Settlement of low-rise structures can be divided into two categories depending on the period of occurrence. Settlement of a structure cannot be avoided, even if we build the structure on rock.
In pile construction In addition, some settlement may occur as the load increases due to design errors.
Buildings constructed on the ground will inevitably settle and the settlement must be within the limits considered in the foundation design recommendation.
The designer's responsibility is to maintain uniform settlement throughout the building, as varying settlement causes problems.
The soil acts as a source which is called through underground reaction in the calculations and carries out the vertical movement of the structure by applying loads. As explained above, this can be done in two steps as described below.
- Elastic settlement or instant settlement
- Consolidation processing
In this article we discuss elastic settlement or immediate settlement of shallow foundations using a practical example.
Elastic laying of shallow foundations
Elastic settlement occurs during the construction of the structure and immediately after its construction.
However, consolidation occurs over time. It is created by reducing irrigation water pressure in saturated clay. Consolidation occurs in two phases, namely primary and secondary consolidation.
This article explains how to calculate elastic settlement. The method to calculate elastic settlement based on elasticity theory is explained using a practical example for better understanding.
Elastic settlement calculation method
Elastic settlement, If, according to the book Principles of Foundation Engineering
S t =q 0 (αB')((1-μ 2 S )/E S )EU S EU F
Where,
P 0 – Net pressure in the foundation
μ S – Poisson’s Ratio of the soil
E S – Average modulus of elasticity of the soil under the foundation, measured from Z=0 to approximately Z=4B
B' – B/2 for the center of the foundation and 'B' for the corner of the foundation
EU S – Form factor (Steinbrenner, 1934)
EU S =F 1 + ((1-2μ S )/(1-μ S ))F 2
F 1 = (1/π)(A 0 + A 1 )
F 2 = (n'/2π) tan -1 A 2
A 0 = m'ln { ( 1+(m' 2 +1) 0.5 )(M' 2 + n' 2 ) 0.5 } / {m'(1+(m' 2 +n' 2 + 1) 0.5 )}
A 1 = ln { (m' + (m' 2 +1) 0.5 ) (1 + n' 2 ) 0.5 } / (m'+(m' 2 +n' 2 +1) 0.5 )
A 2 =m' / (n'(m' 2 +n' 2 +1) 0.5 )
EU F = depth factor (Fox, 1948) = f (D F /B, μ S and L/B
α = factor that depends on the location of the foundation where the settlement is calculated
The following values are used to calculate the settlement in the middle of the foundation.
α = 4, m' = L/B and n' = H / (B/2)
The settlement at the corner of the foundation can be calculated using the following values.
α = 1, m' = L/B and n' = H/B
Due to the existence of defensive layers of earth beneath the foundation, E S will vary from layer to layer. Weighted average of E S is taken into account in the calculations as recommended by Bowels (1987). S can be calculated using the following equation.
E S = (∑E S (I) ∆z ) / Z 0
Where,
E EU) = modulus of elasticity of the soil within a depth ∆z
Z 0 = H or 5B, whichever is smaller
The equation and theories above are from the book “Principles of Foundation Engineering”.
The Wikipedia article on Foundation (Engineering) discusses the type of foundations to be used in construction.
