FEATURED PRODUCTS
-
3/16" Carbon Steel Plate
Regular price From R$ 817,52Regular priceUnit price per -
Carbon Steel Sheet 1/2"
Regular price From R$ 2.179,83Regular priceUnit price per -
3/8" Carbon Steel Plate
Regular price From R$ 1.630,22Regular priceUnit price per
SAC 350 PLATES - A572 GR50
-
1/4" Carbon Steel Sheet
Regular price From R$ 12.759,45Regular priceUnit price per -
1/4" Carbon Steel Sheet
Regular price From R$ 10.928,61Regular priceUnit price per -
1/4" Carbon Steel Sheet
Regular price From R$ 10.928,61Regular priceUnit price per
-
STEEL SHEET
STEEL SHEETS DISTRIBUTOR / SUPPLIER OF STEEL SHEETS Contact us and request...
-

CARBON STEEL COILS
As Carbon Steel CoilsThey possess excellent forming properties. They are suitable for...
-

WEATHERING STEEL SHEET
CARBON STEEL WEATHERING PLATE ASTM A572 GR50 - SAC 350 - SAC...
-

STAINLESS STEEL MICROTUBE
We manufactureStainless Steel MicrotubesPrecision Stainless Steel. DispLevels in thin-walled and thick-walled tubes,...
-

METAL CASINGS FOR CAISSONS AND PILES
Metal jackets, steel caissons and carbon steel pipes EXECUTION OF FOUNDATION AND...
-

Checker plate steel floor
As Checkerboard Floor PlatesThese planks have a textured surface that provides anti-slip...
-

Galvalume steel coils
O Galvalume steelIt is an extremely durable material. OurGalvalume coils,They are continuously...
-

GALVANIZED STEEL COILS
As Galvanized Steel CoilsHot melt zinc is subjected to an acid washing...
-

Carbon Steel Pipes
We supply carbon steel pipes and offer a wide variety of products,...
-
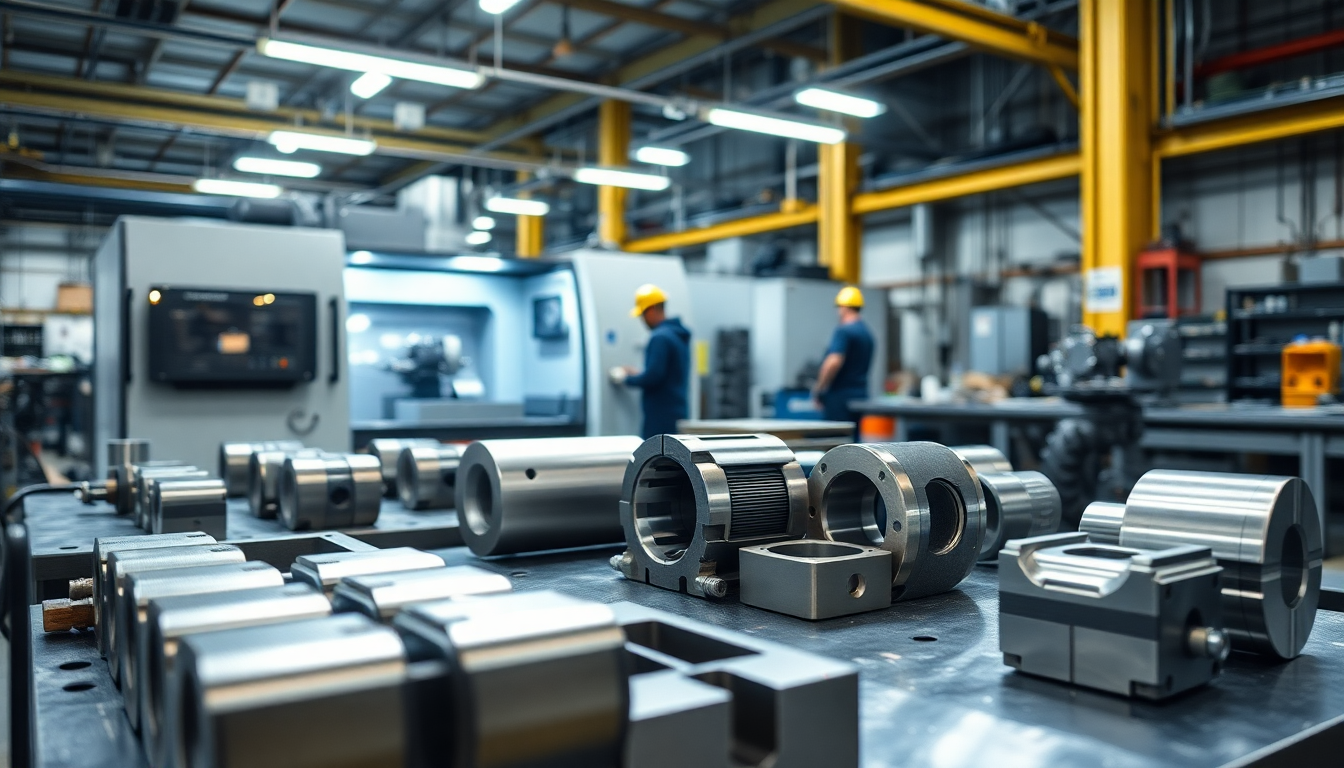

