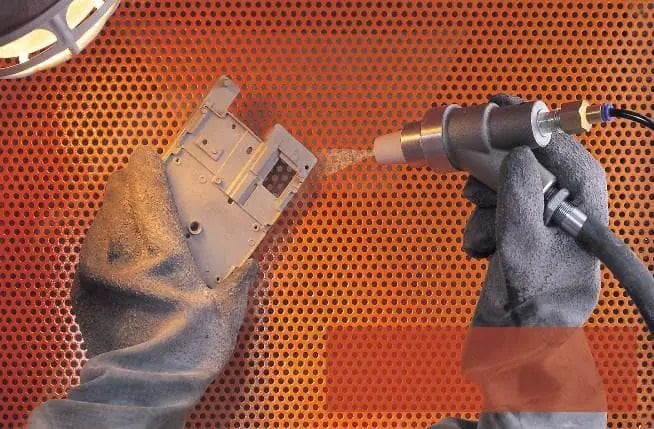
What is sandblasting?
Sandblasting uses compressed air as a power source to create a high-speed jet that drives abrasive materials (such as copper ore sand, quartz sand, diamond sand, iron sand, and Hainan sand) onto the surface of the part of work that needs to be addressed. This causes changes to the outer surface or surface shape of the workpiece.

Due to the impact and cutting action of the abrasive material on the surface of the workpiece, the surface of the workpiece obtains a certain degree of cleanliness and different levels of roughness, thereby improving the mechanical properties of the workpiece surface.
As a result, the fatigue strength of the part is increased, the adhesion between the part and the coating is increased, and the durability of the coating is prolonged. This method is also beneficial for leveling and decorating the coating.
Main application scope of sandblasting
(1) Sand blasting for pretreatment of workpieces before coating or adhesive can remove all pollutants such as rust and establish a crucial surface texture, commonly known as “matte surface”. Different levels of roughness can be achieved by using different grain sizes of abrasive material, such as abrasive from sandblasting equipment, which greatly improves the adhesion between the part and the coating or galvanizing, or strengthens the adhesion of adhesive joints and improves the quality.
(2) Sandblasting can clean all the pollutants on the surface of castings and heat-treated parts, such as residual oxide and oil stains, and polish the surface to improve the smoothness of the part. This process can present a uniform metallic color, making the appearance of the piece more beautiful and attractive.
(3) Sandblasting can clean small burrs on the surface of machined parts and make the surface smoother, eliminating burr damage and improving the quality of the workpiece. Sandblasting can also create small rounded corners at the joint surface of the part, making it more beautiful and precise.
(4) After sandblasting, mechanical parts can produce uniform and fine concave-convex surfaces on the surface, which can store lubricating oil, improve lubrication conditions, reduce noise and extend the service life of machinery.
(5) Sandblasting can achieve different levels of reflectivity or undergloss for some special workpieces, such as polishing stainless steel, plastic and jade, underglazing the surface of wooden furniture, creating patterns on sandblasted glass surfaces, or blurring the surface of fabrics. It can also play a decorative role.
Things to Note During Sandblasting Work
- Before starting work, protective equipment must be worn and bare arms are not permitted during work. The minimum number of workers must be two.
- The storage tank, pressure gauge and safety valve must be checked regularly. Dust should be discharged from the storage tank every two weeks, and the sand tank filter should be inspected once a month.
- Check that the ventilation pipe and sandblasting machine door are sealed. Ventilation and dust removal equipment must be activated five minutes before work. If the ventilation and dust removal equipment fails, the sandblasting machine will be prohibited from operating.
- The compressed air valve should be opened slowly and the air pressure should not exceed 0.8 MPa.
- The sandblast particle size must be appropriate to the requirements of the job, generally between 10 and 20, and the sand must be kept dry.
- During operation of the sandblasting machine, unrelated people are prohibited from approaching it. When cleaning and adjusting operating parts, the machine must be stopped.
- It is not allowed to blow dust on the body or play with compressed air.
- After work, ventilation and dust removal equipment should continue operating for five minutes before shutting down to discharge internal dust and maintain site cleanliness.
- In the event of a personal or equipment accident, the location must be maintained and reported to the competent department.
Sandblasting process
The pre-treatment step of the sandblasting process refers to the surface treatment that must be carried out on the part before it is sprayed or coated with a protective layer.
The quality of the pretreatment phase in the blasting process affects the adhesion, appearance, moisture resistance and corrosion resistance of the coating. If pretreatment is not done correctly, rust will continue to spread under the coating, causing the coating to peel off in pieces.
The life of a coating can differ 4 to 5 times between a thoroughly cleaned surface and a generally clean part when using the exposure method for coating comparison. There are many methods for cleaning surfaces, but the most widely accepted methods are solvent cleaning, acid pickling, hand tools, and power tools.
The sandblasting process uses compressed air as energy to form a high-speed jet, which sprays abrasive materials onto the surface of the part, causing changes in the appearance of its surface. Due to the impact and cutting effect of the abrasive on the part surface, the surface obtains a certain degree of cleaning and different roughness, thus improving the mechanical performance of the part surface.
