To build any automobile, the chassis is the basic requirement: Chassis is a French term and was initially used to denote the chassis or main structure of a vehicle. It is widely used in complex vehicles except bodywork. A vehicle without a body is called a chassis.
Basic Chassis Construction
The chassis is the backbone of the vehicle. Vehicle components such as power plants, transmission systems, axles, wheels and tires, suspension, control systems such as brakes, steering, etc., and also electrical system parts are mounted on the chassis structure. It is the main assembly of all components, including the body. Therefore, it is also called a transport unit.
- Automobile chassis components and drive system
- Different Types of Chassis Used in Motor Vehicles
Main chassis components
1. Frame
2. Front suspension
3. Steering mechanism
4. Engine, clutch and gearbox
5. Radiator
6. Propeller shaft
7. Wheels
8. Rear and front springs and shock absorber
9. Differential unit
10. Universal joint
11. Brakes and braking systems
12. Storage battery
13. Fuel tank
14. Electrical systems
15. Silencer
16. Shock absorbers, fuel tank, gasoline and hydraulic piping cables and some means of mounting these components.
Chassis classification
Chassis can be classified into different types based on the following.
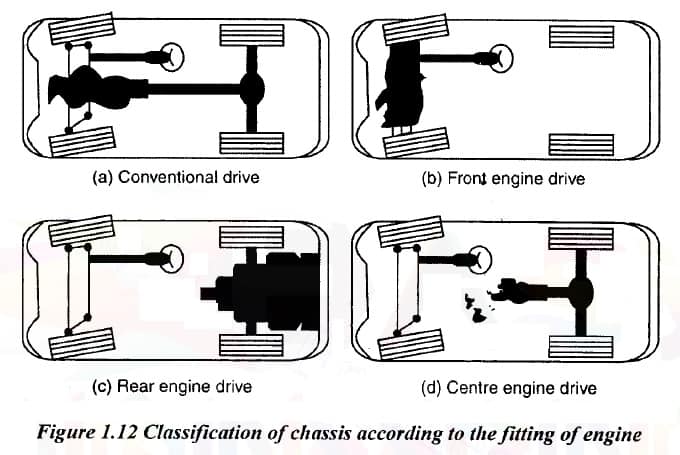
1. According to engine assembly:
(a) Full advance
(b) Semi-advanced
(c) Bus chassis
(d) Rear engine
(e) Engine in the center.
In the fully advanced chassis, the engine is installed outside the cab or driver's seat. Example: Mahindra cars and jeeps.
In the semi-advanced chassis, half of the engine is located exactly in the driver's cabin, while the remaining half is in the front, but outside the driver's cabin. Example: Tata SE series of vehicles.
 chassis as assembled
chassis as assembled In bus chassis, the entire engine is mounted in the driver's cab. It provides a larger area in the vehicle. The driver's seat is just above the front wheel. Example: buses and trucks.
In most vehicles, the engine is installed in the front of the chassis. Traction is given to the front wheels only. Example: Matador vehicles. In some vehicles, the engine is installed at the rear of the chassis. Example: Volkswagen cars, Leyland buses from England. In some vehicles, the engine may be installed in the center of the chassis. Example: Delhi Transport Royal Tiger World Master Bus.
2. Depending on the number of wheels installed on the vehicles and the number of driving wheels:
(a) 4 x 2 driving chassis – It has four wheels, of which 2 are driving
(b) 4 x 4 driving chassis – It has four wheels and all of them are driving
(c) 6 x 2 driving chassis – It has six wheels, 2 of which are driving
(d) 6 x 4 driving chassis – It has six wheels, 4 of which are driving.
Types of automobile chassis
1. Full front chassis:
This type of chassis consists of an engine installed in front of the driver's seat or driver's cab. It is commonly used in old model TATA cars and trucks. The driver cannot see the road just in front of the front tires because it is behind the engine, far from the front axle. To help the driver see as close as possible to the wheels, tilt is provided in the mudguard. Furthermore, passengers or goods cannot be transported on a part of the chassis where the engine is installed.
2. Semi-Advanced Chassis:
In this chassis, the engine is mounted in such a way that half of it is placed in the driver's compartment and the other half is placed outside the driver's compartment. These extra passengers or luggage can be placed in the part of the chassis thus saved. Semi-advanced chassis are used in standard Bedford pickup trucks and Tata-Mercedez trucks.
3. Bus Chassis:
To allow the driver to see the road just in front of the front wheels, as well as to make driving easier and smoother, especially in congested areas, the all-front chassis was modified by mounting the engine completely inside the driver's cabin. As well as providing an extra clear view of the road ahead of the front wheels, it provided an increased floor area to accommodate three extra seats.
4. Engine in front chassis:
This chassis is used in most heavy vehicles and is of three common types.
(i)In this type, the engines are mounted at the front, but the drive to the wheels is provided by the rear wheels (rear-wheel drive).
(ii) In the second type, the engine is mounted at the front and traction is also provided by the front wheels (front-wheel drive), as in the case of Matador vehicles.
(iii) In the third type, the engine is mounted transversely at the front and traction is also supplied to the front wheels as in the case of BMC Minis.
5) Rear-mounted engine:
In this chassis, the engine is mounted at the rear of the vehicle, thus saving a lot of space in the front, eliminating long propeller shafts and providing a clear view of the road in front. This system is used in popular vehicles such as Renault, Daulphine and Volkswagen. The engine is also
mounted on the rear end of the chassis on imported Leyland Double Decker buses. In this set of chassis controls, such as gear lever, oil and fuel gauge, the accelerated connection is very complicated. Furthermore, there is also a lack of natural air flow to the radiator due to the forward movement of the vehicle.
6) The engine installed on the central chassis:
In this chassis, the engine is mounted centrally and centrally under the chassis to remove defects from the engine mounted on the rear chassis and make full use of the floor space. This chassis was used in Royal Tiger Wordmaster buses previously operated in Delhi by the Delhi Transport Undertaking.
7) Long wheelbase chassis:
Standard truck chassis are used to make trucks and to allow the truck to carry the exact weight it was designed for, the load is stacked. However, in the case of bus chassis, the seats are fixed and the distance between each seat is fixed in accordance with the Motor Vehicle Rules, therefore the vehicle will travel with less weight, as fewer passengers can travel in it. To accommodate more passengers and carry more weight, bus chassis are provided with a longer wheelbase (i.e. the center distance of the front and rear wheels), resulting in longer chassis.
8) Protruding chassis:
In order to increase space to accommodate more goods and passengers, a certain length of the chassis is extended after the rear axle (rear overhang) and after the front axle (front overhang).
9) Half integral and half frame chassis:
It is an improved form of chassis used in Fiat Padmani cars. In this chassis, the half-frame bolted to the vehicle floor is fixed to the front end, where the engine gearbox and front suspension are fixed. The rear part of the floor serves as the vehicle's body structure.