Machining - Production and Services
COMPRACO offers a wide range of CNC machining services, using state-of-the-art machines...
-

ALL PRODUCTS
Products for industry in general, raw materials, services and technology.
LEARN ABOUT OUR PRODUCTS
STEEL COILS
We sell Steel Coils High-strength material for a variety of industrial and manufacturing applications.
Check out the best delivery conditions and prices.
COMERCIAL@COMPRACO.COM.BR
(19) 3377 5412
Stainless Steel Coils
Efficiency, durability, corrosion and heat resistance are the prominent characteristics of these coils They acquired them in order to achieve the peak of their market demands.
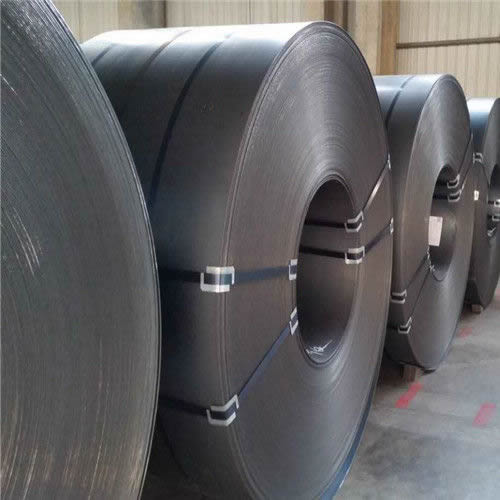

Carbon Steel Coils
A steel coil Hot-rolled laminate is rolled from sheets in a hot rolling mill. It can be found on the market in the form of coil ou plate and is subsequently processed into finished products by the manufacturer.
A hot coil It is produced as a raw material for cold coil e coated coil...but also for direct use in a variety of industrial applications, including steel pipes used in transportation, construction, shipbuilding, gas containers, pressure vessels, power pipelines, and various other branches of activity.
O Rolled Steel Cold-rolled steel is a 'flat' steel product. The material is manufactured from... rolled steel hot strips, whose thickness is further reduced in a strip mill without the use of heat. The resulting thinner and flatter material is known as rolled steel Cold formed. Typical thickness is 0.15 to 5 mm. Typical width is 600 to 2,100 mm.
A steel coil Cold-rolled finished steel possesses excellent formability, electromagnetic properties, paintability, and weldability. It is suitable for manufacturing by molding, pressing, and bending. Applications include household applications, automotive manufacturing, lighting fixtures, electrical components (stators, rotors), various types of sections, roofing applications, etc. sheets profiled and wall elements.
SPECIFICATIONS: SAE 1006, SAE 1008, SAE 1010 ASTM A36, A131, A283 GR C, USI SAC 350, SAC 300, ASTM A572 GR 50, SAE 1012, SAE 1045, Z 275, Z 100.
Boron Alloyed Coils: Usiminas 15B30 / CSN 27MnCrB5
Stainless Steel Coils
Stainless Steel Coils Laminates, both hot-rolled and cold-rolledProduct widely used in Manufacturing of containers for container construction, medical equipment, food industry, cold storage, building materials, kitchen sinks, cutlery, elevators, automotive applications, industrial applications, tools, etc.
Steel Coils Galvanized e Galvalume
Steel Coils Galvanized e Galvalume steel They are an economical solution for many industrial applications, but cost is only one of the many benefits.
- Durability: The products of galvanized steel They enjoy a long lifespan. It is not uncommon for products to last more than fifty years in some applications. Even with exposure to weather or other environmental conditions, the steel coils Galvanized steel stands out for its longevity. Their corrosion-resistant properties allow them to function optimally for decades.
- Strength: When it comes to tenacity, steel coils Galvanized steel is definitely strong. The metallurgical relationship between zinc and steel ensures excellent strength and durability.
- The products of galvanized steel They generally arrive ready to use, making them an incredibly practical solution for today's industries. The introduction ofo galvanized steel It is done almost directly on its production line.