Classification of sandblasting machines
Sandblasting machines are the most used products in abrasive jet machining. Sandblasting machines are generally divided into two categories: dry sandblasting machines and liquid sandblasting machines. Dry sandblasting machines can be divided into suction type and pressure type.
I. Suction type dry sandblasting machines
- General Components
A complete suction type dry blasting machine generally consists of six systems: structural system, media power system, piping system, dust removal system, control system and auxiliary system. - Working principle
Suction-type dry sandblasting machines use compressed air as a power source. Negative pressure is formed in the blast gun by the high-speed movement of the air flow, and the abrasive is transported through the sand transport tube. The abrasive is sucked into the blast gun and ejected from the nozzle onto the surface being processed, achieving the expected processing objective. In suction type dry sandblasting machine, compressed air is the supply.
II. Pressure Type Dry Sandblasting Machines
- General Components
A complete working unit of a pressure type sandblasting machine generally consists of four systems: pressure vessel, media power system, piping system and control system. - Working principle
Pressure-type dry sandblasting machines use compressed air as a power source. The working pressure is established in the pressure vessel by compressed air and the abrasive is transported through the sand outlet valve. The abrasive is ejected from the nozzle onto the surface being processed, achieving the expected processing objective. In pressure type dry sandblasting machine, compressed air is the supply.
III. Liquid sandblasting machines
Compared with dry sandblasting machines, the biggest advantage of liquid sandblasting machines is the effective control of dust pollution during the sandblasting process, which improves the working environment of sandblasting operators. sand.
- General Components
A complete liquid sandblasting machine generally consists of five systems: structural system, media power system, piping system, control system and auxiliary system. - Working principle
Liquid blasting machines use the grinding liquid pump as a power source to feed the grinding liquid (a mixture of abrasive and water) into the blast gun after shaking. The compressed air accelerates the grinding liquid and ejects it from the nozzle to the surface being processed, achieving the expected processing objective. In the liquid sandblasting machine, the grinding liquid pump is the feeding energy source and the compressed air is the acceleration energy source.
Cleaning level
Also known as cleaning, there are two representative international standards: one is “SSPC-” formulated by the United States in 1985, and the other is “Sa-” formulated by Sweden in 1976, which is divided into four levels, namely Sa1, Sa2, Sa2.5 and Sa3. It is a commonly used international standard, and the detailed introduction is as follows:
Level Sa1 – equivalent to the US SSPC-SP7 level. The general and simple method of manual brushing and sanding is used. This is the lowest level of the four cleaning levels and the protection of the coating is only slightly better than that of untreated parts. Technical standards for Sa1 level treatment: the surface of the part must not have visible dirt, such as oil, grease, residual oxide film, rust stains and residual paint. The Sa1 level is also called the hand brushing cleaning level (or sweeping level).
Level Sa2 – equivalent to the US SSPC-SP6 level. The sandblasting cleaning method is used, which is the lowest level of sandblasting treatment, that is, the general requirement, but the coating protection is much higher than that of manual brushing cleaning. The technical standards for Sa2 level treatment: the surface of the part should have no visible oil, dirt, oxide film, rust, paint, oxide, corrosion and other foreign substances (excluding defects), but the defects are limited to no more than 33% surface area per square meter, including light shadows; slight discoloration caused by defects and rust corrosion; oxidized skin and paint defects. If there are grooves on the original surface of the workpiece, slight rust and paint will remain at the bottom of the groove. The Sa2 level is also called the commercial cleanliness level (or industrial level).
Level Sa2.5 – is commonly used in industry and can be used as a technical acceptance requirement and standard level. The Sa2.5 level is also called the near-white cleaning level (almost white or off-white level). The technical standards for Sa2.5 level treatment: same as the first half of the Sa2 requirements, but defects are limited to no more than 5% of the surface area per square meter, including small shadows; slight discoloration caused by defects and rust corrosion; oxidized skin and paint defects.
Sa3 level – equivalent to US SSPC-SP5 level, is the highest treatment level in the industry, also called white cleaning level (or white level). Technical standards for Sa3 level treatment: same as Sa2.5 level, but 5% of shadows, defects, rust, corrosion, etc.
Others
Sandblasting: Technical term for gold and silver coin casting technology. It involves using metallic sand particles of various sizes and shapes in the gold and silver coin production mold to pulverize the patterned areas into extremely detailed matte surfaces. During the production of gold and silver coins, a beautiful silver layer appears in the stamped areas, increasing the sense of three-dimensionality and layering.
Sandblasting (referring to removing rust or coating on metal surfaces) uses quartz sand, ordinary quartz sand and refined quartz sand: with high hardness and good rust removal effects, the physical and chemical indicators are the following: SiO2≥98—99.8%, Fe2O3≤0.06—0.005%, refractoriness of 1750-1800℃, uniform particle appearance, commonly used particle sizes are 1-3MM and 0.1-0 .3MM, pure white.
The particle size range is mainly between 5 and 220 mesh and can be produced according to user needs. Its main uses are in the metallurgical, silicon carbide, glass and glass products, enamel, steel casting, water filtration, flower alkali immersion, chemical and sandblasting industries.