Building a foundation is not always a challenge unless the building soil is weak. Compared to other types of foundations such as driven piles and cast-in-place wide piles, construction can be carried out very easily. However, if weak soil is found, construction can be challenging.
What is foot?
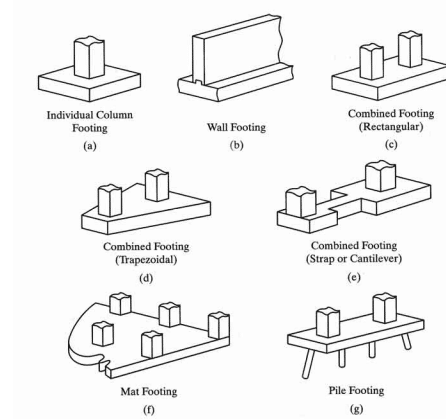
A footing is a type of foundation used to support a structure. It is built on soil with sufficient bearing capacity.
There are different types of foundations and they are selected based on soil conditions, structural requirements and foundation construction requirements.
The different types of foundations include individual foundations, combined foundations, strip foundations, strip foundations, etc.


The type of soil and load capacity influence the construction of the foundation
The foundations are designed so that the pressure applied at the serviceability limit state does not increase the allowable load capacity.
Soil types have a significant impact on the design and construction of foundations. Weak soil reduces bearing capacity and makes construction difficult.
If the soil does not have the necessary bearing capacity to withstand the loads that will occur, the soil must be improved. This is a challenge for the contractor and also increases construction costs. Furthermore, the groundwater level has a significant impact on the bearing capacity of the soil and the construction of the foundation.
Foundation size and dimensions
Foundation dimensions are based on the allowable load capacity and applied operational load. The greater the applied load, the greater the area of the foundation. The greater the allowable load capacity, the smaller the size of the foundation.
The foundation area can be calculated using the following equation.
Foundation area = operational load of the column / allowable load capacity
The thickness of the foundation depends on the loads in the ultimate limit state. The flexural design and shear design under which we drill shear and vertical shear are the parameters considered for the final thickness of the foundation.
Foundation digging depth
It is very important to determine the correct excavation depth for foundation construction. When deciding the depth of the foundation, some important factors must be taken into consideration.
When calculating the depth of the foundation, many factors must be taken into account, as explained below. Additionally, the minimum foundation depth can be calculated using the Rankine formula. The article, Foundation Depth For more information, see this page.
- Soil type
There are different layers of soil and we need to place the base in the right layer of soil that will not deteriorate. The upper layers of the soil are exposed to deterioration. Therefore, we need to excavate to a depth of about 900 mm to avoid these layers of soil.
This should be decided on site in consultation with the engineer.
- Geotechnical recommendation
Geotechnical investigations are carried out to determine the allowable bearing capacity. The soil test report will indicate the depth to which excavation should be limited.
- Groundwater level
It is always advisable to avoid groundwater when constructing the foundation. It influences the allowable bearing capacity of the soil.
Furthermore, this can also affect the durability of the structure. Most importantly, it is very difficult to build the foundations if you have to dig above the water table.
If a ground survey recommends or requires excavation above the water table, backfilling above the water table can be accomplished using materials such as sand and quarry dust, or ABC.
Procedure/steps to build the foundation
- It is necessary to excavate to the correct depth indicated on the construction drawing.
- If you have done additional excavation and the soil conditions are acceptable, a foundation can be placed at this height. If refilling is necessary, the backfill soil must be sufficiently compacted.
- The table is then set. Grade 15 concrete is typically used. The thickness of the screed is between 50 and 100 mm. It depends on the nature of the soil and must correspond to the approved drawings.
- The foundation reinforcement mesh must be placed over the covering blocks.
- Reinforcement coverage is generally 40-50 mm. Depending on terrain conditions, the reinforcement coverage can be increased up to 100 mm to provide protection against chemical attack. For marine structures, reinforcement coverage is 75–100 mm.
- The concreting process takes place after fixing the side walls.
- Waterproofing is not common in foundation construction. However, if the structure is at risk of corrosion, sealing can be done as recommended by the civil engineer.
Soil improvement in foundation construction
We verified that the land is not suitable for construction. If weak soil is found, building the foundation will be a challenge. In these situations, it is advisable to conduct a soil survey and obtain a design and construction recommendation.
There are several methods for improving soil. For more information, see the following article.
- Ground improvement for low-rise buildings
- Soil improvements
- Soil stabilization
Some other important factors to consider when building foundations
- Match
Staking is carried out in accordance with issued construction plans.
- Excavations
Foundation excavation work must be carried out in accordance with construction drawings. The depth of excavation should be as specified and advice from an engineer should be sought if necessary.
- Concrete hardening
Concrete must cure for at least 7 days. An appropriate curing method must be used during construction. For more information about healing, see the following articles.
-
- Factors that affect concrete curing time
- Concrete hardening