Get in touch and schedule a consultation.We are very pleased to assist in providing raw materials and manufacturing for your project.
METAL JACKETS AND PIPES
FABRICAMOS Metallic Shirt, Tubulão, Steel casings, tubular piles or metal pilesThese are used in construction projects pertaining to a tubular steel system filled with concrete. For these Metal FoundationsA detailed analysis of the system at different stages of construction is provided, and verification of the design of the main components and connections under various load conditions is discussed.
We manufacture metal jackets and pipes.
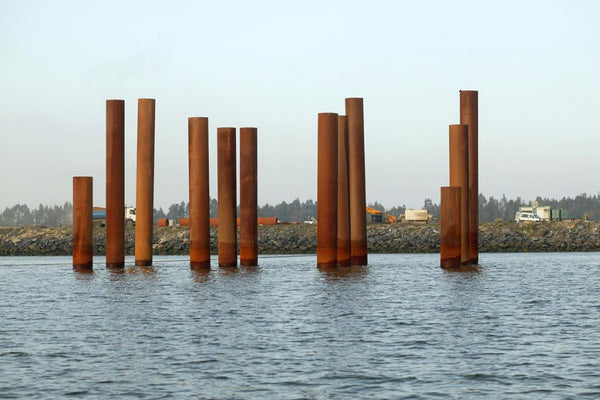


The structural efficiency and resistance capacity of Metallic ShirtsThis exists due to the high performance of the steel materials filled with concrete, reinforcing the strength of the... steel pipes.
- Bridges
- Viaducts
- Foundations
- Caissons
The bridge and viaduct system provides a unique solution to the various challenges associated with the construction of overpasses and water crossings, such as limited vertical restraint, undesirable or impractical placement of intermediate piers, and extremely limited traffic control during construction.
A bridge or viaduct is a structure built to cross an obstacle, such as water, valleys, or roads, in order to provide passage over that obstacle. In the public works sector, metal structures such as bridges or viaducts are made using materials such as concrete, reinforced concrete, metal, etc. Our factory provides large-diameter welded pipes and rolled tubes, frequently used in the manufacture of bridges and viaducts.
Check out other equipment we manufacture.
We supply raw materials for all equipment.
Is there a specific piping project your company needs that you would like more information about? Get in touch, we can definitely help..
STAINLESS STEEL PIPES
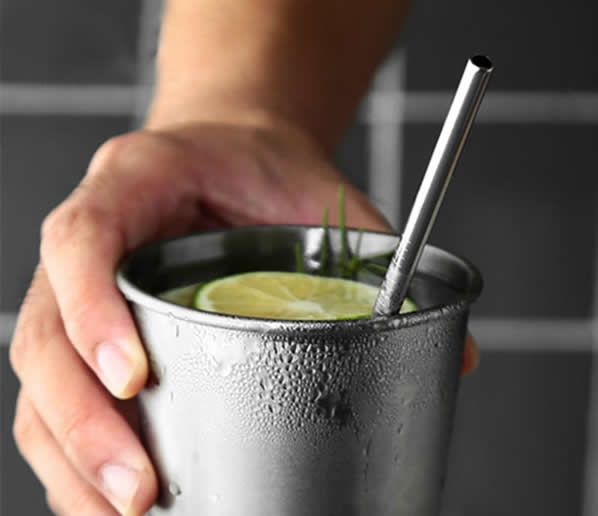
THE BEST STAINLESS STEEL STRAWBERRY IN BRAZIL
The benefits of using stainless steel straws. Buy the best from us. Stainless Steel Straw From Brazil. We manufacture. Straws Of unique quality, with measurements made solely for the commercial use of the product. We supply to pubs, bars, restaurants, and fast-food chains. The food market is extremely demanding regarding the sustainability of the products used, aiming for the least possible waste and cost.
Made in Brazil.
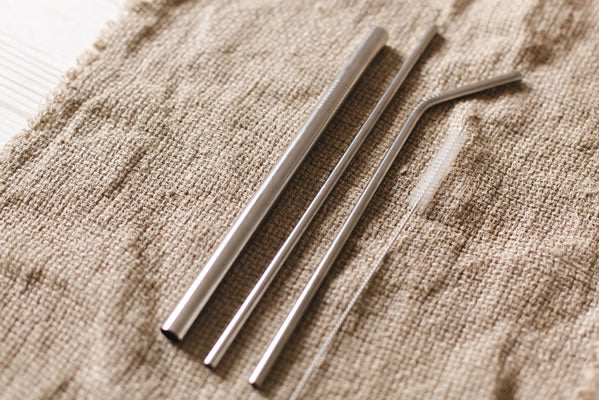

