Mat foundations are also known as slab foundations. These are thick concrete slabs placed on the ground as the base of the structure. Mat foundations are constructed for various occasions, such as construction of buildings, bridges, towers, etc.
If we are talking about shallow foundations, the last option is a slab foundation.
With increasing axial loads on the structure or due to poor soil conditions, the area of foundations (isolated, combined, strip foundation etc.) must be increased.
Increasing the dimensions of the foundation causes the stress balls to overlap, creating a weak zone. With this in mind, we selected slab foundations.
What is a Mat base?
A mat foundation is not always a flat slab placed on the ground to provide support for the superstructure. There are different versions depending on the type of load application.
If the loads acting on the slab foundation are smaller, we build a flat slab. However, as the load increases, various methods are introduced, which will be discussed in this article, to increase the stiffness of the plate.
Additionally, we could use slab foundations to support buildings up to 10 stories high.
Furthermore, an increase in axial loads leads to higher construction costs. You could even build a pile foundation above a certain level.
Types of treadmill bases
The categorization of mat foundations is based on the modifications made to the flat slab.
An addition to the foundation plate serves to improve the bending stiffness of the foundation.
The depth of the slab foundation is increased, especially in the support positions, to be able to absorb the high bending moments and shear forces.
The following categorization discussed in the article Types of Foundations For more detailed information about this, you can contact us.
- Flat plate
A thick concrete slab placed on the ground as a base is a flat raft.
Other than the concrete shear walls, there are no projections to stiffen the mat foundation.
- Flat slab foundation with under-column thickening
The increase in column axial loads leads to an increase in flexural and shear reinforcement.
This leads to an increase in construction costs. In addition, at a certain level it is necessary to increase the thickness of the slab foundation.
If we increase the thickness of the entire treadmill base, it will not be an economical solution.
Therefore, we increased the thickness of the treadmill base below the supports. Since the projection is below the flat plate, construction can be difficult.
Fix the reinforcement, seal, etc. It may not be that easy.
- Thickening of the flat slab foundation above the support
The protrusion above the flat plate is also the same as the protrusion below the plate.
The construction of the plate projection above its surface is very simple. But this is only possible if we do not use the license plate or if the remaining distance is sufficient for the purpose to be used.
- Beam and slab foundation
A further increase in the axial load of the column cannot be supported by the flat plate or the flat plate projections. Beams are provided to strengthen the foundation.
Using beams, the panel thickness can be significantly reduced.
- Cellular slab foundations
A further development of the beam plate is the cellular plate foundation. In this type of foundation we also place the upper slab.
This further increases the rigidity of the carpet base.
- Pile slab foundations
Plié slab foundations are built in tall buildings, in situations where the pile cannot be anchored in the rock and when the final support of the pile is insufficient, etc.
Planning and constructing a pile slab foundation is a complex process.
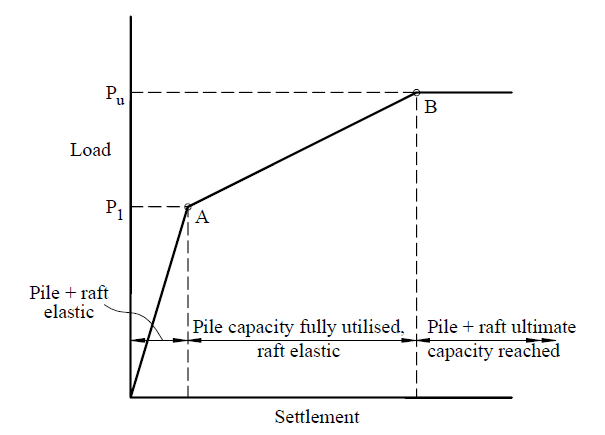
First, the pile takes on the load and then begins to share it with the foundation slab.
Once the piles are fully mobilized, the raft begins to fully absorb the load. Ultimately, the raft carries all the load.
The following figure shows the load calculation curve.


For more information, see the published article on pile slab foundations.
The following image shows the different types of slab foundations available for your projects.


