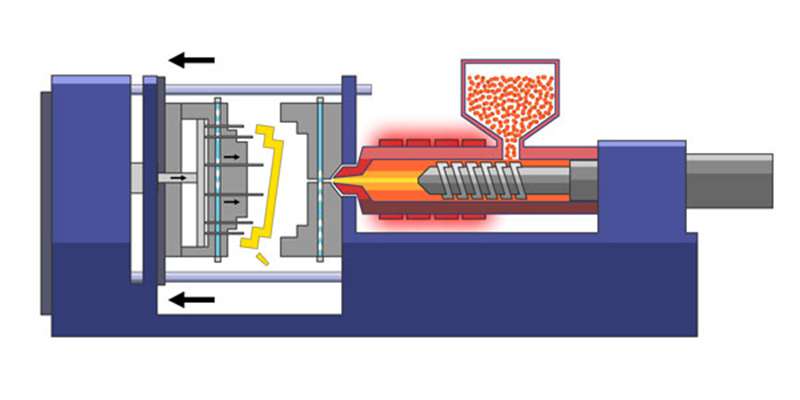
Injection molding is one of the most popular manufacturing processes for mass producing plastic parts. Many industries use this process due to its numerous advantages, such as precision and repeatability. This article explains how plastic injection molding works, the different types of injection molding techniques, and what to consider at each step of the molding process.
What is injection molding?
Injection molding is a molding process in which parts are manufactured by injecting their molten form into molds. After cooling and hardening, a final product is obtained that takes the shape of the mold. Injection molding is used in the mass production of parts where product consistency is an important concern. Furthermore, this manufacturing process is compatible with thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers.
How does plastic injection molding work?
The injection molding setup consists of the molding machine, mold and plastic material. For the sake of simplicity, plastic injection molding occurs in several steps. Below is a step-by-step explanation of how it works.

1. Fusion phase
- The first step is to melt the plastic pellets;
- Then place the pellets in the machine's hopper.
- This enters the cylinder, where the rotating screw liquefies the plastic through heat and friction.
2. Injection phase
This is the most important step. Any error can affect the quality of the final piece. Here the molten plastic is injected into a mold under high pressure and at a uniform speed.
3. Cooling phase
Once the plastic resin is in the mold, it hardens and cools. As plastics are generally poor conductors of heat, this cooling phase can be time-consuming.
4. Ejection phase
Once cool enough, open the mold and remove the plastic part using the ejector pins integrated into the mold. Now close the mold and repeat the process to make more identical pieces if necessary.
5. Post-treatment
This final step involves removing or cutting out any physical defects and applying a variety of surface finish options to add more shine to the piece if necessary.
Common Types of Injection Molding Technologies
Below are some of the injection molding technologies and their applications.

1. Structural foaming
Structural foam molding is a cost-effective technology used in low-volume plastic molding. This molding technology combines an inert gas (usually nitrogen) with molten plastic in the mold. This puts even more pressure on the plastic, increasing its strength and durability and reducing its weight.
Structural foam molding is widely used in the automotive industry for the production of automotive parts.
2. Thin wall formation
Thin-wall forming is ideal for parts with thin, light walls (less than 2 mm) and is therefore suitable for forming parts with less material. Although the cycle time is short and the error rate is low, the machines are quite expensive. Furthermore, the plastics used must have good fluidity properties. Thin-wall molded products can be found in many food packaging.

3. Liquid silicone injection molding
Liquid silicone injection molding is the exact opposite of traditional injection molding. In liquid silicone injection molding, the mold cavity is heated before cold silicone is pressed into it and then vulcanized.
This process allows for the mass production of flexible and stable parts. This molding technology is important in the medical industry due to its biocompatibility and easy sterilization.
Plastic materials used in injection molding
However, there are many plastics available for injection molding. Below are the top options and their unique features.