Stainless steel straw without engraving or logo.
VALUES FOR CANUDOS NO LOGO ENGRAVING - INOX 304 - WHOLESALE PRICES
| Stainless steel straws without logo engraving. | 50 to 100 | 101 A 500 | 500 to 1500 |
| Straight Smooth / Twisted 6 mm x 200 mm | 5.10 | 4.29 | 3.61 |
| Straight Smooth / Twisted 6 mm x 160 mm | 5.10 | 4.29 | 3.61 |
| Straight Smooth 8 mm x 200 mm | 5.10 | 4.29 | 3.61 |
| Straight Smooth 8 mm x 160 mm | 5.10 | 4.29 | 3.61 |
| Curved Smooth 6 mm x 216 mm | 5.10 | 4.29 | 3.61 |
| Curved Smooth 8 mm x 200 mm | 5.10 | 4.29 | 3.61 |
Stainless steel straw with logo engraving.
PRICES FOR ADDING YOUR COMPANY OR PROJECT LOGO TO YOUR CANUDOS - INOX 304 - WHOLESALE PRICES
| Stainless steel straws with logo engraving. | 50 to 100 | 101 A 500 | 500 to 1500 |
| Straight Smooth / Twisted 6 mm x 200mm | 10.29 | 5.87 | 5.12 |
| Straight Smooth / Twisted 6 mm x 160mm | 10.29 | 5.87 | 5.12 |
| Straight Smooth 8 mm x 200 mm | 10.29 | 5.87 | 5.12 |
| Straight Smooth 8 mm x 160 mm | 10.29 | 5.87 | 5.12 |
| Curved Smooth 6 mm x 216 mm | 10.29 | 5.87 | 5.12 |
| Curved Smooth 8 mm x 200 mm | 10.29 | 5.87 | 5.12 |
*For orders over 1500 items, please contact us so we can create a quote with better pricing terms.
- For engraving your company logo or project on Stainless steel strawsWe request that you send the logo artwork in vector format. If you have any questions, please contact us and we can provide further explanations.
Use our reusable stainless steel straws instead of straws We can reduce plastic waste to help the environment, in order to maintain a cleaner planet, not only for ourselves but also for our children and grandchildren.
The differences between stainless steel straws and plastic straws.
Most disposable plastics are made from polypropylene, which is extracted from petroleum. They also contain BPA, bisphenol A, which can leach into the liquid you are using it for. straw. While the Stainless steel straw It is made of food-grade stainless steel, making it non-corrosive and not absorbing flavors or odors. These straws They can be used repeatedly after washing.
Ours reusable straws They are made of stainless steel Food grade. GGenerally considered non-toxic to humans and the environment. They also last much longer than others. reusable straws such as bamboo, which degrades over time, and glass straws, which can break after continued use.
100% Recyclable Stainless Steel Straws
Are stainless steel straws easy to clean?
Yes. Most of Stainless steel straws are sold with cleaning brushesThis makes cleaning much easier, as you can wash its entire length. The washing process is extremely easy.
Can metal straws be used for hot drinks?
Yes. How the Stainless Steel Straws They conduct heat very quickly; therefore, there are silicone tip covers on the market so that the straw adapts to hot drinks.
CDo stainless steel plugs give off a metallic or strange taste?
No, they don't taste like metal. Os Straws They are made of medical-grade stainless steel, which is non-corrosive and non-reactive so that the straws They do not absorb flavors or odors. Those straws They can be used repeatedly.
We have more details in an article on our blog describing the... characteristics of our stainless steel straws.
How to Buy Stainless Steel Straws?
As the supplier of Stainless steelCompraço has several items that can meet the needs of your business, whether it's bars, pubs, restaurants, supermarkets, hypermarkets, or other businesses that are migrating to this extremely interesting market niche.
Can you print your logo on the straws?
Yes, we can create your business logo. Contact us for a quote.
Stainless steel straws are often referred to as Microtubes, which are part of our line of drawn tubes.So if you hear that name around, remember that we provide you with the highest possible quality.
The ban on plastic straws will continue, will you be willing to join us?
CHESS PLATES
As Checkerboard Floor Plates It can be divided into three types: checkered carbon steel, galvanized steel chess e steel sheets stainless checkered . It can be supplied in coils or sheets.
Galvanized Carbon Steel Checker Plate
Os Galvanized Flooring usually refers to steel sheet Hot-dip galvanized with a zinc coating layer. The galvanization on the surface of the...steel plate will help prevent rust when the plate if exposed to the environment and humidity. The amount of zinc coating will meet the requirements of national or international standards. With a certain degree of slip resistance, good corrosion resistance, good appearance and economical cost, the aço Galvanized steel is widely used in elevators, shop decoration, engineering, building exteriors, etc.
Checkerboard Floor Plate in Carbon Steel
This is the basic metal for the plate Galvanized, supplied without additional coating. It costs slightly less compared to galvanized products. However, it can be damaged over time, but it is still a widely used material.
Stainless Steel Checker Plate
O aço Stainless steel has good mechanical properties, including excellent corrosion resistance and heat resistance.
Stainless Steel Checker Plate for Flooring It is widely used in conditions requiring high corrosion resistance, such as chemical, hospital, and food-related environments, details as below:
- As parts of steps or decks for large chemical industry equipment or industrial tanks.
- Components or accessories for medical instruments, tableware, kitchenware, cookware
- Food processing
- Hospital Equipment
- Architectural purposes, interior and exterior decoration for construction and escalators.
Metallic raw materials of aço Stainless steel has a stable chemical composition and mechanical properties. It will not react easily with other elements. Therefore, checkered plate The finish makes it suitable for use in harsh environments, such as chemical plants.
The corrosion resistance and weather resistance characteristics, along with surface treatment, also make it suitable for exterior architectural uses such as facades and wall panels, ceiling panels, etc.
Its weight can be reduced compared to common steel grid plates due to the high intensity of use per unit area. By using material of aço Stainless steel, so customers don't need to worry about rust.