The selection of the type of blanket foundation is based on the load acting on the foundation system.
Design of a mat base
There are basically two methods for building slab foundations.
- Conventional Methods – Use manual calculations and graphs
- Finite element analysis methods – Use a computer package to solve the design
Sizing of slab foundations using conventional rigid method
When designing mat foundation using conventional rigid construction method, the following steps can be followed.
- Calculate the total load applied to the mat foundation
- Calculate the pressure under each column, taking into account the eccentricity of the load. Axial stress and bending stress due to the eccentricity of the load center are considered to determine the pressure under each column.
- Check whether the allowable liquid pressure is greater than the applied pressure.
- The carpet is then divided into strips according to your arrangement.
- Determine the bending moment and shear forces.
- Determine the effective depth of the foundation. This can be done based on diagonal tensile shear near different columns.
- From the bending moment diagrams calculated above, determine the positive and negative bending moments per unit width.
- Calculate the area of reinforcement per unit section width
In addition to this procedure, there are other methods, such as Approximately flexible method analyzing and sizing slab foundations.
Finite element analysis methods
With the finite element analysis method, the flexible behavior of the soil is taken into account in the structural analysis. With this method, the soil is modeled and its behavior is included in the analysis and design.
There are different methods of shaping the floor.
We can model the soil under the foundation with its material properties. Software like Plaxis can be used for this purpose. In this type of analysis it is very important to select the correct material model for the soil. If we don't consider the idealization correct, we will end up with wrong results.
Additionally, we could use software like SAFE Foundation Analysis and Design to determine bending moments and shear forces.
The soil can be modeled as a surface spring. Surface springs can be calculated as given in the Bowels Foundations Analysis and Design Book.
The spring area is the underground Reaction of the ground. There are many methods for calculating the background response. In this article we will discuss the simplest method described in the book Bowels Foundation Analysis and Design.
Source area = SF x 40 x BC – for settling 25 mm of the slab foundation
Where SF is the safety factor taken into account to calculate the allowable load capacity and BC is the allowable load capacity.
The above equation applies to a slab foundation settlement of 25 mm. Deviations beyond this value may lead to incorrect results.
Therefore, the above equation needs to be adjusted based on the settlement specified in the geotechnical investigation report to determine the allowable bearing capacity or based on the calculated settlement.
Source area = SF x (1000/settlement) x BC
Once the ground surface extents or subsoil response of the soil have been calculated, these can be applied to the computer model created using appropriate software.
After loads have been applied to the column positions, foundation analysis can be performed. The bending moment and shear forces can then be determined.
The reinforcement calculation is carried out according to the analysis results.
Special note on analysis and construction of slab foundations
- It is recommended that computer-aided software be used for the analysis and sizing of blanket foundations.
- Modeling and idealizing the real behavior of the foundation must be done with great care and caution.
- The ground can be shaped with surface springs. It's the underground reaction. We define the background reaction in the software and assign it to the computational model.
- Subsurface response can be estimated using several available methods. This can be based on the SPT value, test results, soil bearing capacity or any method.
- The foundation can be modeled together with the superstructure to match the behavior of the superstructure and the foundation. The deformation of the foundation can affect the superstructure, and the behavior of the superstructure can be included in the foundation deformations.
- Furthermore, the foundation could also be a model without a superstructure. The column load can be applied directly to the model. Shear walls Inclusion in the model could be considered.
- Mat foundations must be designed to withstand bending and shear forces.
- The foundation must be tested for vertical shear and punching forces. The amount of punching can be determined according to the relevant standard under which the construction is carried out. The article on drilling shears For the construction and definition of the cutting scope, reference may be made to the project.
- Particular attention must be paid to shear forces during construction. The requirements for shear connections must be checked and, if necessary, shear connections must be specified as calculations.
- The design of a pile slab analysis is a complex process and must be carried out taking into account the relevant published literature.
Rug base construction
The construction of the mat foundation is also carried out with great care and in compliance with quality control and assurance.
Let's discuss the construction process step by step.
