Air conditioning is not a process of just heating or cooling to the desired temperature. Air conditioning deals with conditioning or controlling air. The complete air conditioning process includes the following processes.
1. Cool or heat air
2. Adding moisture to the air (Humidification) or removing moisture from the air (Dehumidification)
3. Controlling air movement
4. Air purification
5. Adding fresh outside air
6. Air distribution
Definition of air conditioning:
Air conditioning can be defined as the simultaneous control of temperature, humidity, movement and purity of air within an enclosed space.
OR
It can also be defined as the science that deals with the provision and maintenance of desirable internal atmospheric conditions, regardless of external conditions.
Air conditioning principle
In air conditioning system, the device or unit that provides conditioned air is called air conditioner. This device continuously draws air from an internal space that needs to be cooled, it cools in the refrigeration system and discharges it back into the same internal space. This continuous cyclical process of extracting, cooling and recirculating cooled air keeps the interior space cool at the lowest temperature required for comfortable cooling.
Air conditioning system components
The basic components of the air conditioning system are,
1 . Fans: For air circulation
2. Filters: To clean the air
3. Heating element: Air heating (can be electric heater, steam, hot water)
4. Control system: Automatically regulates the amount of cooling or heating.
5. Grille: Adjusts the direction of the air conditioner to the room.
6. Tray: It collects condensed water
Classification of air conditioning system / Types of air conditioning system:
1. According to the arrangement of the equipment
The. Unitary Air Conditioning System
In this system, different components of the air conditioning system are manufactured and assembled as a unit in a factory. This unit is installed in or near the space to be conditioned.
Example: Window air conditioning and split air conditioning
B. Central Air Conditioning System
In this system different components are manufactured in the factory and assembled on site. This type of system is used for air conditioning in theaters, cinemas, restaurants, exhibition halls, large manufacturing spaces, etc.
In the central air conditioning system all the components are grouped in a central room and the conditioned air is then distributed from the central room to the required locations through the extension duct system. The main components of the central system are compressor with motor drive, condenser with cooling coil and throttling devices. This system used large capacity drives. (over 25 tons).
Central air conditioning is direct or indirect.
2. According to the purpose
The. Comfort air conditioning system
B. Industrial air conditioning system
3. According to the season
The. Winter air conditioning system
B. Summer air conditioning system
w. Year-round air conditioning system
4. According to the working substance used in the system:
The. The entire air system.
B. Chilled water system
w. air-water system
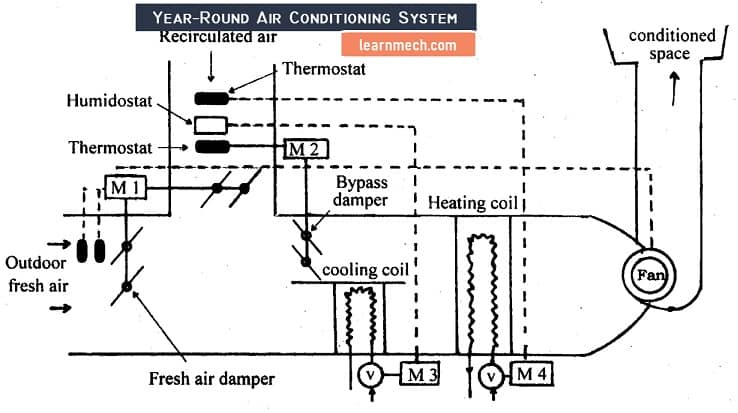
Year-round air conditioning system
The year-round arrangement of the air conditioning system is shown in fig. The amount of fresh outside air and recirculated air is controlled by the engine. The air conditioning has been designed in such a way that when the outside air temperature is above or below a certain selected value, it assumes the season as Summer or Winter, respectively.
