“Brakes are as important as a car engine”, said with great reason, as if we needed an engine to operate a vehicle and also brakes to stop it. This statement also resembles Newton's first law, which we are all familiar with. As we know nowadays, in light vehicles, we use the hydraulic braking system to stop or slow down the vehicle. But the question arises: Is the hydraulic braking system effective when it comes to heavy vehicles? If not, then what do we need to stop or slow down heavy vehicles like buses and trucks? Let's hunt for the answers.
See more information:
Construction and operation of air brake system used in automobiles
Types of Brakes Different Types of Brake System
Air brake system is a type of braking system generally used in heavy commercial vehicles or vehicles that require a really powerful and efficient braking system. It is a kind of friction brake where instead of hydraulic fluid, air is used as a compression medium for brake pads.
Pneumatic air brake system is generally used in heavy vehicles such as buses and trucks.
Air brakes were invented by George Westinghouse for use on trains. After proving their caliber on trains, pneumatic brakes were later adapted for use on heavy vehicles. The safety and braking confidence that air brakes provide to heavy vehicles are proven to this day.
There is a need for different braking systems due to the following reasons:
- As the load on light vehicles and heavy vehicles varies, the braking force required to stop the heavy vehicle is much greater than that of the light vehicle, therefore heavy vehicles must be equipped with a braking system that can provide sufficient braking force to stop or slow down the vehicle.
- When we talk about light vehicles, hydraulic brakes provide more than enough braking force to stop or slow down the vehicle due to its small size, but when it comes to large heavy vehicles, the effectiveness of the hydraulic braking system is the great concern. .
- As the fluid is used to press the piston in the hydraulic braking system, safety is a major concern, as if there is any leak in the hydraulic system components, braking efficiency is promptly reduced or even lost completely, as air is always available therefore , brake failure due to leakage is less of a concern in the air brake system.
- The size of the components (master cylinder, brake lines, etc.) of the hydraulic brake system increases with the increase in vehicle size, which in turn makes its installation very complex, which is not a problem with the hydraulic brake system. air brake.
- Due to safety measures like brake failure and efficiency, the government has made it mandatory for heavy vehicles like buses and trucks to use air brake system.
Therefore, due to the reasons mentioned above, in March 1872, George Westinghouse introduced the air braking system to the braking system in railways due to its fail-safe feature.
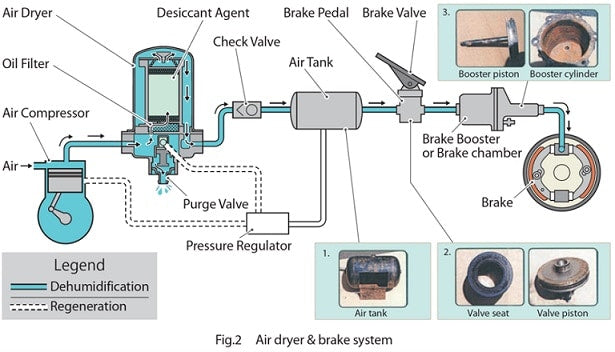
 air brake system diagram
air brake system diagramCOMPONENTS
1. Air compressor-
It is the compressor that pumps air from the atmosphere into the air storage tank and is driven by the engine using a belt drive.
2. Air compressor governor
It is the regulating device used in the air brake system that controls the compression pressure of the air that is pumped into the air storage tank through the air compressor.
3. Air dryer-
It is the device used to remove moisture content from the air from the atmosphere to prevent water condensation in lines and air storage that can cause brake failure, such as during winter, due to freezing of condensed water.
4. Air storage (reservoir)-
It is the tank that serves to store the compressed air sent by the compressor. This storage always has enough compressed air so that the brakes can be applied several times and also prevents brake failure when the air compressor malfunctions.
5. Brake pedal-
It is the mechanism activated by the driver and used to activate the brakes to stop or slow down the vehicle. The brakes, when pressed, push compressed air which in turn applies the brakes to the moving tire.
6. Dirt Collector-
It is the device that is placed inside a brake pipe where a branch is separated and taken to the triple valve that removes dirt from the air before sending it to the triple valve
7. Brake cylinder or brake chamber-
It is the device that consists of a cylinder and a piston on which compressed air pressure is applied to push the brake pads which in turn make frictional contact with the disc or drum to stop or slow down the vehicle.
8. Brake valve or triple valve
Brake actuation and release requires continuous release and increase of pressure within the brake lines and brake cylinder in accordance with the movement of the brake pedal. This is done by the triple valve used in the air brake system.
