What is a brushless motor ?
A brushless DC motor is a mechatronic product consisting of a motor body and a driver.
Unlike synchronous motors that require a starting winding on the rotor to start under heavy load with variable frequency speed regulation, the brushless DC motor operates in self-control mode. It does not produce oscillation or become out of step when there are sudden changes in load.
Most small and medium-sized brushless DC motors use rare earth, neodymium, iron, and boron (Nd-Fe-B) magnets due to their high level of magnetic energy.
As a result, the rare earth permanent magnet brushless motor has a smaller housing size than a three-phase asynchronous motor of the same capacity.
What is a racing engine ?
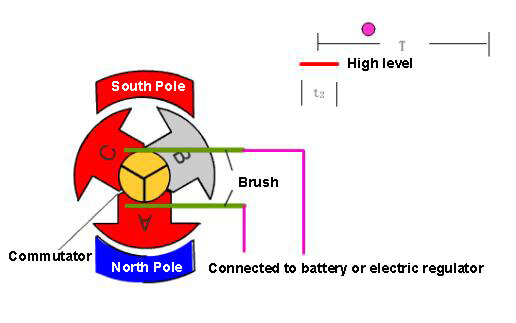
A brush motor is a rotating motor that uses a brush device to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy (such as a motor) or mechanical energy into electrical energy (such as a generator). Unlike brushless motors, a brush device is used to introduce or extract voltage and current.
The brush motor is the basis of all motors, having several advantageous features such as quick starting, timely braking, smooth speed regulation over a wide range, and a relatively simple control circuit.
Difference between brushless motor and brush motor in working principle
1. Working principle of brush motor
The brushed motor is the first type of motor we come into contact with and is often used as a model to illustrate motors in high school physics classes.
The main components of a brushed motor are the stator, rotor and brushes.
Rotary torque is generated through a rotating magnetic field, which allows the output of kinetic energy.
The brushes and commutator are in constant contact and friction and perform important driving and commutating functions during rotation.


The brush motor uses mechanical commutation, where the magnetic poles remain stationary while the coil rotates.
During operation, the coil and commutator rotate, while the magnetic steel and carbon brush remain stationary. The commutator and brush rotating with the motor allow completion of the alternating change of coil current direction.
In a brushed motor, this process involves arranging the two power input terminals of each coil group into a ring. The power input terminals are separated from each other by insulating materials and form a cylinder connected to the motor shaft.
A small column composed of two carbon elements (carbon brush) is used to pass the power supply. The carbon brush moves from two specific fixed positions under the action of spring pressure. Energizing a group of coils is achieved by pressing the two points on the cylinder of the upper coil power input ring.
As the motor rotates, different coils or different poles of the same coil are energized at different times. This creates a suitable angular difference between the NS pole of the magnetic field generated by the coil and the NS pole of the nearest permanent magnet stator. The magnetic field attracts and repels each other, generating force and making the motor rotate.
The carbon brush slides onto the coil connector, similar to a brush on the surface of an object, hence the term carbon “brush”. However, sliding between them causes friction and loss, making regular replacement of the carbon brush necessary.
Additionally, on-off switching between the carbon brush and coil connector generates electrical sparks, produces electromagnetic disruption, and interferes with electronic equipment.
2. Working principle of brushless motor
In a brushless motor, commutation is performed by the control circuit inside the controller. Typically this involves a Hall sensor and controller, although more advanced technology such as a magnetic encoder can also be used.