In the summer season, the bypass damper is almost closed and most of the air passes through the cooling coil. The cooling coil can be an evaporator of the refrigeration system or a coil through which cold water passes. All air passes through the heating coil. In winter, the bypass damper is almost open. Most of the air passes directly to the heating coil, bypassing the cooling coil.
 year-round air conditioning system diagram
year-round air conditioning system diagramWinter air conditioning system
In winter air conditioning, the air is heated, usually followed by humidification. The schematic arrangement of the system is shown in Fig. External air flows through a damper and mixes with recirculated air (which is obtained from the conditioned space). The mixed air passes through a filter to remove dirt, dust and other impurities. The air now passes through a preheating coil to prevent possible water freezing and control the evaporation of water in the humidifier. After that, the air passes through a reheat coil to bring it to the designed dry bulb temperature. Now, conditioned air is supplied to the conditioned space by a fan. From the conditioned space, part of the air used is expelled into the atmosphere by exhaust fans or fans. The remaining part of the used air (known as recirculated air) is conditioned again as shown in Fig. The outside air is drawn in and mixed with the recirculated air in order to compensate for the loss of conditioned (or used) air through exhaust fans or ventilation of the conditioned space.
 winter air conditioning system diagram
winter air conditioning system diagramSummer air conditioning system
This system is used in summer air conditioning applications. In this system the air is cooled and generally dehumidified. The schematic diagram is shown in the figure. Outside air flows through the register and mixes with recirculated air obtained from the air-conditioned space. The mixed air passes through a filter to remove dirt, dust and other impurities. The air now passes through the cooling coil. The coil has a temperature much lower than the required dry bulb temperature of the air in the conditioned space. The cooled air passes through a perforated membrane and loses its moisture in condensed form which is collected in a reservoir. The air now passes through a heating coil which heats
the air slightly so that the air reaches the required DBT and relative humidity. Now the conditioned air passes into the conditioned space by a fan. From the conditioned space, part of the air is expelled into the atmosphere by exhaust fans or fans. The remaining part of the used or recirculated air is conditioned again as shown in the figure. Outside air is drawn in and mixed with recirculated air to compensate for loss of conditioned air or used through exhaust fans or conditioned space fans.
 summer air conditioning system diagram
summer air conditioning system diagramRoom air conditioning
Ambient air conditioning consists of a box divided into two parts by a vertical partition, that is, an external part and an internal part.
The internal part installed in the room consists of an evaporator, motorized fan, expansion device and control planet, air filter, power connection and tray. The condenser is connected to the evaporator by a capillary tube through a filter. The evaporator is connected to the compressor via the suction piping and the compressor is connected to the condenser via the discharge piping.
 Room air conditioning diagram
Room air conditioning diagramWindow air conditioner
Window air conditioner is mainly used to condition the air in the room. It is typically mounted in a window, which is why it is known as a window air conditioner.
The window air conditioning unit consists of the following components as shown in fig.
Refrigeration unit
Evaporator/cooling coil, condenser, compressor, expansion device Air circulation fan
 window air conditioning diagram
window air conditioning diagramWorking
The hot air coming from the room flows into the evaporator (cooling coil), the cooling coil absorbs the heat from the air. Moisture in the air is removed from the surface of the cooling coil by the process of air condensation. This way the air is cooled and dehumidified to meet the air conditioning comfort requirements in the environment. The filter cleans the air leaving the room before it passes through the cooling coil. Tray is provided below the cooling coil (evaporator) to collect moisture that condenses from air recirculation.
The flow of hot air (from the room) and cooled air (to the room) occurs through the evaporator fan. The refrigeration unit provides a cooling effect on the evaporator. The condenser fan circulates air on the outside of the condenser tubes, the refrigerant in the condenser rejects heat to the outside atmospheric air. The required fresh air can be mixed with ambient air recalculated to meet ventilation requirements. The ventilation air is controlled by the ventilation damper. Room temperature is controlled by a thermostat using an on-off power supply to the compressor motor.
Limitations
- It produces noise in the room because the compressor is very close to the room.
- The evaporator and condenser are included in a single unit. Therefore, the evaporator cannot be used as an interior of a room because the condenser requires outside air for cooling.
- Requires an appropriate size window or hole in the wall to accommodate the conditioner.
