Bearings are crucial components in machines and equipment, serving as support for rotating mechanical bodies to decrease the equipment's coefficient of friction during transmission and reduce mechanical load.
Bearings are categorized into different types based on various factors. This includes the bearing direction or its nominal contact angle, which divides bearings into radial and thrust bearings.
Furthermore, bearings can be classified based on the type of rolling element, with the options being ball bearings and roller bearings.
Alignment ability is another factor, leading to the division into aligned and non-aligned (rigid) bearings.
The number of rows of rolling elements is another factor that leads to the division into single-row, double-row and multi-row bearings.
The separability of parts is another factor, leading to the division into separable and non-separable bearings.
There are also classifications based on the shape and size of the structure.
This article mainly focuses on the features, differences and appropriate applications of 14 common types of bearings.
1. Angular contact ball bearing

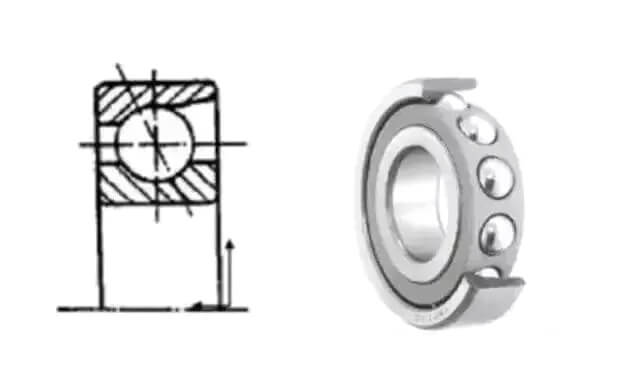
The contact angle between the tip and the ball is one of the key factors in determining the characteristics of a bearing. There are three standard contact angles: 15°, 30° and 40°. A larger contact angle provides greater axial load capacity, while a smaller contact angle is more suitable for high-speed rotation.
A single row bearing can support radial loads and unidirectional axial loads. By combining two single row angular contact ball bearings on the same shaft, the structure can support radial and bidirectional axial loads. The inner and outer rings are shared between the two bearings, providing a more robust and versatile solution.
Main applications:
Single line: machine tool spindle, high frequency motor, gas turbine, centrifugal separator, small car front wheel, differential pinion shaft.
Double Row: Oil pump, Roots blower, air compressor, various transmissions, fuel injection pump, printing machines.
2. Self-aligning ball bearing

Two-row steel balls have a spherical-type outer ring inner race, allowing automatic adjustment of misalignment caused by shaft or housing deflection or misalignment.
Tapered roller bearings, designed for easy mounting using fasteners, mainly support radial loads.
Main applications:
- Woodworking machines
- Transmission shafts for textile machines
- Vertical self-aligning bearings with housings.
3. Spherical roller bearing

This type of bearing features spherical rollers located between the outer ring of the spherical race and the inner ring of the double race. It is divided into four types based on their internal structure: R, RH, RHA and SR. Since the center of the outer ring raceway arc is aligned with the center of the bearing, it has self-aligning capability.
This allows automatic adjustment of shaft misalignment caused by deflection or misalignment of the shaft or housing, and can withstand radial loads and bidirectional axial loads.
Main applications:
- Papermaking Machines
- Reduction gears
- Railway vehicle axles
- Rolling Mill Gearbox Seats
- Roller tables for rolling mills
- Crushers
- Vibrating screens
- Printing machines
- Woodworking machines
- Various industrial reducers
- Vertical self-aligning bearings with housings and more.
4. Spherical thrust roller bearings

In this type of bearing, the spherical rollers are arranged obliquely. The track surface is spherical and has self-aligning performance, allowing the shaft to tilt slightly. This bearing has a large axial load capacity and can withstand various radial loads under axial load. It is usually lubricated with oil during use.
Main applications:
Hydrogenerators, vertical electric motors, propeller shafts for ships, reducers for rolling screws, tower cranes, coal mills, extruders and forming machines.
5. Tapered roller bearing

These bearings are equipped with cylindrical rollers guided by the large ribs of the inner ring. The points where the tapered surfaces of the inner ring race, outer ring race, and roller bearing surface intersect are designed to be on the centerline of the bearing. Single row bearings can support radial and unidirectional axial loads, while double row bearings can support radial and bidirectional axial loads, making them suitable for handling heavy and shock loads.
Main applications:
- Automotive: front and rear wheels, transmissions, differential pinion axles
- Spindles of machine tools, construction machines, large agricultural machines, gear reduction devices for railway vehicles, rolling mill roll necks and reduction devices.
6. Deep groove ball bearing

