It is very important for civil and civil engineers to know soil types and their geotechnical parameters. When designing or building, it is very important to know the types of soil available on the construction site.
There are different soil classifications and different soil classification methods based on the parameters listed below.
The classification of soils is mainly based on their technical properties, such as particle size distribution, yield limit and plasticity limit.
There are two main classification systems.
- AASHTO
AASHTO is an acronym for American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials.
AASHTO rating systems are primarily used in highway construction and not in civil engineering.
- ASTM
ASTM stands for American Society for Testing Materials.
The unified soil classification system according to ASTM standards
ASTM D2487-17: Standard Method for Classifying Soils for Engineering Purposes (Unified Soil Classification System) is used
In addition to the points mentioned above, let's look at the main types of soil available.

 Image from the internet
Image from the internet
Different types of soil
Essentially there are the following types of soil:
- gravel floor
- volume
- Silty soil
- sand
- Peaty soil
- Limestone soil
- Clay soil
Let's discuss each soil type in detail.
gravel floor
Gravel is a loose collection of rock fragments as defined on Wikipedia.
Gravel is formed by sedimentation and erosion of rock. The size of gravel starts from 2 mm and can go up to 200 mm and more. Gravel can be classified based on particle size distribution as follows.
| classification | Particle size (mm) |
| Fine gravel | 2-6 |
| Medium gravel | 6-20 |
| Coarse gravel | 20-60 |
| Very thick gravel | 60-200 |
| stones | >200 |
 
|
 
|
There are other types of gravel whose particles are clearly separated from the clay. Generally, gravels are rounded materials that we can find near gravels, canals, etc.
Gravel is one of the most important building materials in the world. It is used together with sand in the production of concrete. Additionally, gravel is often used in road construction.
Clay or clayey soil
Clay is a fine-grained natural soil material that contains clay minerals.
The particle size of clay is generally less than 0.002 mm.
The main characteristics of clay can be listed below.
- Very sticky and rolls like plasticine when wet
- Due to its sticky nature, clay can store more water than other types of soil
- Clay swells when wet and shrinks when dry
Clay is a useful building material, but it can sometimes be harmful when building foundations.
For example, in the construction of rockfill dams, a layer of clay is used to retain water in the reservoir. Clay with a certain permeability allows a very small amount of water to pass through. However, it acts as a barrier to water movement.
The same method is also used for earthen dams. For more information, see the article Types of dams could be forwarded.
 
|
 
|
Let's discuss: clay is not an easy building material.
What happens if there is a layer of clay under the foundation?
There is irrigation water in the saturated clay. As the foundation is built or the clay layer is loaded with a slab, the stress exerted on the clay layer increases.
By applying additional tension, the irrigation water pressure in the clay layer increases because the hydraulic conductivity of the clay is very low. It will take some time for the excess irrigation water pressure to dissipate. As the water pressure dissipates, it is gradually transferred to the ground. This gradual increase in effective stress in the clay layer leads to settlement over time and is known as consolidation.
When planning, it is important to pay attention to when the soil under the foundation turns into clay soil. There are several methods for controlling foundation settlement or for constructing a building without Consolidation Processing .
- Preload
To allow the clay to settle, a similar or different pressure could be applied, calculated based on the allowable settlement and prestressing time.
This occurs for a period based on the consolidation agreement.
- Assembling the structure on the pile foundation
In existing clayey soils, other types of soil such as peat, silt, etc., which are compressible under load, may also be present.
They could move sideways when stressed. Therefore, the preload option must also consider the magnitude of the load.
However, if we build the structure on a pile foundation, such problems will not arise. In this case, it is more advisable to erect the slab as a suspended slab.
- Soil stabilization method
Clay soils can be stabilized with a mixture of slaked lime and cement lime.
Binder mixtures such as lime, cement, blast furnace slag, fly ash and gypsum are now frequently used in construction to improve clay soils.
Sludge
Silt is a granular material with a particle size between clay and sand.
Sludge particle size is generally in the range of 0.002 – 0.005 mm.


