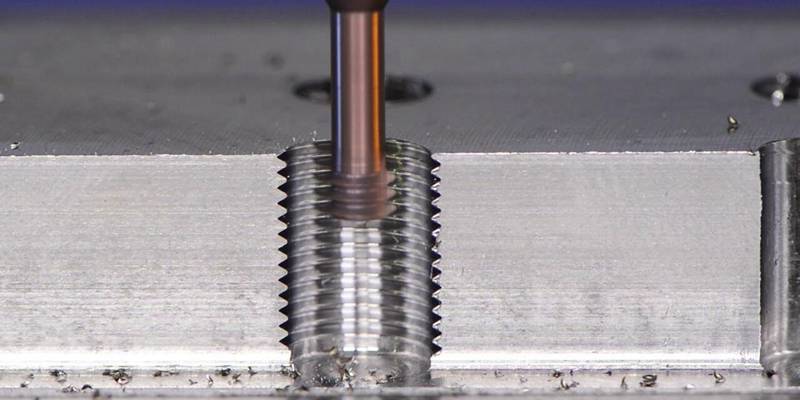
As long as screws are still present in machined parts, threads will continue to be an important aspect of metallurgy. They allow parts to be connected cost-effectively, making them ideal for use with fasteners, accessories and connectors.
In addition to knowing what threads are, it is also important to find the right type of thread for your project. So what exactly does the term machine thread mean? What types of machine threads are there? Read on as we answer these questions and provide other important information about threading.
What is thread machining in parts manufacturing?
Thread machining is one of the most important applications on a CNC machining center. It is a subtractive method to produce external and internal threads of different sizes. This machining is carried out by the circular movement of a rotary tool calibrated for the required thread depth and density.
The main function of a thread is to act as a coupling agent between two mechanisms. During the coupling process there is movement between the parts.
A thread consists of different parts. These include the peak, trough, slope angle, steepness and steepness. Let's look at these parts in detail.
Main parameters for thread

Helix angle : When machining, the feed angle is the angle between the thread axis and the feed for a straight thread or the angle formed by the tapered feed area of a thread for tapered threads.
root : This is the bottom of the thread. It is the adjacent surface of the projected cone or cylinder.
Combing : The comb is the end of the strand. It is the area furthest from the projected cone or cylinder. The ridge is also the surface of the thread that connects the flanks.
Flank : This threaded part connects the root to the tip. Theoretically, the intersection of a flank surface with an axial plane is a parallel line.
pitch : The pitch diameter is theoretically the same as that of the cylinder or cone. Pitch is the distance measured between surfaces on adjacent threads. The measured parallel surfaces must match.
Types of machining threads
There are many types of threads according to different classification standards. For the unified thread system, UNF thread (thin thread) and UNC thread (coarse thread) are standard. However, the two main types of threads are internal and external threads.

internal thread
An internal thread, also called an internal thread, is machined using a single-lip threading tool. In addition to this single-lip tool, a conventional screw cap can also be used to cut CNC internal threads. It is important to note that internal threads are only cut on concave surfaces.
So when is an internal thread needed? You will need one if your workpiece requires screw inserts. Machinists use manual or mechanical taps to cut internal threads.
External thread
This type of thread is also known as screw thread and is used in screws, bolts, pins and limit gauges. Using a lathe is one of the most effective methods for producing external threads.
Another method is to cut the external thread manually using a round die. The round die used remains in a fixed die stock. In addition to round cutting dies, there are also hexagonal square cutting dies, which are ideal for positive use.
How do you cut a machine thread?
Thread cutting is ideal for producing parts with threaded connections. Knowledge of thread cutting is an advantage. With this knowledge you can, for example, make an entire screw or nut or repair it if necessary. Furthermore, threading machines are not always available.
This is how you cut the wires.

1. How to cut an internal thread
Do you want to cut an internal thread? First, get the right tools, including safety glasses, a pillar drill (for machine taps), an adjustable tap wrench (for manual taps), an internal tap, a twist drill and a 90-degree countersink.
Once you have the right tools, the next step is to determine the diameter of the hole you want to tap into. Once the diameter has been determined, the next step is to find the right tap to cut. To determine the diameter of the center hole, subtract the thread pitch from the tap diameter.
To begin cutting the internal thread, first center it with a center punch and then drill a center hole with a twist drill. To create a chamfer in the center hole, use the 90-degree countersink. When cutting the thread, turn the screwdriver with the tap attached to the center hole.