The brushless motor employs electronic commutation, with the coil remaining stationary while the magnetic pole rotates.
To detect the position of the permanent magnet's magnetic pole, the brushless motor uses a set of electronic equipment that incorporates the hall element.
Based on this detection, the electronic circuit timely changes the direction of the current in the coil to ensure that the motor generates magnetic force in the correct direction to drive it.
The disadvantage of brushed motor is eliminated in brushless motor.
These circuits are known as motor controllers.
The brushless motor controller can also perform various functions that a brushed motor cannot, such as adjusting the power switching angle, braking, reversing, locking, and interrupting the motor's power supply using the braking signal. The electronic alarm in battery-powered cars makes the most of these functions.
A brushless DC motor, which comprises a motor body and a driver, is a standard mechatronic product.
Since the brushless DC motor operates in self-control mode, it does not require a starting winding on the rotor like the synchronous motor that starts under heavy load with variable frequency speed regulation. It also does not produce oscillation or go out of sync when there is a sudden change in load.
Performance differences
1. The brush motor has simple structure, long development time and mature technology
As early as the 19th century, when the motor was first developed, the practical motor was brushless. It refers to the squirrel cage AC asynchronous motor, which became widely used after the generation of AC.
However, the asynchronous motor has many insurmountable defects, which makes the development of motor technology difficult. In particular, the brushless DC motor was not commercially available for a long time. Only in recent years, with the rapid advancement of electronic technology, has it become available for commercial operation.
However, brushless DC motor still belongs to the AC motor category.
Soon after the invention of the brushless motor, the brushless DC motor was developed. Brushless DC motor is popular because of its simple mechanism, easy production and processing, convenient maintenance and easy control.
DC motor also has features such as fast response, large starting torque and ability to deliver rated torque from zero speed to rated speed. As a result, it became widely used as soon as it was introduced.
2. Brushless DC motor has fast response speed and large starting torque
The DC brush motor has several advantages, including fast starting response, significant starting torque, stable speed change, minimal vibration from zero to full speed, and the ability to drive heavier loads during starting.
On the other hand, the brushless motor has some disadvantages, such as high starting resistance (inductive reactance), resulting in low power factor and relatively small starting torque. It also produces a humming sound during starting and strong vibrations, and can only drive minor loads during starting.
3. DC brush motor works stably and has good starting and braking effect
The brush motor is voltage regulated, ensuring stable starting, braking and constant speed operation.
On the other hand, brushless motors are typically controlled by digital frequency conversion. This process involves converting AC to DC and then back to AC, and using frequency changes to control speed.
As a result, brushless motors can exhibit unstable performance and significant vibration during starting and braking. They only become stable when operating at a constant speed.

4. High control precision of brushless DC motor
A brushless DC motor is typically combined with a reducer and a decoder to increase the motor's output power and improve control accuracy.
With a control accuracy that can reach 0.01 mm, the motor can stop moving parts in virtually any desired position.
DC motors control all precision machine tools.
However, the brushless motor is not stable during starting and braking, and the moving parts will stop in different positions each time.
To achieve the desired position, a locating pin or stop must be used.
5. DC brush motor has the advantages of low cost and convenient maintenance
DC brush motor is widely used due to its simple structure, low production cost, large number of manufacturers and mature technology. It is commonly used in factories, processing machine tools, precision instruments and other applications.
In case of engine failure, simply replace the carbon brush. Each carbon brush costs just a few yuan, making it an affordable solution.
On the other hand, the technology for brushless motors is still immature, the price is high and the range of applications is limited. It is best suited for constant speed equipment such as variable frequency air conditioners and refrigerators. If the brushless motor is damaged, it can only be replaced.
6. Brushless, low interference
The brushless motor eliminates the use of brushes, resulting in a significant change: there is no generation of electrical sparks during operation. This has a direct impact on reducing interference caused by electrical sparks in remote control radio equipment.
7. Low noise and smooth operation
A brushless motor operates without brushes, resulting in significantly reduced friction, smoother operation and much lower noise levels. These benefits contribute greatly to the operational stability of the model.
8. Long service life and low maintenance cost
Since a brushless motor operates without brushes, the main source of wear is in the bearing. From a mechanical point of view, brushless motors are practically maintenance-free. When necessary, simple dust removal maintenance is enough.
Difference of speed regulation mode
The control of the two motors is done through voltage regulation. Brushless DC motors use electronic commutation and can be accomplished with digital control, while traditional analog circuits such as thyristors can be used for carbon brush commutation in brushed DC motors, making it relatively simple.
1. The process of regulating the speed of a brush motor involves adjusting the motor's supply voltage. The set voltage and current are converted through the commutator and brush to change the strength of the magnetic field generated by the electrode, thereby changing the speed. This process is known as variable voltage speed regulation.
2. In contrast, the speed regulation process of a brushless motor involves keeping the motor's power supply voltage unchanged while changing the electrical regulation control signal. The switching rate of the high-power MOS transistor is changed by a microprocessor to change the speed. This process is called variable frequency speed regulation.