Get in touch and schedule a consultation; we are happy to assist in supplying raw materials and manufacturing for your project.
rolled sheets
We supply the Steel Tank Industry. rolled sheets We manufacture carbon steel tanks for various market segments such as oil, sugar and ethanol, agriculture, chemicals, and water. We offer vertical or horizontal tanks in various capacities. Our main focus is to supply the industrialized raw material so that companies only have to carry out the assembly on the construction site.

Rolled Steel Sheets for Fuel Storage
- Gasoline Storage
- Ethanol Storage
- Diesel fuel storage
- Bulk storage of kerosene
- Aviation fuel storage
We provide rolled steel sheets already manufactured and industrialized, both for cutting and bending, squaring, chamfering and Calendered for assembly on construction sites.
Rolled sheets For steel tanks with the best price and service quality on the market. As current fuel prices rise and environmental regulations expand, you need to ensure your fuel storage tank is safe enough to meet standards and assembly requirements.
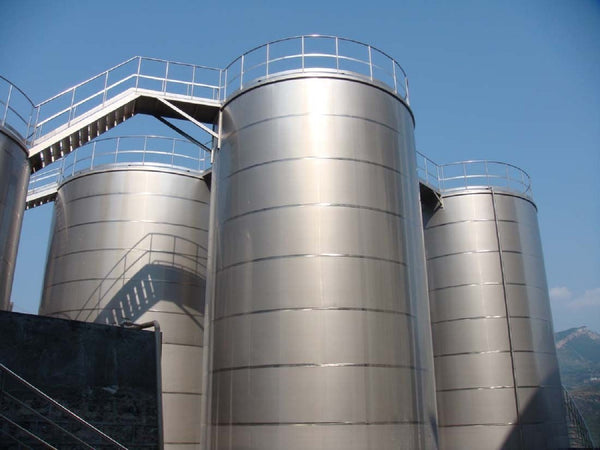

Quality of our rolled sheet materials for steel tanks and reservoirs.
We meet your needs by relying on proven tank and reservoir manufacturing processes, using materials made exactly to your specifications. rolled sheets Offering engineering innovation. The technology and engineering invested in our products are unparalleled.
The exceptional quality of our services in the manufacturing of rolled sheets Our commitment to tanks and reservoirs begins with the pride each of us takes in skill, expertise, and service. We take our commitments to our partners seriously because we know you can't rely on our services without our expertise. sheet metal rolling From tanks to trusting our production staff, our team of professionals is dedicated to providing the best solution for your project, making us an extremely reliable partner.
Check out some of the other products we manufacture.
Is there a specific project involving steel tanks that your company needs? I would like more information. Get in touch, we can definitely help..
HOT ROLLED THIN STEEL SHEETS
Check out our line of carbon steel coils.
Market segments that use Cold Rolled Thin Steel Sheets and Hot
- Automotive Industry
- Naval Industry
- Petrochemical Industry
- Metallurgical Industry
- Agricultural Industry
- Hospital Industry
- Electronics Industry
- Industrial Furnaces
- Manufacturers of Machinery and Equipment
- Overhead Cranes
- Sugar Mills
- Energy
- Furniture maker
- Civil Construction
Compraço offers an extensive stock of thin steel sheets in various gauges and materials, including:
Hot Rolled Steel, Cold Rolled SteelGalvanized Steel and Checker Plates.