Some of the most important aspects of slime are as follows.
- Sludge is usually mixed with bulk and sand or sediment mixed in suspension with water.
- Silt consists of rocks and mineral particles
- Sludge deposits are created by the transport of ice, water and wind.
Silt is special compared to other types of soil. Let's look at why we need to know about silt in structural and geotechnical projects.
As explained above, slime also has different states. When silt mixes with sand it is called silty sand, and when silt mixes with clay it is called silty clay. Clay silt can cause problems, as explained above.
Due to its fineness, silt tends to retain moisture and does not dry out like other types of soil due to poor drainage. This can cause the settled soil to expand and push against the foundation, causing unfavorable conditions.
sand
Sand is a granular material consisting of finely dispersed rocks and mineral particles.
Generally the particle size is in the range of 0.05 – 2.0 mm. Sand is finer than gravel and coarser than silt.
Sand is the most used construction material in the world because most works require it from other types of soil.
The most common component of sand is silica or silicon dioxide. The sand comes in the following form:
- My sand
- River sand
- Sea sand
- Manufactured sand
Peat or peat soil
Peat is a collection of decaying vegetation and organic matter.
Peat occurs when plant material fails to rot in acidic, anaerobic conditions.
From an engineering point of view, these are peaty soils with a higher proportion of organic matter.
At 43.54%, North America's peat area is the largest of the world's peat areas. In Asia and Europe the proportion is 28.08% and 24.02%, respectively.
The bulk density of peat is in the range of 800-1200 kg/m 3 compared to other minerals in the range of 1800-2000 kg/m 3 This is mainly due to the lower specific gravity and higher water holding capacity.
It has poor consolidation properties and cannot be easily compacted to support foundations. Furthermore, due to the compressibility of the material, greater settlement occurs in the foundations.
Furthermore, due to the greater fluidity of the material, there is the possibility of lateral movement under load, which can lead to excessive settlement of the foundation.


When there are layers of peat in the construction, we have two options.
- Completely remove the peat and replace it with suitable material such as sand, quarry dust, etc.
- Conduct peat construction with some improvements or precautions.
How do you build if you find peat?
Let's discuss how we can build with peat on site, as this is quite demanding.
-
Use the acceleration method for consolidation
- Preload : In short, a similar or slightly higher load is applied to the soil over the calculated time until the expected settlement is reached.
- Stage construction : To avoid ground failure, preloading can be done gradually during preloading.
- Vertical drains : provide to shorten drainage routes.
-
Soil improvement techniques
- Stone pillars
Stone pillars consist of compacted, unconsolidated stone fragments (gravel) or sand. They serve as a supporting element that penetrates the weak soil layer.
-
- Cement columns
Cement columns are made by mixing cement and peat soil at the construction site or by making a prefabricated column outdoors and inserting it.
-
- Soil Columns
Soil columns are made from imported fill material, unlike cement columns which are made from locally grown materials. In general, the fill material consists of fine-grained aggregates. A certain amount of cement is also used as a binder in soil columns.
-
- Geopier
Geopire is an intermediate foundation system consisting of very rigid aggregate pillars reinforcing weak, compressible peat and highly organic soils. The geopier must completely penetrate the peat and highly organic layer.
-
- Surface reinforcement
Surface reinforcement can be done with geotextiles, geogrids, wooden or bamboo mattresses, concrete slabs, etc.
-
- Vacuum Overload and Bias
-
Soil stabilization methods
- Peat is mixed with binding agents such as cement by mechanical mixing when the mass is stabilized.
- Use cement as a binder and silica fume as an additive.
- Stack method
Pile foundation can be used as an alternative to the shallow foundation method.
Limestone soil
Limestone soils largely consist of calcium carbonate from sediments.
This soil is alkaline with a pH in the range of 7.1-10.
In areas with limestone soil deposits, well water is hard.
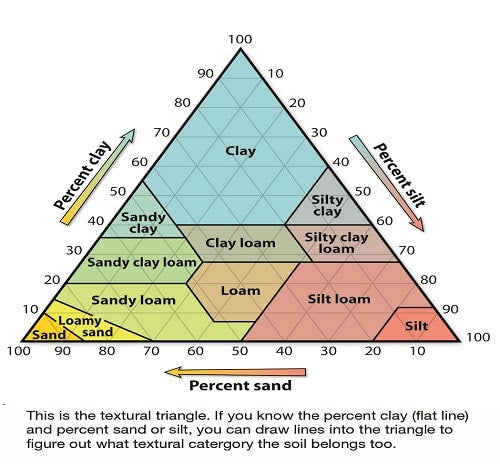
Clay soil
Clay soil is evenly mixed with sand , silt and clay.
Clay soil has excellent structure, good drainage quality, ability to retain moisture, etc. and is very useful in cultivation.
Clay soils also come in clay loam and sandy loam forms.
In addition to the soil classification method described above, soil types can be classified in the following ways.
Classification of soil types as a type of material
- Organic soils
Organic soils containing organic matter.
Organic soil contains decaying plant material, microorganisms, worms, etc.
- Inorganic soils
Means that do not contain organic substances. And they have a neutral pH value because they are free of impurities
Classification of soils by formation
- residual soil
- Alluvium or sedimentary soil
- Transported soil
- Aeolian soil deposits
- Glacier floor
- Lake bottom
- ocean floor
Let us discuss some of the above points that are important for civil engineers.
residual soil
Residual soil is the material created by the weathering of rock.
The nature of the weathered soil depends on the source rock.
Contains clayey or silt materials, silt, sand, etc.
Alluvial deposits
Alluvial deposits are material deposits along rivers.
These types of soil contain silt, sand, clay, gravel , organic substances etc.