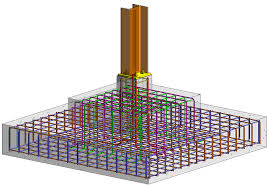
The details of rebar for foundations are not as complicated as other types of structural elements. This article mainly covers the reinforcement arrangement of combined foundations, strip foundations, etc.
We design foundations for bending and shear; Vertical line punching and shearing and reinforcement are provided accordingly.
Normally the details of each foundation reinforcement do not include shear connections, because we normally try to design them without shear connections by controlling the depth of the foundation. If it appears that we need to provide shear connections to the foundation, we increase the thickness of the base around the pillar as shown in the figure below to increase the shear capacity.


However, depending on the applied load and the geometric properties of the foundation, the combined foundation reinforcement details sometimes also include shear connections.
Let's discuss some of the important details and detailing rules for foundation reinforcement. This article is mainly based on this BS 8110 Part 01.
Details and Detailing Methods for Foundation Rebar
Let's examine them one by one.
- Reinforcement distribution
In general, we distribute reinforcement needs evenly. However, as the axial load increases, we need to increase the area of reinforcement near the column where the bending moments and shear forces are greatest.
If I C > (3c/4 + 9d/4), two thirds of the required reinforcement must be concentrated in a zone that extends from the axis of the column to a distance of 1.5d from the face of the column.
Otherwise, the reinforcement can be evenly distributed throughout l. W .
here c is the width of the support, d is the effective depth, l C – half the distance between the column centers (for multiple columns) or the distance to the edge of the block (whichever is greater)
- Crack Control Reinforcement
Generally, crack control reinforcement is not included in the foundation reinforcement details. The unreinforced surface is always under pressure when loaded. However, if the design requires it, we must provide it.
We may consider providing crack control reinforcements in the following cases. This information is just a guide. We need to review requirements during planning.
-
- If the thickness of the foundation exceeds 500 mm, we can check for cracks. The section crack width can be considered and limited according to the design or specification requirements. We normally limit the crack width to 0.3 mm for normal structures.
- As the thickness of the foundation increases, reinforcement can be added to prevent cracking of the immature concrete. The article, early thermal cracking More information and methods for calculating reinforcement requirements based on design crack width can be found at.
- Furthermore, the use of high quality concrete -similar C40 can also cause concrete cracking at higher concrete thicknesses due to the heat of hydration.
- Shear Connections
Construction scissor connections must be provided as hooks. The typical hook arrangement is as follows. The hook distance in both directions must meet the design requirements.


These types of connections are only provided when top reinforcements are present and are required by the design.
- Typical foundation reinforcement details obtained for the standard structure detailing method through IStructE are as follows. This information has been provided in accordance with Eurocode 2 .