Cold Rolled Steel Sheet

Hot Rolled Steel Sheet
MEASUREMENT CHART FOR COLD AND HOT ROLLED THIN SHEETS
Cold Rolled Thin Sheet
|
BITOLA
|
THICKNESS (mm)
|
WEIGHT Kg/m²
|
|
30
|
0.30
|
2.40
|
|
28
|
0.38
|
3.04
|
|
26
|
0.45
|
3.60
|
|
24
|
0.60
|
4.80
|
|
22
|
0.75
|
6.00
|
|
20
|
0.90
|
7.20
|
|
19
|
1.06
|
8.48
|
|
18
|
1.20
|
9.60
|
|
16
|
1.50
|
12.00
|
|
14
|
1.90
|
15.20
|
|
13
|
2.25
|
18.00
|
|
12
|
2.65
|
21.20
|
Hot Thin Plate
|
BITOLA
|
THICKNESS (mm)
|
WEIGHT Kg/m²
|
|
18
|
1.20
|
9.60
|
|
16
|
1.50
|
12.00
|
|
14
|
2.00
|
16.00
|
|
13
|
2.25
|
18.00
|
|
12
|
2.65
|
21.20
|
|
11
|
3.00
|
24.00
|
|
10
|
3.35
|
26.30
|
|
9
|
3.75
|
30.00
|
|
8
|
4.25
|
34.00
|
|
7
|
4.50
|
36.00
|
|
3/16"
|
4.75
|
38.00
|
|
-
|
5.00
|
40.00
|
Get in touch and schedule a consultation; we are happy to assist in supplying raw materials and manufacturing for your project.
THICK SHEETS
Thick carbon steel plate
As Thick Carbon Steel Sheets It has many applications. A good example where the steel sheet It can be found in the manufacture of pressure vessels. Thick Plates They are also used by the Mining, Shipbuilding, Automotive (in Heavy Vehicle Frames), Railway, Hydroelectric, Gas and Oil industries. among other various types of large-scale metal structures. Therefore, they offer the ability to withstand enormous weights and pressures. We offer Various sizes, widths, lengths, and specifications.
Check out our product line of THICK SHEETS
ASTM A36 - Carbon Structural Steel
This specification covers structural quality forms for use in riveted, bolted, or welded constructions in bridges and buildings. Its use is for general structural purposes.
ASTM A572 - High-Strength Low-Alloy Structural Steel
A specification of Steel Sheets Low Alloy High Strength Structural steel sheets High-quality material with guaranteed mechanical properties and chemical composition. Used in equipment where high mechanical properties are required to maintain good weldability and toughness.
ASTM A588 - Standard Specification for High-Strength Low-Alloy Structural Steel
This specification covers forms for welded, riveted, or bolted construction, but is primarily intended for use in welded bridges and buildings where weight savings or increased durability are important. This has resistance to atmospheric corrosion. aço in most environments it is substantially better than that of carbon steels with or without the addition of copper.
ASTM A514 - Standard Specification for Steel Sheets High Performance Alloy, Quenched and Tempered
This specification covers steel sheets-Tempered and annealed structural quality alloys intended primarily for use in the construction of welded bridges and other structures.
ASTM A285 - Standard Specification for Pressure Vessel Plates
This application covers carbon steel sheets of low and medium tensile strength and intended for fusion-welded pressure vessels. sheets They are available in three classes with different levels of resistance.
ASTM - A515 - Standard Specification for Pressure Vessel Plates in Intermediate and High Temperature Service
This specification is for carbon steel sheetsSilicon is primarily used for intermediate and high-temperature services in welded boilers and other pressure vessels. The plates are available in three grades, each with different strength levels.
ASTM A516 - Standard Specification for Pressure Vessel Plates for Moderate and Low Temperature Service
This specification covers carbon steel sheets Designed primarily for use in welded pressure vessels where improved notch hardness is important. The plates are available in four grades, each with different strength levels.