9. Brake drums –
Brake drum is the component through which the braking force due to the frictional contact between the brake pads and the drum lining is transferred to the wheel in order to stop or slow down the vehicle. The outer surface of the brake drum consisting of the drum lining rotates with the wheel and the inner part consisting of the brake shoes remains in a rest state when the brake pedal is not pressed.
Note – Normally brake drums are used in air brake system but with proper arrangement disc brake can also be used in air brake system.
WORKING PRINCIPLE
A typical air brake system configuration for a heavy vehicle consists of service brakes, parking brakes, a foot control, and an air storage tank. Parking brakes in this configuration consist of a set of disc or drum brakes held in the locked position by a spring mechanism. Air pressure is then needed to release the parking brake and set the vehicle in motion. In the case of service brakes used for regular vehicle operation, a pedal is pressed to stop or engage and disengage the brake.
 air brake system working
air brake system workingGenerally, a pressure of 6.8 to 8.2 bar is used for this type of application. Most heavy commercial vehicles use drums with air brake systems, although now the use of disc brakes is also approaching. Every vehicle equipped with air brakes has a pressure gauge mounted on the dashboard and in the driver's line of sight, which allows the driver or vehicle operator to be fully aware of the operating pressure in the compressor. In addition, there are suitable safety systems and mechanisms that alert the driver or operator if there is a malfunction or a sudden drop in operating pressure. As a fail-safe emergency mechanism in the event of a sudden, extreme drop in air pressure, the spring-loaded parking brakes immediately apply, bringing the vehicle to a safe stop.
The basic principle of an air brake system is similar to any other type of brake system, with the only differentiating factor being the use of compressed air instead of hydraulic fluids.
So, in principle, it's just a conventional braking system.
Supply system: The heart of any air brake system is the compressor. Compressor is the device that generates and somewhat regulates the flow of compressed air in the system. The compressor is powered directly by the engine and uses the common lubricant available in the engine.
Compressed air is pushed through a cooling coil and into an air dryer. From here, the air is stored in a reservoir tank for use. The reservoir tank is connected to an intricate network of circuits for front brakes, rear brakes and parking brakes. The supply system also contains the drain valve, pressure limiting valve and safety valve.
Control system: The control system basically consists of the service brake circuit, the parking brake circuit and the trailer brake circuit (if applicable). The service interrupt circuit consists of two individual interrupt circuits, each for the front and rear brake. Both circuits are connected to their special reservoirs for greater safety in case the master reservoir fails.
The parking brake circuit is connected to a spring mechanism in which air pressure is used to hold the spring in the unlocked position. A drop in pressure in this circuit results in the parking brakes engaging. The trailer braking system has its own operating lines and is used when there is a trailer attached to the vehicle. It has a supply line and a control line. The supply line is fed from the master reservoir and the control line receives the signal from the service interruption system for better braking.
When the driver of a vehicle presses the brake pedal to stop or slow down the vehicle, the following processes occur-
1. When the driver starts the engine, the brake compressor starts as it is driven by the engine, which in turn starts to compress the atmospheric air and through the compressor governor this compressed air with ideal pressure is sent to the compressed air reservoir which always has some amount of air stored from the previous cycle.
2. When the driver presses the brake pedal, the triple valve's outlet valve closes and the inlet valve opens, which in turn allows compressed air from the reservoir to pass through the system's brake lines.
3. This compressed air flowing through the brake lines is then transferred to the brake cylinder which has a piston inside it.
4. When compressed air applies pressure to the piston inside the brake chamber, the piston moves away from its original position, converting this pneumatic energy into mechanical energy.
5. At the wheel end of the brake cylinder, brake drums are placed, inside which there is a mechanical actuator housing like springs or gaps, having brake pads at its outer end.
6. Due to the movement of the piston due to the pressure applied by compressed air, the mechanical actuator inside the brake drum expands, which in turn pushes the brake pads outward in order to make frictional contact with the rotating lines of the drum.
7. With this frictional contact between the brake pads and the rotating drum lines, brakes are applied to the wheels to stop or slow down the vehicle.
FORMS
Due to its property of preventing brake failure, air brake systems are widely used in various vehicles, but in heavy vehicles such as trucks and buses, due to government vehicle regulations, air brake system is mandatory.
1. It is used on railways
2. All trucks and buses on the road today use air brake systems, few of them do.
- Volvo 9400PX bus.
- Bharat Benz 3123R Truck.
- trucks with multiple trailers,
- high speed long distance bus,
- military utility vehicles and
- semi trailers

























































1comment
Gostei muito desta informação, gostaria de uma informação nos caminhos tem umas linha de ar vermelho e verde qual delas tem ar direito