2. How to cut an outside line
Tools needed to cut external threads include file, die, round and groove cutting tool, bar, vise (for gripping), and cutting spray.
To cut external threads, first file the edges of the rod and then chamfer it at a 45-degree angle. Make sure the chamfer is larger compared to the thread depth.
The next step is to clamp or hold the round cutting tool to keep it firmly in place. This prevents unwanted movement, as the rod requires a lot of pressure to cut the external thread optimally. Use cutting sprays to improve the surface quality of the part.
Great Tips for Thread Cutting
Knowing how to machine threads brings several benefits. However, good machining tips can make the difference between an ideal thread and a sub-optimal thread. So here are some tips for thread machining.
- Add a chamfer to externally threaded end pieces.
- Make sure the starting end of the line has a flat surface. Also make sure it is aligned with the center axis of the line.
- Complete the internal thread with a countersink;
- Pipe parts are often subjected to compressive loads during thread forming or cutting, so they must have greater wall thickness;
- While it's okay for unique thread sizes, using a standard thread size is more economical.
- In the absence of thread specifications, lower height threads are preferred over higher height threads.
Common thread machining methods in the CNC process
There are several CNC thread machining processes. These different procedures have special characteristics and advantages. Here we discuss the most common ones and what differentiates them.
1. Typing
Tapping is ideal for creating internal threads. It is an economical and efficient thread cutting method. This CNC method is suitable for threaded holes with low positional accuracy and small diameter holes.
As a thread machining method, this method has reduced the downtime of CNC threading machines. Furthermore, the editing structure here is quite simple compared to other methods. Furthermore, threading is a high-speed cutting process that significantly improves machining productivity and efficiency.
The cutting tools used in this machining process are cheaper, thus reducing manufacturing costs. Furthermore, it is a versatile process with a wide range of applications.

2. Thread milling
This is another method of making screw threads. This process uses a milling cutter and a 3-axis machining center. Circular interpolation of the three main axes is also used: linear feed x, y and z. Thread milling is ideal for threading large parts or high-value materials.
Thread milling is characterized by high processing speed, high precision and efficiency. The milling tool used generally contains hard alloys. Milling tools are also versatile, so different tools are not necessarily needed for different milling operations. For example, the same milling cutter can cut left-hand and right-hand threads with the same thread pitch. You can adjust hole diameters, tolerances and material cutting with minimal effort.
Threads made by milling have a high-quality, burr-free surface. This process is ideal for producing thin-walled parts, machining blind holes and asymmetric/non-rotating parts.

3. CNC thread cutting on lathes
Thread cutting on a lathe is another common thread cutting process with a wide range of applications. CNC lathes make it easy to produce high-quality threads. This method allows machinists to produce various taper threads, main threads, and thread pitches.
Rigid threading and single-point threading are two of the most common methods in CNC turning. Single-point thread cutting uses an indexable insert tool whose shape and size matches that of the finished screw head.

4. Thread grinding
This is ideal for threading hardened parts. Two main types of grinding wheels are used for this process: multi-row grinding wheels and single-row grinding wheels. The single line grinding wheel has a pitch accuracy of 5 to 6. It also has a surface roughness of R1.25 to 0.08 μm.
Single line grinding is ideal for producing precision screws, worm threads, thread gauges, blade grinding mills and thread cutting in small quantities.
Multi-line grinding is divided into plunge and longitudinal grinding processes. The main difference between these two methods is the width of the grinding wheel. In the longitudinal process, the width of the grinding wheel is smaller than the length of the thread to be ground. On the other hand, the width of the grinding wheel used in the grooving process is larger than that of the thread.
Get Thread Machining Services at WayKen
Request a free quote now
Concluding
To produce high-quality parts, it is important to have in-depth knowledge of the various manufacturing processes. This knowledge also shows how to deal with some machining problems such as machining vibration.
Thread machining is an important aspect of most products that require coupling or connection. Knowing how they work, what their parameters are, and the different machining methods available will help you make the right machining decisions.
Common questions
Is thread milling faster than threading?
Threading is generally faster than thread milling. However, thread milling machines sometimes have additional cutting edges to compensate for the reduced speed.
What is the difference between a thread mill and a tap?
The main difference between thread milling and threading is the smoothness of the cut. Thread milling produces smoother, more consistent cuts, while threading cuts are rough and irregular.
What is the thread cutting process on the lathe?
This process creates a spiral burr with uniform cross-section on the workpiece. This involves making successive cuts into the workpiece using a thread cutting tool. It is important to note that the tool used for this operation must have the same shape as the required thread.