MEASUREMENT CHART FOR THICK SHEETS
| ESPESSURA |
PESO THEORETICAL KG/M² |
|
| POL. | MM | |
| 1/4" | 6.30 | 49.39 |
| 5/16" | 8.00 | 62.72 |
| 3/8" | 9.50 | 74.48 |
| 1/2" | 12.50 | 99.00 |
| 5/8" | 16.00 | 125.44 |
| 3/4" | 19.00 | 149.50 |
| 7/8" | 22.40 | 175.84 |
| 1" | 25.00 | 198.00 |
| ESPESSURA |
PESO THEORETICAL KG/M² |
|
| POL. | MM | |
| 1.1/4" | 31.50 | 247.27 |
| 1.1/2" | 37.50 | 299.00 |
| 1.3/4" | 44.45 | 350.00 |
| 2" | 50.00 | 392.50 |
| 2.1/2" | 63.00 | 494.55 |
| 3" | 75.00 | 588.10 |
| 3.1/2" | 88.90 | 697.80 |
| 4" | 100.00 | 785.00 |
Get in touch and schedule a consultation; we are happy to assist in supplying raw materials and manufacturing for your project.
CALENDERED TUBES
We provide Rolled Steel Tubes For projects involving structural steel, such as mining, agriculture, hydroelectric power, pressure vessels, silos, tanks, reservoirs, cyclones, screw conveyors, tunnel construction, metal casings for bridges and viaducts, and dust collectors, we understand the importance of using ferrous materials to make the structure safer. Rolled Steel Tube And rolled sheets are one of our main products, with a production capacity exceeding 2 million kg per month.
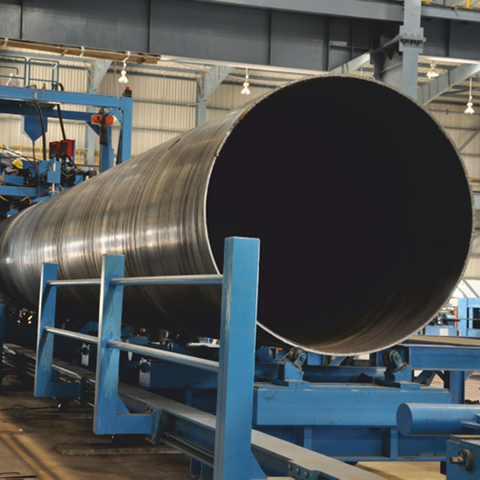

We produce different lengths of rolled steel tubesReady for individual installation, prefabricated. In addition to steel pipes straight lines, transition pieces, we offer additional services such as components of aço Secondary. This being a special aspect in our product portfolio, ready-to-install piping components streamline our customers' processes.
Rolled sheets up to 2" thick
Rolled Steel Tubes and carbon steel and stainless steel pipes up to 120". Also called Structural Rolled Steel Tubes e Rolled Sheets, used in the construction of technological plants, where there is extensive use of tanks containing liquids, gases, or vapors. There are requirements regarding the bending of the pipes used for the operation of technological systems. Numerous solutions can be adopted for the manufacture of Rolled Steel Tube of the parts used in heat exchangers, rolled steel pipes and rolled plates for geotechnical engineering, shipbuilding, cogeneration systems, sanitation stations, steel pipes Bends for industrial plants, pipe bends for civil systems.
Each project has its own unique characteristics, for this reason, attentive to new technologies and methods in relation to all aspects of rolled steel pipeWe are able to satisfy the widest variety of market requests in the field of large rolled sheets. Fproviding a high-quality standard derived from a precise and tested production system.
Tubular Solutions for Infrastructure Projects such as Bridges and Viaducts
Rolled Tubes These are structures used as support in civil construction and foundation support. The use of rolled steel tubes It is becoming increasingly common in large civil engineering projects, such as stadiums, train stations, shopping centers, and airports, since steel is an element that allows for larger and "cleaner" structures from an architectural point of view. rolled steel pipe It is commonly used in foundation construction, especially in maritime projects; see the example below.

All of our rolled steel tubes They are manufactured using our available raw materials. Check out our line of Carbon Steel Sheets..
Here are some other types of services and equipment we provide:
Get in touch and schedule a consultation; we are happy to assist in providing... rolled steel tubesRaw materials and industrialization for your project.
-

WELDED BEAMS AND PROFILES
SEE WHAT WE CAN DO FOR YOUR COMPANYerfis and welded beamsThey are widely used in industrial structures that need to support heavy loads. They are generally subjected to large loads.
-

HEAVY EQUIPMENT
SEE WHAT WE CAN DO FOR YOUR COMPANYFocus on the most diverseInfrastructure companiesfrom the Brazilian market. Providing solutions for large projects in diverse areas ofheavy equipmentand large in size.
Recollectible content
rolled sheet
We supply the Steel Tank Industry. rolled sheets We manufacture carbon steel tanks for various market segments such as oil, sugar and ethanol, agriculture, chemicals, and water. We offer vertical or horizontal tanks in various capacities. Our main focus is to supply the industrialized raw material so that companies only have to carry out the assembly on the construction site.

Rolled Steel Sheets for Fuel Storage
- Gasoline Storage
- Ethanol Storage
- Diesel fuel storage
- Bulk storage of kerosene
- Aviation fuel storage
We provide rolled steel sheets already manufactured and industrialized, both for cutting and bending, squaring, chamfering and Calendered for assembly on construction sites.
Rolled sheets For steel tanks with the best price and service quality on the market. As current fuel prices rise and environmental regulations expand, you need to ensure your fuel storage tank is safe enough to meet standards and assembly requirements.

