Geometric Dimension Tolerance (GD&T) is the foundation of modern precision manufacturing. It is an efficient system for designers to communicate functional mechanical tolerance and form requirements to manufacturers. The GD&T date is a fundamental concept in this system and important for production and quality professionals to understand.
In this article, we cover topics like date definition, date types, and date symbol. Read on for a fascinating discussion on this interesting topic.
What is date in GD&T?
Let's start by defining a date definition. ASME Y14.5 (1994) defines a datum as “a theoretically exact point, axis, or plane derived from the true geometric counterpart of a specified reference feature. A datum is an origin from which the position or geometric properties of a part's features are established.”
Simply put, a die serves as a reference unit for measuring and locating the various geometric characteristics of a part.

There is also more information about use with other GD&T symbols. The reference symbol is compatible with all GD&T symbols except those related to shape tolerances (e.g., flatness, straightness).
To make the matter even clearer, consider this very simple example. Suppose you have drawn a rectangle with a hole in the middle. Now you want to check how far from the center you drew the circle. To do this, you need to measure the distance between the edge of the rectangle and the center of the circle. In this case, your reference point is the edge of the rectangle, as this is the reference line from which you start the measurement.

Understand the basics of dates
Now we can move on to more subtle topics that will help you better understand the above date definition.
Reference point vs. reference element
The terms “date” and “date element” are often confused. To create professional technical drawings, you need to be aware of both.
A datum feature is a physical, tangible feature of the part that establishes the datum feature. Because it is a real entity, it is not exact and may have an irregular shape.
The reference element is a relatively more abstract concept. It is an exact geometric representation of the reference element. For example, if the reference feature is a rough surface, the reference feature is the perfectly smooth plane that best simulates the surface.

Date Reference Frame
The reference frame (DRF) is a shape and position tolerance (GD&T) term that refers to the coordinate system that locks the part's degrees of freedom during inspection and measurement. By “locking” we mean that it aligns and positions the part in space and provides a base system for all tolerance zones. DRF provides a reference system for measuring part characteristics.
Since there are six degrees of freedom for each feature, DRF must block all of them. This is usually done with three levels, which can also be easily simulated in a physical environment.
The following figure shows an example. Several features need to be measured on the part. First, imagine that you want to inspect the part without the blue component. This will be difficult and unreliable as you don't have adequate benchmarks to measure against. The three blue planes form the DRF, which aligns and locates the part.

Primary and secondary data
In the GD&T reference system, a single reference point is generally not enough to completely measure a part. Therefore, engineers use various types of references for comprehensive part sizing.
However, reference points are defined according to priority. The primary reference is most important for the shape and dimensions of the part, while the secondary reference comes after it. In many cases, designers also define a tertiary reference point.
Let's go back to our previous example and update it. You may have discovered that one measurement is not enough to accurately determine the center of the circle. Therefore, a secondary date setting is used for the second measurement in the vertical direction. This completes the measurement.
Reference target in technical drawings
Reference targets are a key concept in technical design and dimensioning. The reference symbol shown below is used for reference features for practical reasons such as measurement and inspection. In this section we answer the question of what a reference target is.

Reference point vs. reference target
The definition of date is clear in the text above. It is an exact geometric unit that serves as a reference in measurements and quality checks.
The datum target is a point, line, or area that serves as additional information and allows engineers to use the datum feature as a reference for measurements. It is a “target” to establish physical contact between the part and the measuring device, essential for taking measurements.

How can I use date goals?
The following figure shows the use of reference points and reference targets. The reference symbol defines the surface in front as the reference point A. The reference target symbol is called three times, each time defining a circular contact zone with a diameter of 15 mm at the reference point A.
Now let's assume this part goes to a quality inspector who uses a coordinate measuring machine to make all measurements relative to reference surface A. To perform these measurements, the inspector must place reference surface A on the work table of the coordinate measuring machine.
In this case, the reference targets serve as guidance for the inspector on how many fixing pins he should use. They also tell you where exactly these pins should be installed. The pins must touch the part within the three target zones for the reference target to be set to specification.
Date symbol: how to classify?
The reference symbol is a central concept in the GD&T system. Because each dimension requires a reference symbol, there are several ways to access the reference symbol. Therefore, it is possible to divide this according to these applications, which include two broad categories.

Reference symbol on a surface or axis
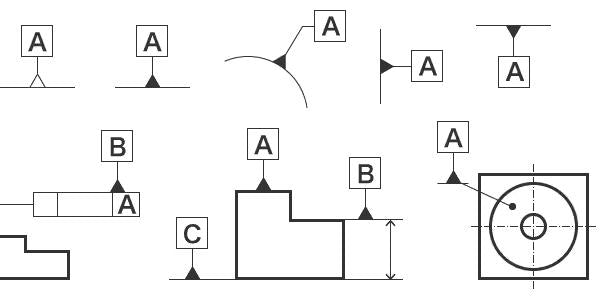
The first method is to declare a surface or axis as a reference point. This is probably the most common use of the GD&T reference point. This means that a flat surface or the axis of a round element serves as a reference point for the dimension.
There are several ways to declare a surface or axis as a reference in a technical drawing. In the following example, reference points A and E are front and back, respectively. Solid and dotted lines show the difference between the front and back.
The figure also shows variations in reference assignment. For example, reference C can be defined either by an arrowhead pointing to the surface or by reference to the auxiliary line drawn for dimensioning.

Reference symbol in a size characteristic
The other case is declaring a size feature as a reference point. A size feature is a geometric feature with one dimension. For example, holes and grooves are size characteristics.
For example, in the following image, reference point A points to the resource with size 1,500. Note that the reference symbol is aligned with the dimension arrow, which distinguishes it from the example above. Reference point C is the axis of the 0.750 holes. If the center of the hole is out of dimension, the reference point will move with it.
These types of data are often useful for tracking technical adjustments and issues such as drift.
Concluding
The GD&T date is undoubtedly a crucial aspect of the GD&T standard. It is the basis for an extensive system of technical drawings that supports our design for the manufacturing industry and ensures that products are manufactured within functional tolerance limits.
Our talented engineering team follows strict quality standards to ensure all products meet GD&T limits and tolerances specified in technical drawings. Please feel free to contact us to discuss your technical projects.

Common questions
Why is date important in GD&T?
The datum element is a fundamental concept in GD&T. It provides a reference for mapping dimensions to geometric features and teaches quality inspectors how to orient and position the part for measurement.
How to select reference points in GD&T?
Reference features must be chosen to create a complete frame of reference. This means that the reference features must limit all degrees of freedom of the part and its features. Additionally, reference features should be geometric features that are most likely to be accurate and accessible during testing.
Which GD&T symbols require a date?
The reference symbol is compatible with all GD&T symbols except for shape tolerances (straightness, flatness, cylindricity, and roundness). Additionally, the designer can call the reference symbol with any other symbol as needed.