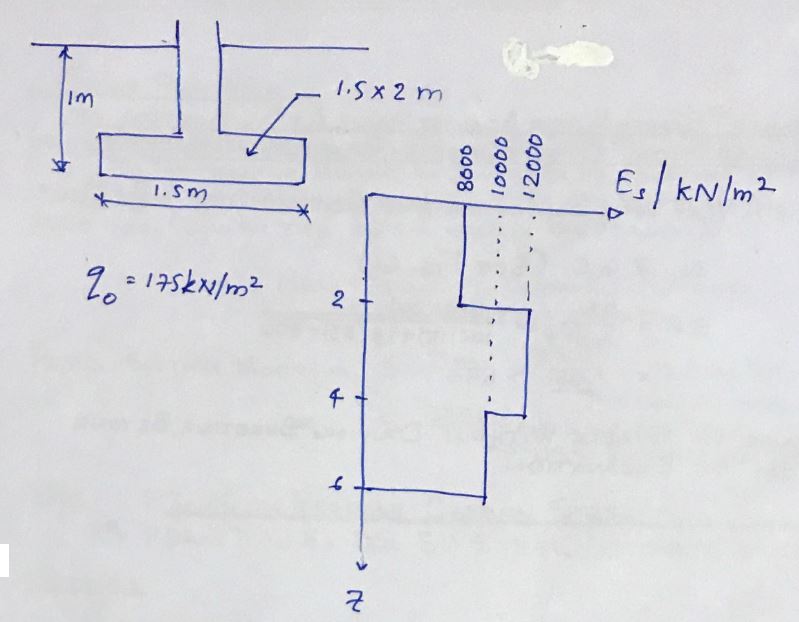
Worked example for calculating settlement of shallow foundations in the intermediate area
Data
- Foundation dimensions 1.5m x 2m
- Net pressure in the foundation, q 0 = 175kN/m 2
- Poisson's ratio of soil μ S = 0.3


B = 1.5m
l = 2m
Average, E S
And S = (8,000 x 2 + 12,000 x 2 + 10,000 x 2) / 6 = 10,000 kN/m 2
α = 4
m' = L/L = 2 / 1.5 = 1.333
n' = H / (W/2) = 6 / (1.5/2) = 8
F 1 and F 2 can be calculated from the above equations after calculating A 0 A 1, and A2. Alternatively, the tables from the book “Fundamentals of Foundation Engineering” can be used.
A 0 = m'ln { ( 1+(m' 2 +1) 0.5 )(M' 2 + n' 2 ) 0.5 } / {m'(1+(m' 2 +n' 2 + 1) 0.5 )}
A 0 = 1.333 x ln { ( 1+(1.333 2 +1) 0.5 )(1.333 2 + 8 2 ) 0.5 } / { 1.333(1+(1.333 2 +8 2 +1) 0.5 ) }
A 0 = 0.760
A 1 = ln { (m' + (m' 2 +1) 0.5 ) (1 + n' 2 ) 0.5 } / (m'+(m' 2 +n' 2 +1) 0.5 )
A 1 = ln {( 1.333 + (1.333 2 +1) 0.5 ) (1 + 8 2 ) 0.5 } / (1.333+(1.333 2 +8 2 +1) 0.5 )
A 1 = 0.934
A 2 =m' / (n'(m' 2 +n' 2 +1) 0.5 )
A 2 = 1.333 / (8 (1.333 2 +8 2 +1) 0.5 )
A2 = 0.020
F 1 = (1/π)(A 0 + A 1 ) = (1/π)(0.760 + 0.934) = 0.539
F 2 = (n'/2π) tan -1 A 2
First calculate tan -1 A 2 in degrees and it is converted to radian
tan -1 A 2 = light brown -1 (0.02) = 1.146 0
Radians = 1.146 0 x (π/180) = 0.02
F 2 = (n'/2π) tan -1 A 2 = (8/2π) x 0.02 = 0.025
EU S =F 1 + ((1-2μ S )/(1-μ S ))F 2 = 0.539 + ((1-2×0.3)/(1-0.3)) x 0.025 = 0.553
EU F can be determined from the table of basic construction principles.
For μ S = 0.3, Df/B = 1/1.5 = 0.667 and B/L = 1.5/2 = 0.75
EU F = 0.755
Founding settlement
S t =q 0 (αB') ((1-μ 2 S ) / E S )I S EU F
in the center of the foundation
S t =q 0 (αB/2)((1-μ 2 S )/E S )I S EU F = 175(4×1.5/2)((1-0.3 2 )/10000) x 0.553 x 0.755 = 0.02m
The foundation settlement is 20 mm.
Reference: Foundation Engineering Basics