To ensure that the reinforcement meets design specifications, testing must be carried out.
In this article we will discuss the order of tests and the different tests available in the build.
Why do we need to do booster testing?
Reinforcement is made from raw steel and is used in the structure to absorb tensile and compressive loads.
If the reinforcement cannot withstand the required load, it can lead to structural failure. In the project we define the resistance of the reinforcement as Characteristic strength. This is the yield point.
In addition to the characteristic stability of the curve, several other tests must be carried out.
- Traction test
- Back bend test
- Chemical analysis
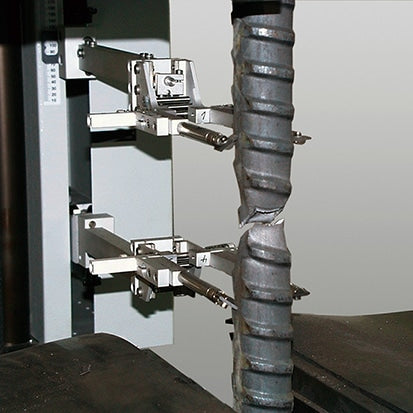
Traction test
The most common type of test performed in reinforcement testing is the tensile test.
The tensile strength and yield strength of reinforcing bars are of great importance for construction.
The reinforcement must have the characteristic resistance assumed in the design. During construction the strength of the reinforced steel was checked using randomly collected samples.
One specimen per 30 t with a minimum of three specimens per nominal diameter is the sampling criteria specified in BS 4449:2005.


This test determines the following parameters.
- Yield resistance characteristic of reinforcement
- Tensile strength of reinforcements
- Percentage elongation
- mass per meter
According to BS 4449, it is checked whether limit values have been exceeded.
Back bend test
This test examines the possibility of surface cracks forming in the reinforcement during bending.
The reinforcing steel is bent and twisted and checked for any cracks on the surface.


The following procedure must be followed when carrying out the bending test in accordance with BS 4449:2005+A2:2009. Backbend testing is also a common test performed in rebar testing.
- Bend the test pieces at an angle of 90 0 around a mandrel with a diameter no greater than that indicated in the table below, age the test piece and then bend it at least 20 0 .
- If there are no visible signs of breaks or cracks, the sample can be accepted.
Table: Chuck Diameter During Reverse Bending Test
| Nominal diameter (d) mm | Maximum chuck diameter |
| ≤ 16 | 4T |
| >16 | 7 days |
Chemical analysis
This test checks the chemical composition and carbon equivalent value.
For more information about boosting, see the following articles.
- Tensile strength of reinforcing bars
- Reinforcement rib – surface geometry of reinforcement bars
- Removing rust from steel reinforcement – a practical approach