1. Nylon (polyamide, PA)
Nylon is available in various qualities and can easily replace metals in vehicle parts. However, nylon can be difficult to mold. This is because nylon shrinks quickly and the mold may not fill properly.
2. Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene is the most used plastic in the manufacturing industry. Depending on the density, there are two forms (high-density polyethylene and low-density polyethylene).
High-density polyethylene is best suited for injection molding because its physical and chemical properties are not changed by the heating and cooling process.
3. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
ABS is the most versatile of all injection molding materials. There are three isomers that perform different functions. Due to its low melting point, it is suitable for injection molding processing. However, parts molded in ABS decompose when they come into contact with UV and solar rays, which limits their use outdoors.
4. Polyoxymethylene (POM, Acetal)
POM is a semi-crystalline polymer used to make high precision parts. In general, this plastic is easy to mold. Due to their excellent dimensional stability and high tensile strength, POM molded parts are also suitable for the automotive and electronics industries.
5. Polypropylene (PP)
This is the second most used plastic in injection molding and is known for its light weight and high melting point. Although polypropylene is easy to mold, it is highly flammable and the molded part is difficult to paint.
6. Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene is strong, rigid and transparent and resists the breakage that occurs during sterilization. It is therefore very suitable for use in the dental and optical industries.
7. Acrylic (PMMA)
Acrylic is transparent and lightweight, making it a great alternative to glass. This plastic has low mold shrinkage but can self-ignite in extreme temperatures. Because of its UV and moisture resistance, you can use it for everything from solar panels to spray paint.
8. Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate is an amorphous thermoplastic with good optical clarity. It presents low and uniform shrinkage as it cools. Additionally, polycarbonate maintains its color after molding. It is used in the manufacture of safety glasses and automotive parts. However, it is not suitable for food packaging.
9. Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE)
TPE is a mixture of rubber and plastic. Therefore, it has properties of both. This plastic material is expensive compared to others. Additionally, TPE can withstand the extreme temperatures encountered during injection molding and does not require vulcanization. Therefore, you can use TPE in medical supplies such as masks and breathing tubes.
10. Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
Although it is a type of TPE, it is popular due to its various advantages. Thermoplastic polyurethane has better elasticity and can withstand extreme temperatures. However, it is more expensive.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Injection Molding Process
Before molding a plastic part, it is important to understand the pros and cons.
Advantages of injection molding
Complex shapes and geometries
Injection molding gives you the freedom to create custom parts. This manufacturing process can produce parts with complex shapes and designs. You can also integrate more functions with the appropriate aluminum or steel mold design.
Product consistency
In injection molding, the mold is used repeatedly before being replaced. Therefore, the next part is identical to the previous one. This increases the overall production speed.
compatibility
The physical and chemical properties of the material are not limiting factors. You can also easily shape colorful materials with different textures.
Low waste generation
Plastic waste generated during injection molding is low. Another benefit is that you can recycle this small amount of waste and use it to make another batch of product.
Low cost per piece
Although the configuration investment is high, the production cost of a single part is relatively low. Furthermore, this process eliminates the need for some surface finishing options. This means that high-quality parts are produced and at the same time injection molding costs are saved.