Split air conditioning
It is a modification of the window air conditioner.
Construction
This unit differs from the window air conditioner. In terms of dividing the unit into two parts. In split air conditioning, the window air conditioning is divided (split) into two parts.
First part: Includes the evaporator, filter, evaporator fan and grille (cooling coil). They placed it inside the room.
Second part: Includes condenser, condenser fan and compressor. This placed outside the room.
The first part (inside the room) and the second part (outside the room) are connected by small diameter pipes. Therefore, a small hole in the wall is necessary to install a split air conditioner.
 split air conditioning diagram
split air conditioning diagramThe advantages of a split air conditioner over a window air conditioner
- The compressor is outside the room, so there is no compressor noise in the room.
- No opening and fixing of windows is required.
- The compressor is outside the room, so there is no compressor noise in the room.
Automotive air conditioning system.
Air conditioners work on the principle that “liquids absorb heat when they become vapor (evaporate). Low pressure R134a vapor entering the compressor is compressed to become high pressure/temperature R134a vapor. This is then circulated together with the lubricating oil to the condenser. As the high pressure/temperature vapor travels through the condenser, heat is released to the cooler ambient air, passing through the condenser tubes, condensing the vapor into a liquid. This high pressure/temperature liquid then travels through the filter drier to the expansion valve, where a small variable orifice provides a restriction against which the compressor pushes.
Compressor suction pulls the high pressure/temperature liquid R134a through the small variable orifice of the TX valve and into the low pressure side of the A/C system. The R134a is now under low pressure/temperature vapor, where cabin heat blown onto the surface of the evaporator coil is absorbed by the cooler low pressure refrigerant. The R134a is then pulled through the evaporator and into the compressor.
 automobile air conditioning diagram
automobile air conditioning diagramDifference between central air conditioning and unitary air conditioning:
Sr. No. Central Air Conditioning Unitary Air Conditioning 1. Ton capacity is more than 40 tons of refrigeration Ton capacity is less than 25 tons of refrigeration 2. Mass flow rate of treated air is about 2,000 m3/min The mass flow rate of the treated air is lower. basement or outside the building. Unitary air conditioning is located in all rooms that require air conditioning. It is quite operational if used as a divided unit.5.All rooms must be maintained in more or less similar conditions.Each room can be maintained in different conditions.6.Requires duct design and installation.No duct design and installation is necessary.7.The capital cost of central air conditioning equipment is lower.The capital cost of unitary air conditioning equipment is higher.8.Maintenance is convenient and easy.Maintenance is difficult.
Air conditioning system applications.
1.Laboratories: to make accurate measurements
2. Printing Industry: Specific temperature and humidity are maintained in the printing industry. Paper becomes very dry in low humidity conditions and poor printing occurs. The paper swells with high humidity and the ink spreads, as well as taking a long time to dry, causing uneven printing.
3. Textile Industry: Relative humidity and temperature are the key factors in the textile industry. Moisture affects the strength and quality of fabric, making it soft and reliable rather than brittle and weak.
4. Pharmaceutical: Industry needs refrigeration to reduce airborne bacteria and dirt to preserve products
5. Photographic- Industry Provides precise temperature and humidity control for manufacturing and processing into photographic films.
6. Machine tool industry – The same machining processes require precise temperature and humidity. Ex. Processing in the manufacture of bearings, scientific instruments, electronic device test gauges and precision gears, etc., where close dimension tolerance is required.
7. Farm Animals
8. Computer rooms:
Industrial air conditioning – Used to control the atmospheric conditions necessary to carry out industrial processes more efficiently, economically and with better quality. Former textile factories, paper factories, printing and photo processing factories, etc.
Comfort Air conditioning – It is provided for maximum comfort of human being Ex-air conditioning system in home, office, etc. In this case, the length of stay of the occupants is prolonged.
Commercial air conditioning – This is similar to comfort air conditioning, except that the occupant dwell time is short. Former air conditioning system is bank, department store, etc.