In this type of bearing, each ring has a continuous, grooved raceway that forms a cross section approximately one-third the circumference of the sphere's equator.
Deep groove ball bearings support mainly radial loads, but can also support some axial loads. When the radial clearance increases, they exhibit angular contact ball bearing characteristics and can support axial loads in two alternating directions.
Compared with other bearings of the same size, deep groove ball bearings have a low coefficient of friction, high limiting speed and high precision, making them a popular choice among users.
Main applications:
automobiles, tractors, machine tools, engines, pumps, agricultural machinery and textile machinery.
7. Thrust ball bearings

It consists of a washer-shaped race ring with a race, a ball and a cage assembly. The race ring that works with the shaft is called the shaft ring, and the race ring that works with the housing is called the seat ring. Bidirectional bearings align the center ring with a solid shaft. Unidirectional bearings can support unidirectional axial loads, while bidirectional bearings can support bidirectional axial loads (neither can support radial loads).
Main applications:
- Automotive steering pins
- Machine tool spindles.
8. Thrust roller bearing

Thrust roller bearings are designed for shafts that experience mainly axial loads. It can also bear combined loads in the axial direction, but the load in the axial direction should not exceed 55% of the total load.
This type of bearing has a lower coefficient of friction, higher operating speed and self-aligning capacity. Type 29000 rollers are asymmetrical spherical rollers that reduce relative slip between rollers and raceways during operation and are large in diameter and length.
These bearings have a high load capacity due to the large number of rollers and are typically oil lubricated. Low speed operations can be lubricated with grease.
Main applications:
hydraulic generators, crane hooks, etc.
9. Cylindrical roller bearing

Cylindrical roller bearings are typically guided by two ribs in a bearing ring. The cage roller and guide ring form a separable assembly that can be separated from the other bearing ring. This type of bearing is easy to install and disassemble, especially when the inner and outer rings need to have an interference fit on the shaft and housing.
These bearings are mainly used to support radial loads, but single row bearings with ribs on the inner and outer rings can support small constant axial loads or large intermittent axial loads.
Main applications:
Large engines, machine tool spindles, axle boxes, diesel crankshafts, automobiles, transformers, etc.
10. Four point contact ball bearing

This type of bearing is capable of supporting radial loads and bidirectional axial loads. A single bearing can replace a combination of angular contact ball bearings, both front and rear. It is ideal for supporting pure axial loads or loads with a large axial load component.
This type of bearing forms one of the contact angles under axial loads in any direction, so that the seal and balls are always in three-point contact on both sides of the contact line.
Main applications:
- Aircraft jet engines
- gas turbines
11. Cylindrical roller thrust bearing

It consists of a washer-shaped race ring (shaft washer and seat ring), cylindrical rollers and a cage assembly. The cylindrical rollers have a convex surface, resulting in uniform pressure distribution between the rollers and the track surface. This type of bearing can withstand unidirectional axial loads and has high axial load capacity and strong axial rigidity.
Main applications :
include oil platforms and iron and steel machines.
12. Needle thrust bearing

The needle bearing can be separate or integrated. The separate bearing consists of a raceway ring, needle roller and cage assembly which can be combined with a stamped thin raceway or a thick cut raceway. On the other hand, the integral bearing is composed of a precisely stamped race ring, needle roller and cage assembly and can support unidirectional axial loads.
This type of bearing takes up little space, making it ideal for compact machine designs. Most needle bearings consist of only the cage and needle roller components and use the shaft and housing mounting surface as the raceway surface.
Main applications:
Automotive transmissions, scarifiers, machine tools, etc.
13. Thrust tapered roller bearing

This type of bearing has a spherical roller (the larger end is spherical), which is precisely guided by the ribs of the raceway ring (shaft ring and seat ring).
The design aligns the apex of each tapered surface of the shaft washer, the roller surface of the saddle ring, and the bearing surface of the rollers to intersect at a single point on the bearing centerline.
Unidirectional bearings are capable of supporting unidirectional axial loads, while bidirectional bearings are capable of supporting bidirectional axial loads.
Main applications:
Unidirectional: Cranes, hooks on oil platforms.
Bidirectional: Rolling necks on rolling mills.
14. External self-aligning ball bearing with housing

External self-aligning ball bearings with housing consist of external self-aligning ball bearings sealed on both sides and cast (or stamped steel plate) bearing housings. The internal structure of the outer self-aligning ball bearing is similar to that of a deep groove ball bearing, with the exception that the inner ring is wider than the outer ring. The outer ring has a truncated spherical outer surface, allowing it to self-align with the concave spherical surface of the bearing seat.
These bearings are commonly used in industries such as mining, metallurgy, agriculture, chemical, textile, printing and dyeing, transportation machinery and others.