Types of tool holders
According to the tool hole taper of the machining center spindle, it is generally divided into two categories:
- SK universal tool holder with 7:24 taper
- HSK vacuum tool holder with 1:10 cone
SK universal tool holder with 7:24 taper
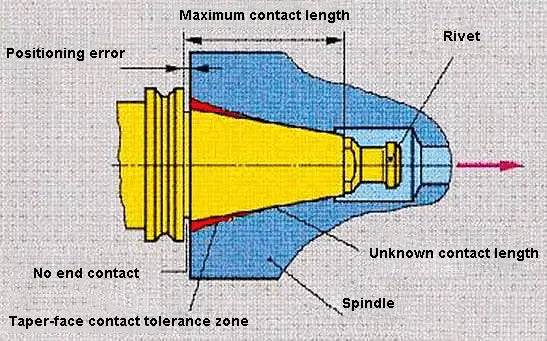
7:24 means the taper of the tool holder is 7:24, which is a single tapered surface positioning with a longer tapered shank.
The tapered surface performs two important functions at the same time, which are the precise positioning of the tool holder relative to the spindle and the clamping of the tool holder.


Benefits:
The non-self-locking design allows for quick loading and unloading of the tool. The cost of the tool holder is relatively low since the tapered angle can be machined with a high degree of precision, ensuring a precise connection.
Disadvantages:
During high-speed rotation, the conical hole at the front end of the spindle will expand. The amount of expansion increases with increasing radius of rotation and speed, which decreases the stiffness of the conical connection. The axial displacement of the tool holder will also change under the action of drawbar tension. After each tool change, the radial dimension of the
There are generally five standards and specifications for universal tool holders with 7:24 taper:
HSK vacuum tool holder with 1:10 cone
- International Standard: IS0 7388/1 (abbreviated as IV or IT)
- Japanese standard: MAS BT (abbreviated as BT)
- German standard: type DIN 2080 (abbreviated as NT or ST)
- American Standard: ANSI/ASME (abbreviated as CAT)
- Type DIN 69871 (abbreviated as JT, DIN, DAT or DV)
Tensioning method.
NT type tool holders are clamped by a drawbar on conventional machines, also known locally as ST.
The other four tool holders are fixed to the machining center through a projection at the end of the tool holder.
Universality.
(1) At present, the most commonly used tool holders in China are DIN 69871 (JT) and Japanese MAS BT.
2) DIN 69871 tool holders can also be mounted on machines with ANSI/ASME tapered spindle holes.
(3) The international standard tool holder IS0 7388/1 can also be installed on machine tools with DIN 69871 tapered bore and ANSI/ASME spindle. Therefore, in terms of versatility, the IS0 7388/1 tool holder is the best.
HSK Vacuum Tool Holder with 1:10 Taper
HSK vacuum tool holders rely on the elastic deformation of the tool holder, not only the tool holder with a 1:10 taper in contact with the 1:10 taper of the machine tool spindle hole, but also the face of the tool holder flange is in close contact with the face of the spindle.
This bilateral contact system is superior to a 7:24 universal tool holder in terms of high-speed machining, connection rigidity and overlapping accuracy.


HSK vacuum tool holder can improve product rigidity, stability and accuracy during high-speed machining, and also reduce tool replacement time, which is essential for high-speed machining. It is suitable for machine tool spindle speeds up to 60,000 rpm. The HSK tooling system is being widely used in the aerospace, automotive and precision mold industries, among others.
HSK tool holders are available in types A, B, C, D, E and F, with types A, E and F commonly used in machining centers with automatic tool change (ATC) process.
The biggest difference between Type A and Type E:
(1) Type A has a transmission slot, but Type E does not. Therefore, Type A has a relatively higher transfer torque, which can withstand heavy cutting. The torque transmitted by the Type E is relatively small, so it can only handle light cuts.
(2) The Type A tool holder has manual clamping holes and steering grooves in addition to the transmission groove, resulting in relatively poor balance. Type E lacks these features, making it more suitable for high-speed processing.
The Type E and Type F mechanisms are identical. The difference between them is that for cables with the same name (such as E63 and F63), the taper of the Type F cable is one size smaller. This means that both E63 and F63 have a flange diameter of φ63, but the F63 cone is just the same size as the E50. Therefore, the F63 will spin faster (with a smaller spindle bearing) compared to the E63.
Way of fixing the tool in the tool holder
Spring c artridge tool holder
It is mainly used for straight tool holders such as drills, milling cutters and taps, or tool clamping.
The elastic deformation of the retaining ring is 1mm and the clamping range is 0.5 to 32mm in diameter.

Hydraulic chuck
- A- Locking screw, which uses an Allen key to tighten the locking screw;
- B- Locking piston, which presses the hydraulic medium into the expansion chamber;
- C- Expansion chamber, which is pressurized by liquid to generate pressure;
- D-Thin expansion bushing, which allows the center of the tool holding rod to be evenly positioned and engaged during the locking process.
- E- Special seals, which guarantee ideal sealing and long service life.

Heated tool holder
Sensing heating technology is used to heat the tool clamping part of the tool holder, causing its diameter to expand. The cold rod is then inserted into the hot tool holder. This results in high clamping force and good dynamic balance, making it suitable for high-speed machining.
The technology also offers high repeatability accuracy within 2μm and radial deviation within 5μm, and has good resistance to smudging and interference during machining.
However, only one tool with a specific shank diameter can be installed for each tool holder specification, and a set of heating equipment is also required.
The principle of fixing the pyrocondensational tool holder:


Comprehensive review and comparison of tool holders
| Assessment | Spring clamp type | Hydraulic type | Pyrocondensational type |
| Structure Diagram |  |
 |
 |
| Versatility | be used in all processes; highly versatile | limited for high speed machining; high maintenance costs | Excellent performance in a wide range of high-speed machining applications |
| Tool holder knock | quality spring clip <10µm | >5µm | about 3 µm |
| Hard | good | good | |
| Dynamic balance | good | in general | good |
| Vibrations | no advantage | can absorb vibrations | no advantage |
| Convenience | accuracy depends on the operator | the fixing structure is easily damaged | standardized operation |
| Cost | in general | Dear | Cheaper than hydraulic type |
Other types of tool holders

Tool holder selection and maintenance
Factors influencing selection
When choosing a tool holder, a few key factors influence your decision:
- Compatibility : You need to ensure that the tool holder fits your machine spindle.
- Tool type and size : You must choose the appropriate holder for the specific tool required.
- Material : Different materials like steel, aluminum or plastic affect the durability and performance of the stand.
- Balance : For high-speed applications, look for tool holders with better balance and minimal runout.
Proper care and handling
To extend the life of your tool holders and maintain their performance, here are the steps to follow:
- Storage : keep my tool holders in a dry and clean environment, away from contaminants and moisture.
- Cleaning : Before and after use, wipe tool holders with a soft cloth to remove debris.
- Inspection : Inspect my tool holders regularly for signs of wear, damage or corrosion. Replace them if necessary.
- Lubrication : When necessary, apply lubricants to prevent rust and ensure smooth operation.
- Handling : To avoid damage, handle tool holders with care, avoiding dropping them or hitting hard surfaces.