- Excavation work for slab foundations
Before construction begins, a decision must be made about the excavation and excavation that will support the system. Depending on the type and depth of construction, a decision must be made on the type of excavation support system.
The Excavation for Foundation article More information on the design and construction aspects of excavation systems can be found here.
More articles Design of excavation safety systems and sheet piling retaining walls For practical examples of earth anchoring systems you can consult.
- Water resistance
In general, all mat foundations are waterproofed. All slab foundations are waterproofed as they are generally constructed below the finished ground level.
Installing a waterproofing membrane protects the foundation from moisture or moisture. Additionally, the movement of water through the concrete also impedes the seal.
The article about the different types of seal Knowledge of the details used in construction can be called knowledge of the arrangement of waterproofing membranes.
- Standing water
In the slab foundation there are construction joints, movement joints, expansion joints, etc. They need to be sealed to prevent water movement through the joint.
The articles Construction Joints And Types Of Concrete Joints For more information about joint details and joint treatment methods, please contact us.
Joint barriers are installed at construction joints and movement joints. Depending on the type of joint, the type of joint barrier to be installed changes.
For construction joints, a water stop is typically placed in the middle of the slab. (See Water Resistance article for typical details). Mild steel or PVC water barriers are typically used in these types of joints.
Joint tapes are provided on movement and expansion joints. (See Water Resistance article for typical detail)
For more information, see the article Still water .
- Reinforcement
There are essentially two types of reinforcement that can be observed in a slab foundation.
These are flexural reinforcement and shear reinforcement.
The flexural reinforcement is tied normally and the shear reinforcement is placed in the column mainly according to the shear requirements. Shear links must meet design requirements. The distribution of shear connections in both directions of the column must meet the design requirements.
- Number of doses
Depending on the type of construction and design requirements Concrete occurs in various pours.
Multiple pours do not necessarily need to be carried out, but single-pore concrete can also be used if the foundation dimensions are smaller and if appropriate resources, such as personnel and materials, are available.
For a large slab foundation, the number of concreting steps depends on the contractor's ability to deliver and place the concrete.
Furthermore, thermal effects are taken into account when deciding on the concreting order. Firstly, the order of concreting is determined so that the thermal load caused by subsequent concreting is minimized. However, this cannot always be avoided. We have to take this into account in planning.
Furthermore, the concreting order is planned for each individual concreting in order to avoid cold joints during concreting. Based on the setting time, the concrete must be poured before it begins to set.
- Temperature control
The increase in concrete temperature, the greater temperature gradient and the temperature difference between the core and the surface are important factors to be considered in temperature control.
In practice, we maintain the maximum increase in concrete temperature due to heat of hydration at 70 degrees Celsius to avoid delayed ettringite formation.
However, by adding fly ash, this value can be increased to 80 degrees Celsius or more. The maximum temperature also depends greatly on the type of cement.
Therefore, it is always advisable to maintain the temperature at around 70 degrees Celsius or below as we cannot observe what is happening in the concrete.
Model tests can be used to verify the temperature rise in concrete due to heat of hydration. Furthermore, it offers other advantages, such as deciding the thickness and type of materials to use as formwork.
The construction must use the same material that was used in the model test and whose temperature rise is acceptable. No changes can be made to the material or material thickness.
The addition of fly ash acts as a filler in the concrete and reduces the cement content. Furthermore, it reduces the increase in temperature during the hydration process.
Generally, one tries to keep the fly ash addition in the range of approximately 20% to 35%.
Furthermore, the use of fly ash in concrete improves the Workability of the concrete .
The other methods of concrete lime temperature are listed below.
-
- Limit installation temperature. Normally the installation temperature is limited to 30 degrees Celsius. However, to limit the temperature rise, the temperature must be reduced further.
- To slow the temperature rise, add ice or ice water.
- Pour the concrete at night
- Add fly ash
- Combine the aggregates
- Use low temperature cement
- Pump concrete from pipes embedded in the concrete.
Similar methods could be used to control the temperature rise of concrete. Through control, we could avoid delayed ettringite formation due to increased heat of hydration, as well as thermal cracking in concrete due to temperature differences and high temperature gradients.