Disadvantages of Injection Molding
High tooling costs
Injection molding requires large capital investments, resulting in a rigorous, expensive and time-consuming mold design and prototyping phase. Before production begins, the mold must be tested repeatedly. However, large-scale production reduces costs.
Small series production is expensive
In mass production of parts, the use of injection molding is recommended. This is because you are using the same format for the pieces. However, when producing small quantities, it is necessary to design molds for different parts. This increases costs and time.
Considerations and tips for the entire injection molding process
Product design phase
This is the most critical phase of the injection molding process. Therefore, make sure your product design is error-free before starting production. Please note the following.
- A uniform wall thickness prevents warping and other injection molding defects.
- Air currents reduce the risk of errors and ensure that the part can be easily ejected from the mold.
- Material selection before production is a crucial process. The shrinkage rate and flow rate define each material. Therefore, using the wrong material will result in inferior performance.
Tool mold design and development
This phase of plastic injection mold design determines the overall quality of the final product. The choice of mold material is the most important aspect. Choosing the right material ensures that quality specifications are met. You can use a steel or aluminum mold for plastic injection molding. Although steel is expensive, it is more durable.
Manufacturing process
The following must be taken into consideration during production
- Overheating of the plastic material may cause burn marks on the surface of the plastic part.
- Strict part tolerances ensure precision during the heating and cooling process;
- Changes in injection speed and pressure can cause the molten material to solidify at different rates.
- Insufficient cooling time will result in uneven shrinkage.
When should injection molding be preferred over other processes?
All manufacturing processes have their advantages and disadvantages. However, opt for injection molding if
- Parts have detailed characteristics that need to be produced in large quantities, such as car parts.
- You want to reduce individual cycle times and shorten the time to market for your product.
- The color and/or texture of the material is incompatible with other manufacturing processes;
- All parts of a lot must be identical;
- You want to keep waste to a minimum.
Injection molded product applications
Many industries produce molded parts because they are lighter and safer.

1. Automotive industry
Injection molded plastics have improved the safety, cost, functionality and performance of automobiles. This is because plastics, as a lighter alternative to metals, improve fuel efficiency.
Automotive parts manufacturers use injection molding for functional parts with complex geometry, such as plastic fuel tanks, bumpers, and door panels.
2. Medical industry
Some injection molded parts are biocompatible and have good optical clarity. They are therefore used by manufacturers in the medical and optical sectors. With plastics, doctors can sterilize devices quickly and easily.
Additionally, molded plastic parts are safer. Examples include sterile gloves, intravenous tubing, and urine bags. All of them can only be used once because production costs are low.
3. Food packaging industry
Common materials for food packaging are glass, metal or paper. Plastics are slowly replacing them because they are cheaper, safer and lighter. Additionally, most molded plastics are resistant to harsh chemicals and extremely hot and cold environments. This protects your food or drinks from odors, unwanted reactions and moisture. Examples include water and soft drink bottles, bags, sachets and potato chip bags.
4. Aerospace industry
Plastics have been used in the aerospace industry for years to produce interior and exterior components. In addition to being lighter, they also require little or no maintenance, allowing planes to stay in the air for longer.
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) is the most commonly used plastic for aerospace parts because it is flame retardant and can withstand UV and solar rays. Turbine blades and casings, landing gear components, panels, casings and containers are all injection molded products.
5. Electronic and electrical industry
Plastics are poor conductors of heat and electricity. Therefore, they are often used by manufacturers when their insulating properties are required. They also reduce the risk of burns and electric shock.
Injection molding plays a critical role in the production of electronic components, as demonstrated by its use in household items, fuse boxes, telecommunications equipment, and more.
Get a Wayken Plastic Injection Mold Tooling Mold
The tool mold is the most important component in the injection molding process because it gives the part the desired shape. The time required to manufacture this tool affects the total time required to manufacture a part. For this reason, it is important to turn to a contract manufacturer to benefit from simplified mold design and rapid tooling production.
Concluding
Injection molding is a plastic processing process with many applications due to its mass production, repeatability and precision. However, the injection molding process requires knowledge and experience to be carried out efficiently. For this reason, the process has been discussed in detail in this article.
Are you having trouble making injection molds? Mistakes can result in wasted time and effort. Please feel free to contact us so we can produce your tool mold and bring your product to market in a timely manner.
Common questions
What are the most common defects in injection molding?
Injection molding errors occur when the pressure, injection speed, or cooling rate changes. Defects include delamination, flash, distortion, weld lines, sink marks, spatter, vacuum voids and more.
Can metals be produced by injection molding?
No, injection molding is only suitable for plastics. For metal parts, use the sister process of die casting.
Can you repair defects in plastic frames?
Yes, you can correct some defects after removing the part. However, to avoid the occurrence of such defects, it is better to follow the manufacturing process. Standard melting temperature and standard injection pressure are used.