Tall building requires a system to absorb lateral loads so that the structure remains stable under lateral loads. Buildings are mainly subject to lateral loads caused by wind and earthquakes.
As buildings get taller, the horizontal loads placed on them increase. Furthermore, the effect of lateral load becomes more severe as the height of the structure increases.
The following types of loads may occur during construction planning.
- wind loads
- Seismic loads
- Water pressure
- Earth pressure
- National cargo
To support lateral loads, different structural systems are used depending on the type of building. Of these methods, the following are commonly used in buildings.
- Frame
- Preparation
- Shear walls
- Wall-structure interaction
- Support systems
- Tuned mass dampers (TMDs)
- Buckling resistant braces (BRBs)
- Structural wall systems
- Hybrid systems
- Outer membrane systems
- Sliding Friction Damper
Frame
If there is a building, the structure is usually made of a frame. Frame structures exist in most buildings.
Interconnected beams and supports form the structure. If the connection between the beam and the column is rigid, the frame can transfer lateral loads to the foundation.
For this reason, rigid frames are considered a lateral load support system. Support column frame structures can be used as a system to support lateral loads up to a height of 15 to 20 stories.
Preparation
Straps are mainly used in steel structures to improve resistance to lateral loads. Furthermore, they are also installed in concrete buildings to improve resistance to lateral loads.
The following types of bracing are used in steel buildings.
- Individual diagonals
- Cross braces
- K Keys
- V keys
This type of bracing resists lateral wind loads, earthquakes and national loads.
The article Types of Structural Forms for Tall Buildings Discuss bracing in more detail.
Wall disk
A concrete wall constructed from the base level to the top of the building is considered a shear wall. Supports lateral loads and vertical loads exerted by the structural element connected to it.
The shear wall alone can support the lateral load of buildings of about 20 stories. Furthermore, the contribution of the cadre could also be taken into account.
Shear walls must be fixed at base level to effectively support lateral loads.
The stiffness of the shear wall is the key factor affecting the shear load resistance of the wall. The length and width of the wall are the main factors that affect the stiffness of the walls.
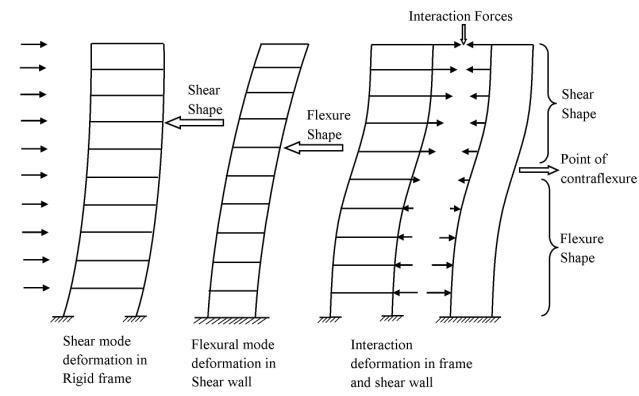
Wall-structure interaction
As explained above, the shear wall can support lateral loads to a certain extent. At a certain level, we need a different method of support to achieve the required load capacity.
Due to the limitations of the floor we cannot continue with the shear walls as we want the necessary rigidity. The most important task is to build a structure that provides the necessary services. Therefore, designers need to find alternatives to improve structural capabilities.
Considering wall-structure interaction is one of the best ways to utilize the inherent capacity of structural systems.


Considering this interaction significantly improves the structural capacity compared to considering only the shear wall.
Support systems
Cantilever systems are horizontal structural elements (cantilevers) that connect the building core to exterior columns or walls. These systems distribute lateral loads over the entire height of the building.
Benefits :
- Efficiently reduces building sway.
- Suitable for tall and thin buildings.
- It can improve overall structural performance.


Tuned mass dampers (TMDs)
TMDs are mechanical devices placed inside the building to counteract fluctuations caused by wind or seismic forces. They consist of a mass (often a large pendulum) that moves in response to lateral movements, mitigating the building's oscillation.
Benefits :
- Effective in reducing occupant discomfort.
- Can be retrofitted into existing tall buildings.
- Improve building stability without increasing structural rigidity.


Buckling resistant braces (BRBs)
Buckling-resistant struts are a type of support structure that provides lateral stability by dissipating seismic forces through energy absorption mechanisms. These brackets consist of a steel core surrounded by an outer shell. During an earthquake, the core remains stable while the casing gives way and absorbs seismic energy.
Benefits :
- Exceptional seismic performance.
- Predictable and controllable flow behavior.
- Minimal permanent deformation after an earthquake.
Structural wall systems
Load-bearing wall systems utilize load-bearing walls in the longitudinal and transverse directions of the building. These walls resist lateral loads by transferring them to the foundation.
Benefits :
- Simplicity and cost-benefit.
- Suitable for mid-rise buildings with repeating floor plans.
- Provides resistance to lateral load and gravity.
Hybrid systems
Hybrid side load handling systems combine two or more of the above methods to optimize performance. For example, a combination of moment frames and shear walls can provide greater lateral strength while allowing architectural flexibility.
Benefits :
- Tailor-made solutions for specific project requirements.
- Synergies between different systems can improve the overall performance of the structure.
- Suitable for complex building geometries.
Outer membrane systems
In some tall buildings, the exterior cladding or curtain wall system may be designed to act as a membrane that resists lateral loads. These systems transfer lateral loads to the building core or other structural elements.
Benefits :
- It allows for an elegant and uninterrupted architectural façade.
- Structural and architectural elements are integrated for efficiency reasons.
Sliding Friction Damper
Sliding friction dampers are passive energy dissipation devices installed in the side load suspension system. They absorb energy allowing controlled sliding between structural components during seismic events.
Benefits :
- Effective in reducing seismic forces and drift.
- Minimum visual impact on the aesthetics of the building.
- It can also be retrofitted into existing structures.
The article Types of Structural Forms for Tall Buildings Also discuss the structural systems used in tall buildings to support subsequent loads.