Quality of our rolled sheet materials for steel tanks and reservoirs.
We meet your needs by relying on proven tank and reservoir manufacturing processes, using materials made exactly to your specifications. rolled sheets Offering engineering innovation. The technology and engineering invested in our products are unparalleled.
The exceptional quality of our services in the manufacturing of rolled sheets Our commitment to tanks and reservoirs begins with the pride each of us takes in skill, expertise, and service. We take our commitments to our partners seriously because we know you can't rely on our services without our expertise. sheet metal rolling From tanks to trusting our production staff, our team of professionals is dedicated to providing the best solution for your project, making us an extremely reliable partner.
Check out some of the other products we manufacture.
Is there a specific project involving steel tanks that your company needs? I would like more information. Get in touch, we can definitely help..
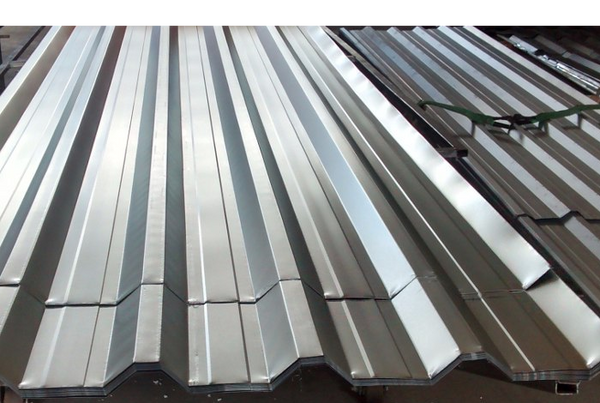
GALVANIZED SHEET
Galvanized Steel Sheet It is basically a sheet of carbon steel coated with zinc on both sides. The process used to do this is known as the continuous hot-dip process. This process results in a layer of zinc that adheres firmly to the base steel; the zinc layer acts as a surface coating.
Galvanized sheet metal can be used unpainted, pre-painted, or post-painted. It is used for applications that require corrosion resistance.
Applications of Galvanized Steel Sheet
- Galvanized Roofing Sheets
- Cutting and Folding
- Automotive Industry
- Electrical boxes
- Boxes and cabinets
- Prefabricated and metal constructions
- Playground equipment
- Equipment and machinery
- Stamping
- Cold welding


Get in touch and schedule a consultation; we are happy to assist in supplying raw materials and manufacturing for your project.
COMPRAÇO STEEL SOLUTIONS
GALVALUME SHEET
STAINLESS STEEL SHEET
STAINLESS STEEL SHEET
A Stainless Steel Sheet It is available in the following types: 304 and 316 stainless steelThe type 304 It can be easily rolled or folded, and its excellent corrosion resistance and weldability make it one of the most popular types. The type 316 It is a highly corrosion-resistant alloy, providing greater resistance to corrosion. Typical uses for the type 316 These include maritime, chemical, paper, textile, and food service applications. Our stainless steel sheet It is dual certified. 316 / 316L, which helps prevent corrosion after welding.

304 / 304L Stainless Steel
Typical applications:
- Handling Equipment
- Dairy Product Processing
- Food and Beverages
- Mauseio de Acidos Acetico, Nitrico e Citrico
- Organic and Inorganic Chemical Products
- Dyes, Crude and Refined Oils
- Hospital Instruments
- Aapplications that require welding.
There are many other types of applications for Sheets 304 Stainless SteelThe items mentioned above are just some applicable examples, as they help identify, based on the cited items, whether this raw material is applicable to the market niche for which your project was conceived.
|
COMPOSITION 304 STAINLESS STEEL
|
|
|---|---|
|
FERRO
|
alloying elements:
|
|
CARBONO
|
0.08% (max)
|
|
CROMO
|
18-20%
|
|
MANGANESE
|
2% (max)
|
|
NICKEL
|
8-10.5%
|
|
MATCH
|
0.045% (max.)
|
|
ENXOFRE
|
0.03% (min)
|
|
SILICON
|
1% (max)
|
316 / 316L Stainless Steel
Typical applications:
- Parts and equipment used in machines for processing paper, textiles, chemicals and pharmaceuticals.
- Applications in aircraft, used for parts requiring low magnetic permeability and good corrosion resistance.
- High resistance to corrosion
- Valves and Pipes
- Chemical Industry
- Pharmaceutical Industry
- Oil Industry
- Textile Industry
- Refrigeration Industry
- Paint Industry
- Ideal for applications involving sulfurous acids, chlorine, alkalis, and saline waters.
There are many other types of applications for the 316 Stainless SteelThe items mentioned above are just some applicable examples, as it is a way to identify them from the items cited.