devices such as watch, camera, flashlight, etc. The battery comes in standard size as shown below.

The standard battery size
These batteries are cheap, small, lightweight and require little to no maintenance.
Some common primary batteries
- Alkaline battery
The alkaline battery mainly consists of zinc and manganese dioxide as electrodes. The alkaline electrolyte is used as potassium or sodium hydroxide. As you can see in the image below, the outer casing is a steel drum and there is a cap on the drum which is a positive terminal. Inside this drum, fine-grained manganese dioxide (MnO2) mixed with coal powder is fused, as shown in the image. This molten mixture is part of the cathode of an alkaline battery. There is another powder filled inside the cathode powder, which is zinc powder with potassium hydroxide. Zinc powder (Zn) is part of the anode of an alkaline battery. Both powders are separated by a paper separator. The paper separator is soaked in potassium hydroxide, an electrolyte between the cathode (MnO2) and the anode (Zn). The brass metal pin is inserted along with the central axis of the alkaline battery, which is a negative collector pin. The pin is in contact with the metal end. There is a plastic cover that separates the metal end from the steel drum. The metal end is the negative terminal of an alkaline battery.

Alkaline battery
This battery is used where low voltage is required. A single cell can supply 1.5V. This is very cheap, so it can reduce the cost of the product. Every clock hanging on your wall or remote controls that control your TV and AC run on these alkaline batteries.
- Button Cell Battery
As you can see, the button cell is shaped like a button leading body to be the cathode, and the anode is isolated on top of the battery. The body is made of nickel-plated stainless steel – a positive terminal of the coin cell. On the top of the CAN, you can see a negative terminal cover. Both the CAN and the top cover are separated by a gasket made of insulating material. Inside the battery there are two materials: lithium metal and manganese dioxide, separated by a separator. The electrolyte used in the battery is lithium salt in organic solvent.

Button cell (source)
Button or coin cells can be seen in watches of different sizes. This also comes under the category of alkaline batteries because it comprises three substances: lithium as the anode and manganese dioxide as the cathode, and alkaline as the electrolyte. These batteries are used to power small devices like watches, pocket calculator RAM, etc.
Secondary Batteries
Batteries that are made for reusable purposes through recharging are called secondary batteries . They are also called rechargeable batteries . They have the same electrochemical reaction as alkaline batteries, but the electrochemical reaction can be reversed. This type of battery is used for portable devices like cell phones, laptops, electric vehicles, etc. Additionally, a rechargeable battery is used with an inverter that stores energy to power our home devices.
Some common secondary batteries
- Lead-acid batteries
The lead-acid battery container is made of hard rubber from a bituminous compound. The container obtains dilute sulfuric acid, which is an electrolyte. Grid-shaped lead plates are dipped into the electrolyte. The positive plate of the lead-acid battery is made of lead peroxide (PbO2). This is a dark brown, hard, brittle substance. The negative plate is made of pure lead in soft sponge condition. A separator separates both electrodes. This separator can be made from cellulose, polyvinyl chloride, organic rubber and polyolefins. The positive and negative are connected at the top of the battery, which is the external positive and negative terminal for connecting the load or device. There is a filter cap with a small hole in the center. The filter cover provides access for adding electrolytes and the holes allow gases to be released to the atmosphere.

Lead-acid battery (source)
These batteries are low cost, reliable, larger and heavy. It is mainly used in heavy-duty applications because it is not portable due to its weight and size. It is used in non-portable applications such as solar panel energy storage, vehicle ignition and lighting, backup power, and load leveling in power generation and distribution.
- Nickel-cadmium batteries
A nickel-cadmium battery (Ni-Cd or NiCad battery) is made of nickel oxide hydroxide as the cathode and metallic cadmium as the anode. Firstly, a layer of nickel oxide NiO2 is maintained around the redox. This layer acts as a cathode. Above this cathode layer, a KOH or NaOH separator is made to provide OH ions. After this layer, the cadmium layer acts as the anode of the ni-cd battery. The nickel layer acts as a positive electrode and the cadmium acts as a negative electrode. The layer arrangement is rolled into a cylindrical shape in a box. The outer box is made of metal with a sealing plate and safety valve, which allow gases to be removed from the container. A cover on the top of the cell is insulated by a gasket, which acts as a positive for the ni-cd battery.

Nickel-cadmium battery. (Source)
These batteries have a relatively lower cost, contain toxic materials and have a high self-discharge rate. It has a greater number of charge and discharge cycles. The energy density is higher than that of lead-acid batteries. It is smaller, lighter and available in different sizes, like alkaline batteries. It is generally used in low-cost devices such as toys, sunlight or cordless phones, etc.
- Nickel Metal Hydride Batteries
Nickel-metal hydride (NiMH or Ni-MH) battery is made of nickel oxide hydroxide as cathode and hydrogen absorbing alloy as anode. The construction of the Ni-MH battery is the same as that of the Ni-cd battery. The nickel oxide hydroxide layer and hydrogen absorbing alloy are laminated with the KOH or NaOH separator. The outer metal case acts as a negative terminal and is connected with a hydrogen absorbing alloy. The cap on top of the cell acts as a positive terminal and is connected to the nickel oxide hydroxide. An insulating sealing ring or gasket separates the negative and positive terminals.

Nickel-metal hydride battery. (Source)
Compared to Ni-Cd, these are more efficient, with higher energy density, less toxic and a lower self-discharge rate. It is relatively expensive when compared to Ni-Cd. It has resistance to overcharge and excessive discharge. It is not very easy to charge and some manufacturers provide specific chargers.
- Lithium Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries have an anode made of graphite and a cathode made of lithium metal oxide. Lithium salt as an organic solvent is used as an electrolyte. When the battery is connected to the circuit or load, the lithium ion migrates from the negative electrode to the positive electrode.
In the image below, the construction of the lithium-ion battery is similar to that of Ni-Cd and Ni-NH batteries, except for the materials. Lithium metal oxide is coated with aluminum foil which is the positive electrode. The graphite is coated with a copper foil which is the negative electrode. Both sheets are rolled into a cylindrical shape with a separator between them. The spectator is doused with electrolyte material which is usually lithium salt as an organic solvent. The outer metal shell is negative and the top cover is the positive terminal. Both are separated by a gasket made of insulating material.

Lithium ion battery. (Source)
Lithium-ion batteries are used in cell phones, laptops, and many portable devices. It is also used in the military and aerospace due to its lightweight nature. It has higher energy density and low self-discharge compared to other types of batteries. It is also available in various sizes. Its single-cell voltage is higher. They present a significant risk of explosion when short-circuited or damaged externally.