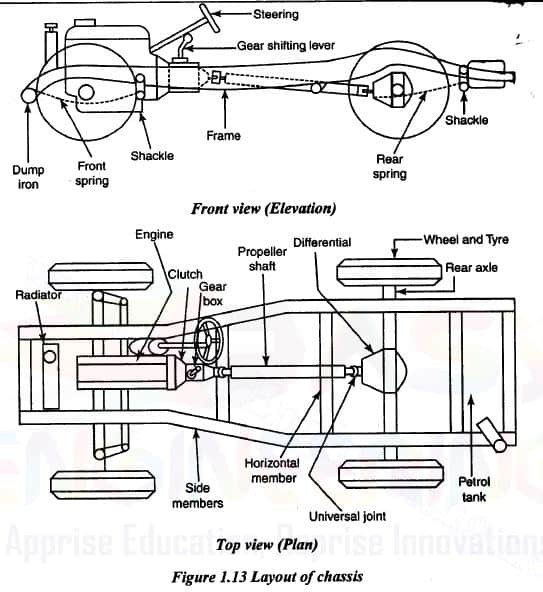
Figure 1.13 shows the front and top layout of a typical chassis. In this layout, the location of the engine is at the front of the vehicle. The engine is connected to the gearbox via the clutch. The engine drive can be connected or disconnected from the gearbox using the clutch assembly. The clutch pedal located close to the driver makes it easy to engage or disengage the clutch with the gearbox whenever necessary. From the gearbox, power is transmitted to the differential via a drive shaft and universal joints and finally to the wheels via the rear axles. The radiator is placed at the front of the engine.
Read More: Different Types of Chassis Used in Motor Vehicles
 car chassis parts
car chassis parts 1. Frame:
The structure is the basis for transporting the vehicle's engine and body. It also carries steering, power train, etc. by means of springs, axles, rubber pads, etc. The structures are made of box, tubular, channel or U-section, welded or riveted together. To make them rigid to withstand shocks, blow twists and vibrating mats, braces or cross braces are used. When the engine, wheels, drivetrains, struts, and steering systems are mounted on the chassis, the assembly is known as the chassis. The frame curves upward into a shape at the rear to provide space for the rear springs. It is tapered at the front to provide room to turn the front wheels while driving.
2. Suspension systems:
Suspension systems are used in vehicles. isolate the wheels and axles of the structure in order to avoid transmitting road effects to passengers when traveling on uneven roads, provide a comfortable ride for passengers and avoid additional stress on the car structure.
3. Steering System:
The function of the steering system is to allow the driver to precisely control the direction taken by the vehicle under all operating conditions. The system must be light and easy to operate, free from as direct shocks and vibrations as possible. The steering system also helps convert the rotary motion of the driver's steering wheel into angled rotating front wheels, as well as multiplying the driver's effort with the leverage or mechanical advantage of turning the wheels.
4. Brake system:
The most vital factor in the operation and control of the modern vehicle is the braking system. To cause the moving motor vehicle to stop or slow down in the shortest possible time, the energy of motion possessed by the vehicle must be converted into some other form of energy. The brake is a friction device for converting the momentum or kinetic energy of the moving vehicle into heat.
5. Internal combustion engines:
In internal combustion engines, combustion takes place inside the engine, unlike steam engines which run on externally generated steam in a boiler. In all internal combustion (IC) engines, air is supplied along with a measured amount of fuel. This fuel burns inside the engine and produces a high-pressure, high-temperature gas.
6. Clutch:
It is a friction type decoupling device. It consists of a single steel disc coated with suitable friction material. It is clamped between two surfaces driven directly by the engine. To disengage the clutch, the two surfaces are positively separated by pressing the clutch pedal. The main function of the clutch is to smoothly remove drive from the engine and release or disengage whenever desired. The clutch is disengaged when changing gears or when stopping the vehicle.
7. Gearbox:
It consists of several types of gears that are constantly meshing. Gear changing occurs by sliding the dogs. The main function of the gearbox is to provide the necessary variation in the torque applied by the engine to the wheel according to the operating conditions. The necessary variations are provided due to the presence of different gear ratios between the various meshed gears.
8. Propeller shaft:
The function is to transmit power from the rear end of the gearbox to the final reduction gear on the shaft. Vertical movement of the rear axle relative to the chassis is also accommodated. It's a regular Hooke joint. The small and limited angular displacement in the rubber gaskets is advantageous for dampening torsional vibrations.
9. Universal joint:
Due to the flexibility of the road springs, the rear axle constantly moves up and down. The propeller shaft mounted on the rear axle must also be free to move up and down. To allow the propeller shaft to rotate, this movement occurs and universal joints are installed at each of its ends. Therefore, the relative movement between the engine and the driving wheel is maintained by the universal joint.
10. Differential:
The differential gear transports power from the propeller shaft to the rear wheel axles. It helps two rear wheels to rotate at different speeds when cornering. The outside wheel must overtake the inside wheels when turning. Differential gearing also ensures that the final output torque is distributed equally between two wheels without any consideration to their relative speeds.
11. Springs:
Springs are installed between the frame and the wheel to prevent the upward movement of the frame along with the up and down movement of the wheel. A spring is a reservoir of energy that is stored in steel springs by bending or twisting them. When the spring returns to its normal state, this energy is released.
12. Front axle:
It is used to direct front wheels carried on stub axles rotating about the ends of the kingpin axle. Steering arms and track rod link, two stub axles are used together to rotate them by a flywheel around the king pins. The steering wheel connected to one of the axle ends per axle, a gearbox and a suitable linkage are operated by the driver's steering wheel. Previously, an axle was used in which a solid beam is used to support the vehicle using springs (axle and spring arrangement). Now, an arrangement known as independent front suspension replaces the axle and spring arrangement. Under the control of the springs, the wheels are free to move up and down independently in a vertical direction relative to each other.
13. Rear axle:
Rear axle or driving axle is a tube like axle that surrounds driving axles with bearings suitable for turning the wheels. It is used to secure the rear wheels. It is enlarged in the center to include the final drive gears used to provide main speed reduction between the engine and drive wheels. The change of direction from the drive shaft line to the transverse line of the axle shafts is also provided by the rear axle.
14. Battery:
In reality, the battery is the heart of a motor vehicle's electrical system. It supplies current to the starter motor and ignition system. The function of the battery is to store electrical energy that can be used whenever necessary. The battery can be called the nerve center of the entire installation because it provides electrical energy to operate all electrical devices and other units except the charging device. It also provides electricity to operate the various electrical devices when the vehicle is not running or running slowly and the generator
speed is insufficient to meet full load requirements.
15. Wheel:
The wheels are mounted below the chassis to support the load of the vehicle and passengers. They are equipped with hollow rubber tires filled with air in rubber tubes under sufficient pressure to carry the load. Shocks caused by irregularities on the roads are absorbed by them. By installing springs between the wheels and the vehicle to allow vertical movement of the wheels in relation to the vehicle, a large proportion of uneven road surfaces are eliminated.